- THE VERTICAL DIMENSION
- Clinical Cases
- Sizes
- Shade Range
- Step by Step
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
- keyboard_arrow_up
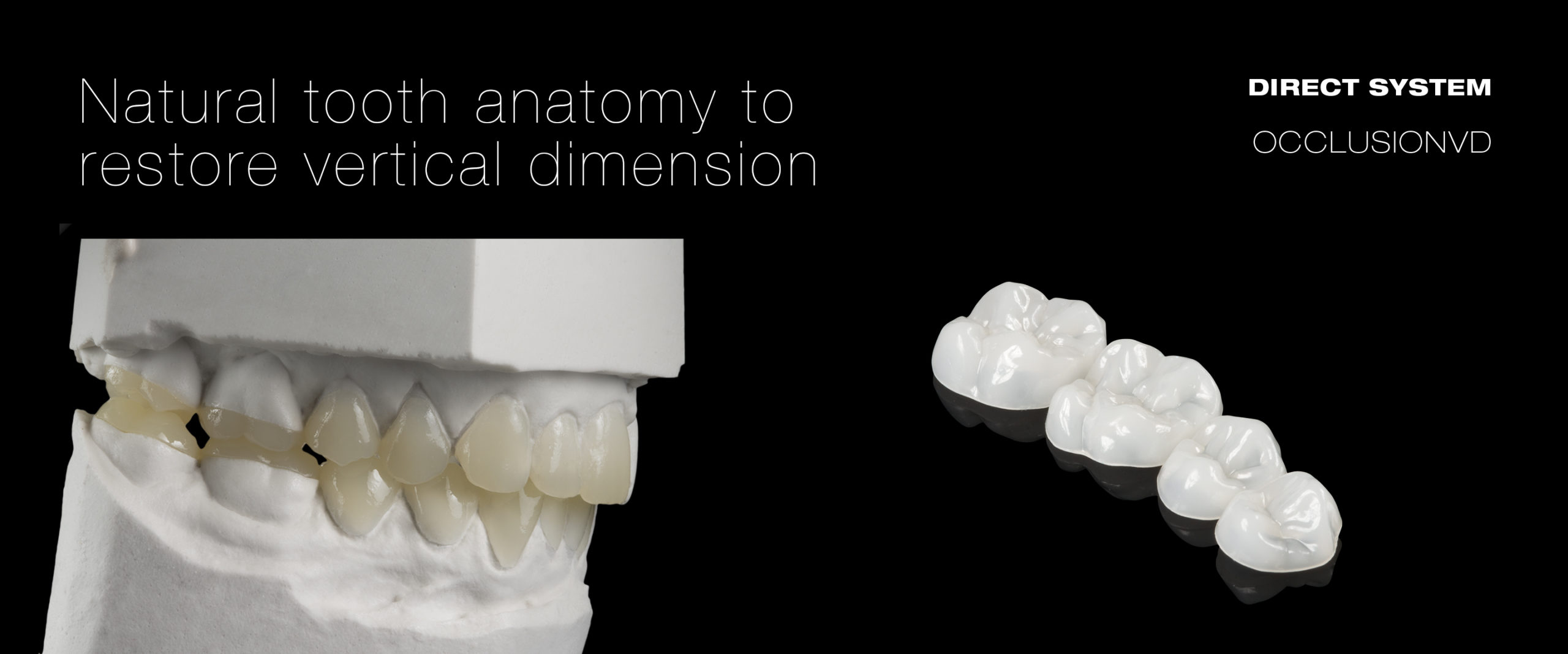
Thanks to their unique laser sintering process, the translucent enamel and occlusion veneers stand out due to their inorganic, ceramic-like surface vitrification and tempered composite body. The occlusions represent the anatomic foundations for single or complete reconstructions and for increasing the vertical dimension (OVD) in the posterior region. Hence, a functioning anterior cusped guidance can also be obtained using edelweiss „VENEERs“.
THE VERTICAL DIMENSION
Function
edelweiss VENEERs & OCCLUSIONVD allow for minimally invasive biomechanical and economical treatment of the cause as well as prevention of cranio-mandibular dysfunction (CMD). Furthermore, malocclusion and deep bites can also be corrected minimally invasively. By covering the occlusal surfaces, usually in the mandible, the mandible is brought into the correct position for the patient in relation to the maxilla. This makes it possible to attain functioning guidance of anterior teeth and cuspids by using edelweiss VENEERs.
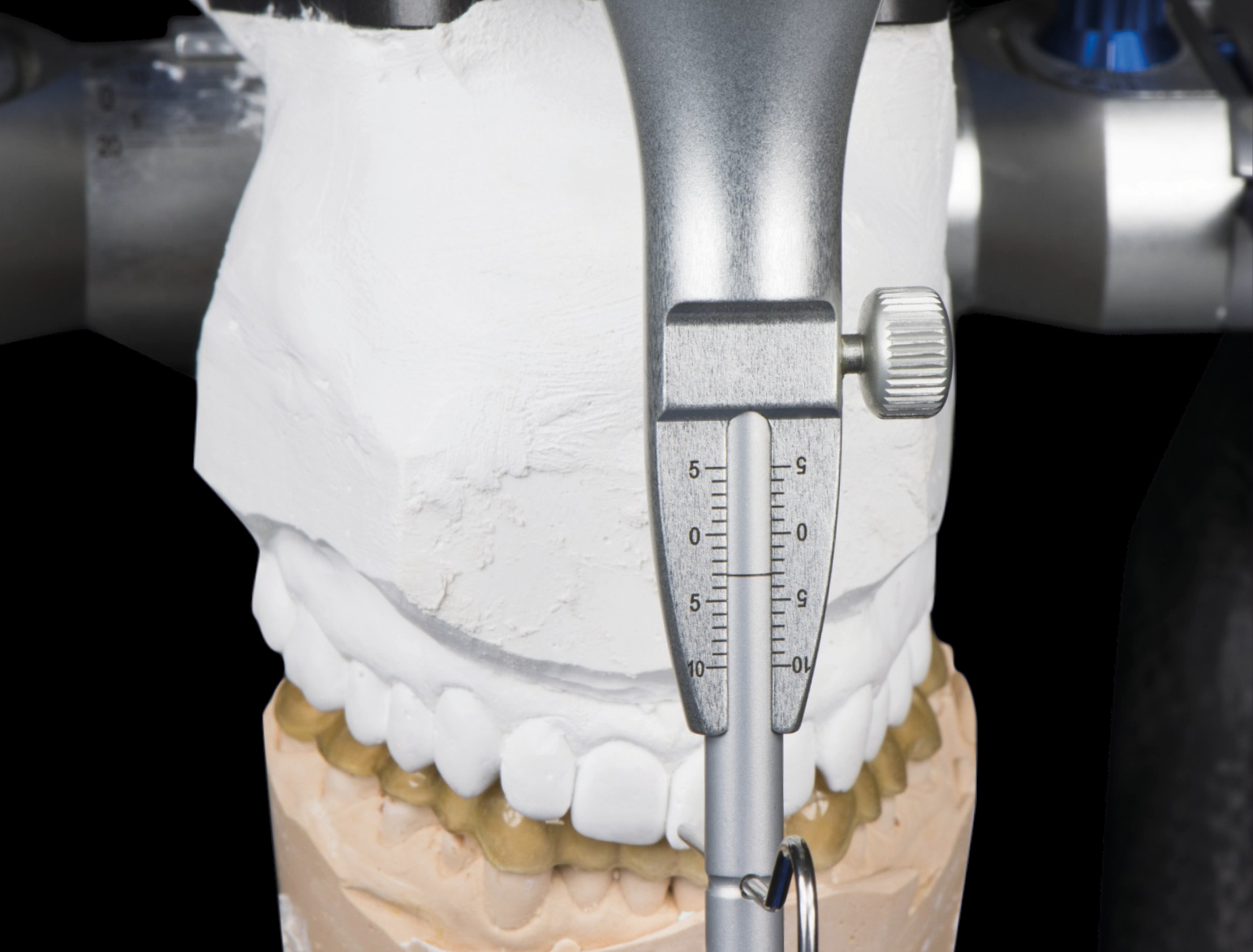
Lifting the vertical dimension
using edelweiss occlusal surfaces. In most cases the mandible is appropriate. It can often be identified by the great difference in height from the cuspid to the premolar (33 to 34 and 43 to 44). However, to ensure that lifting, and protrusion if necessary, is equal on the left and right, this needs to be tested using situation models on the articulator. In the premolar region this can mean capping up to 5 mm, and up to a further 3 mm in the molar region.
Procedure
The maxilla and the mandible models are articulated head-adequate in habitual intercuspation. Protrusion is then performed as required and the supporting pin of the articulator raised. Michigan or Partial bite splints with “stops” are prepared for the mandibular quadrants. These are fixed temporarily in the mouth, in other words, provisionally. After a few weeks this will already represent the ideal position of the mandible, possibly requiring re-occlusion. On the basis of these bite splints the mandible is articulated anew against the maxilla.
Indirect Application
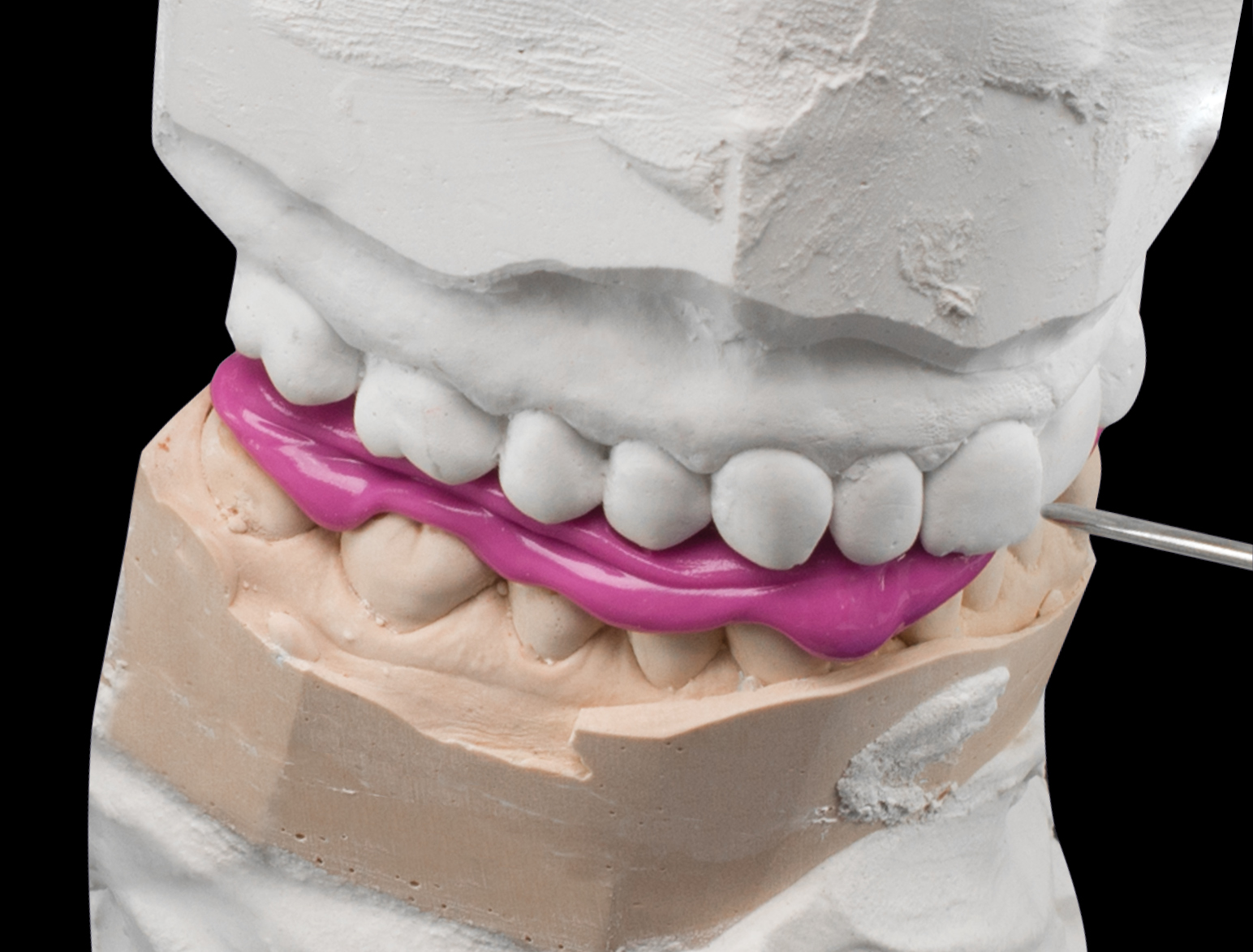
By relining the prefabricated occlusal surfaces on existing model occlusal surfaces with composite, one can simply create a new functioning biomechanical, balanced and smoothly working masticular apparatus without irritations. Then the occlusions are transferred from the model to the patient’s occlusions and attached via bonding and composite.
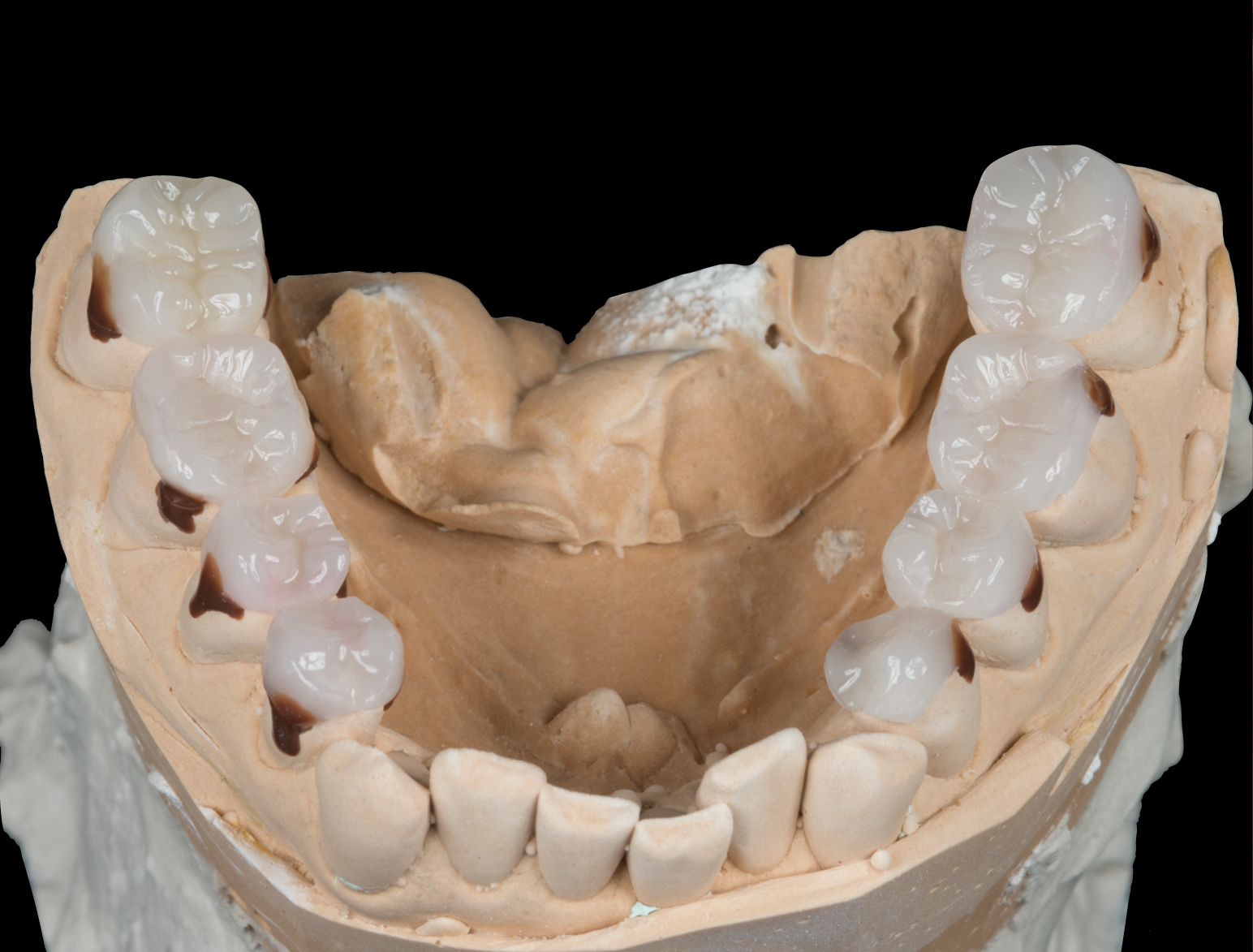
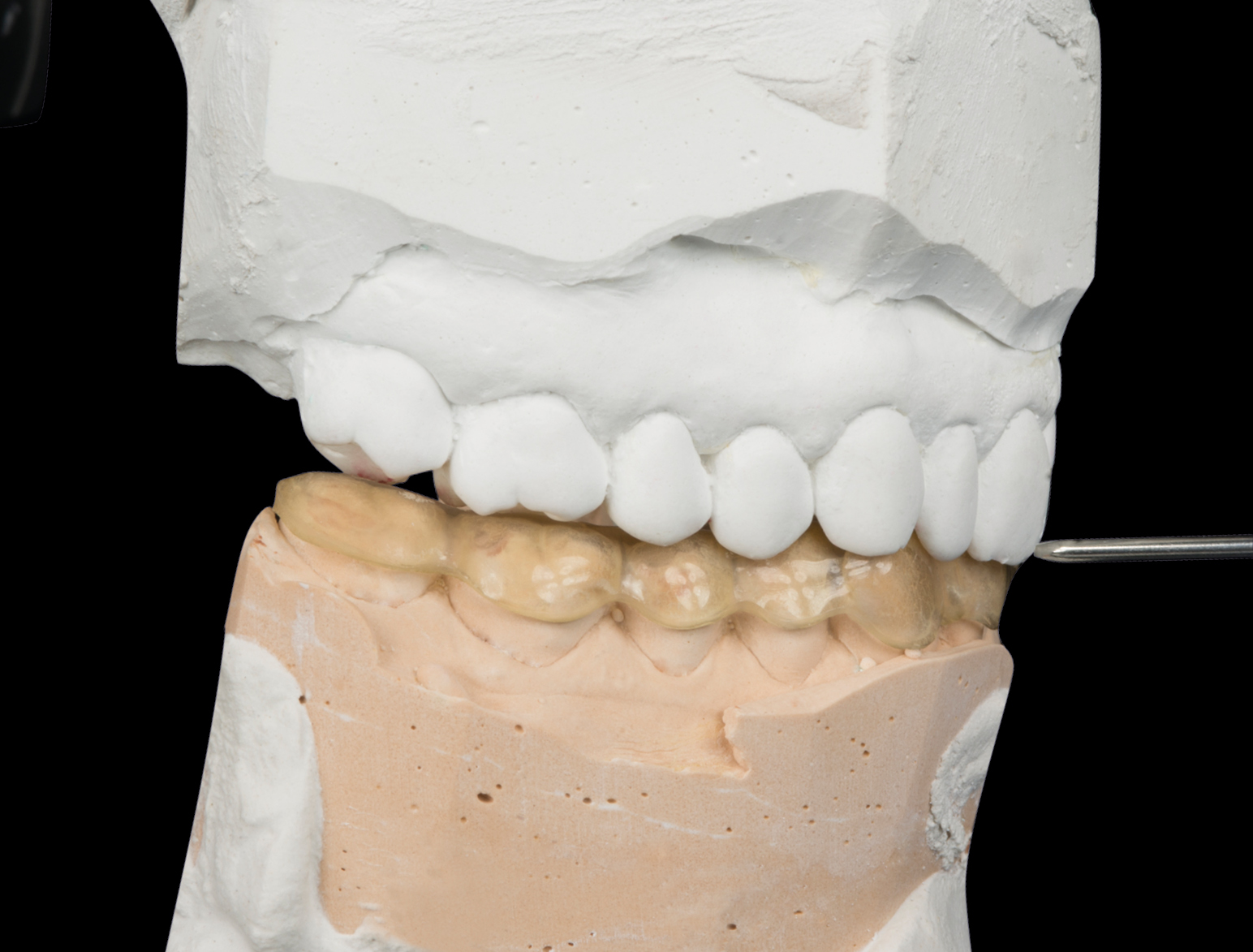
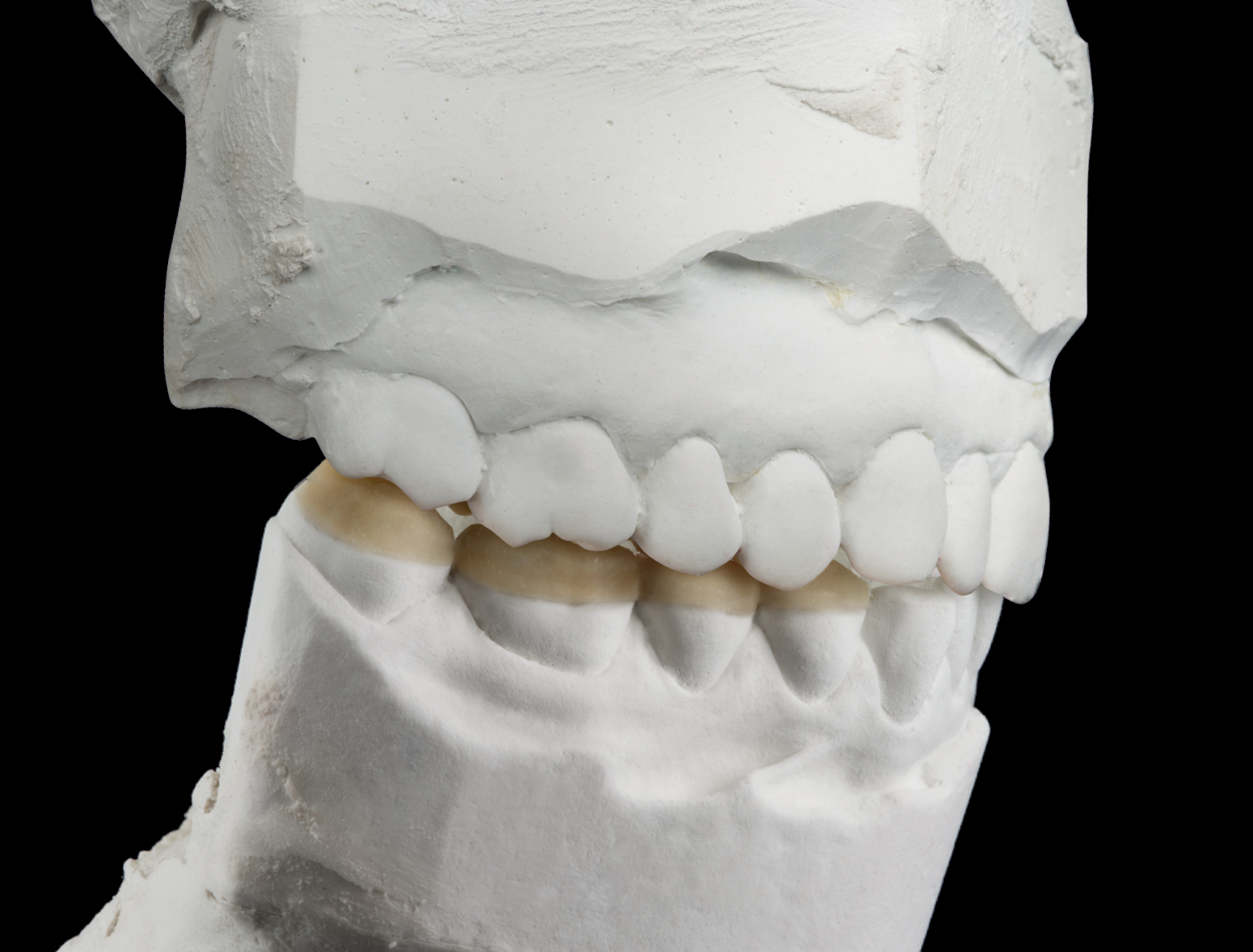
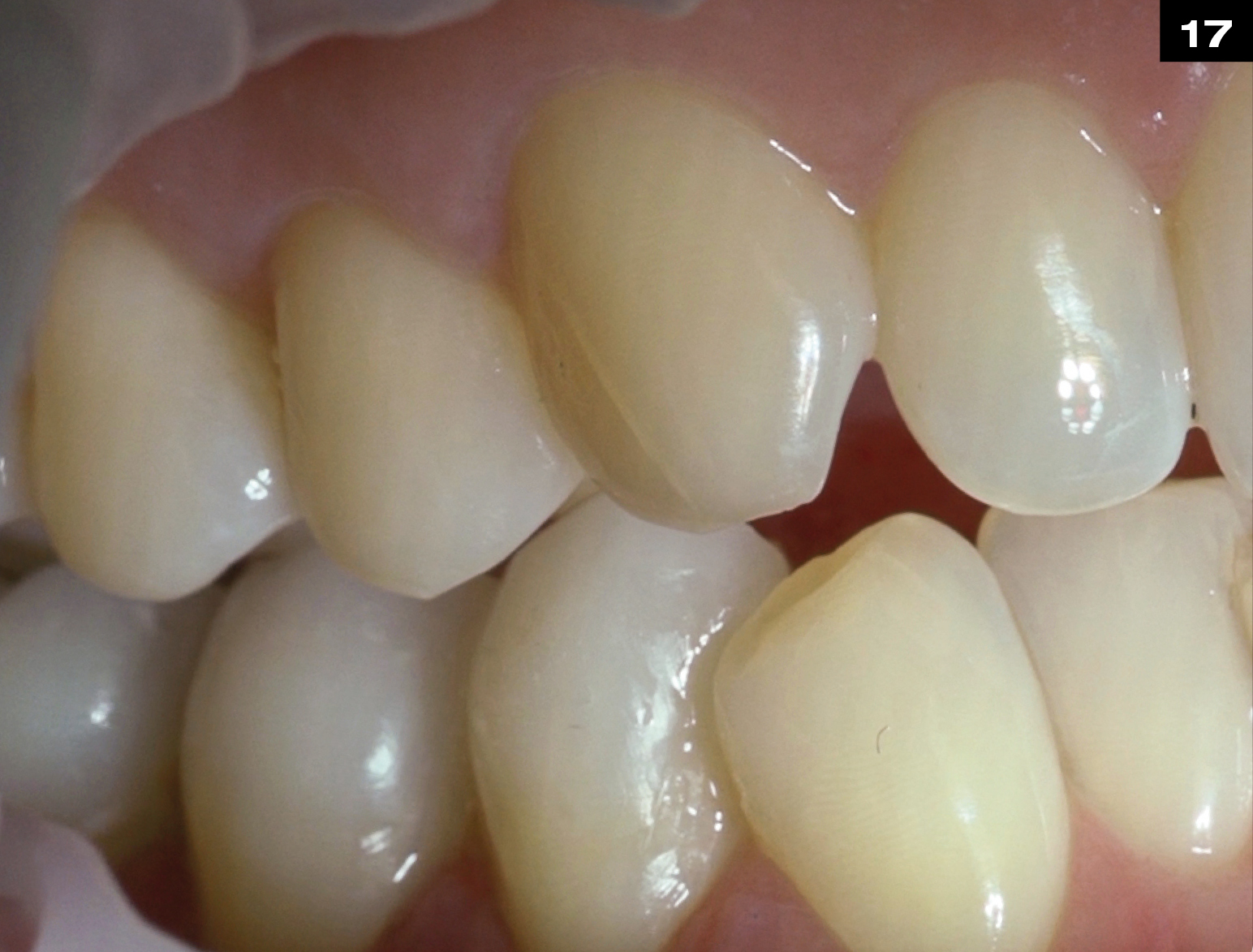
OCCLUSIONVD ENAMEL SHELLS LOWER JAW
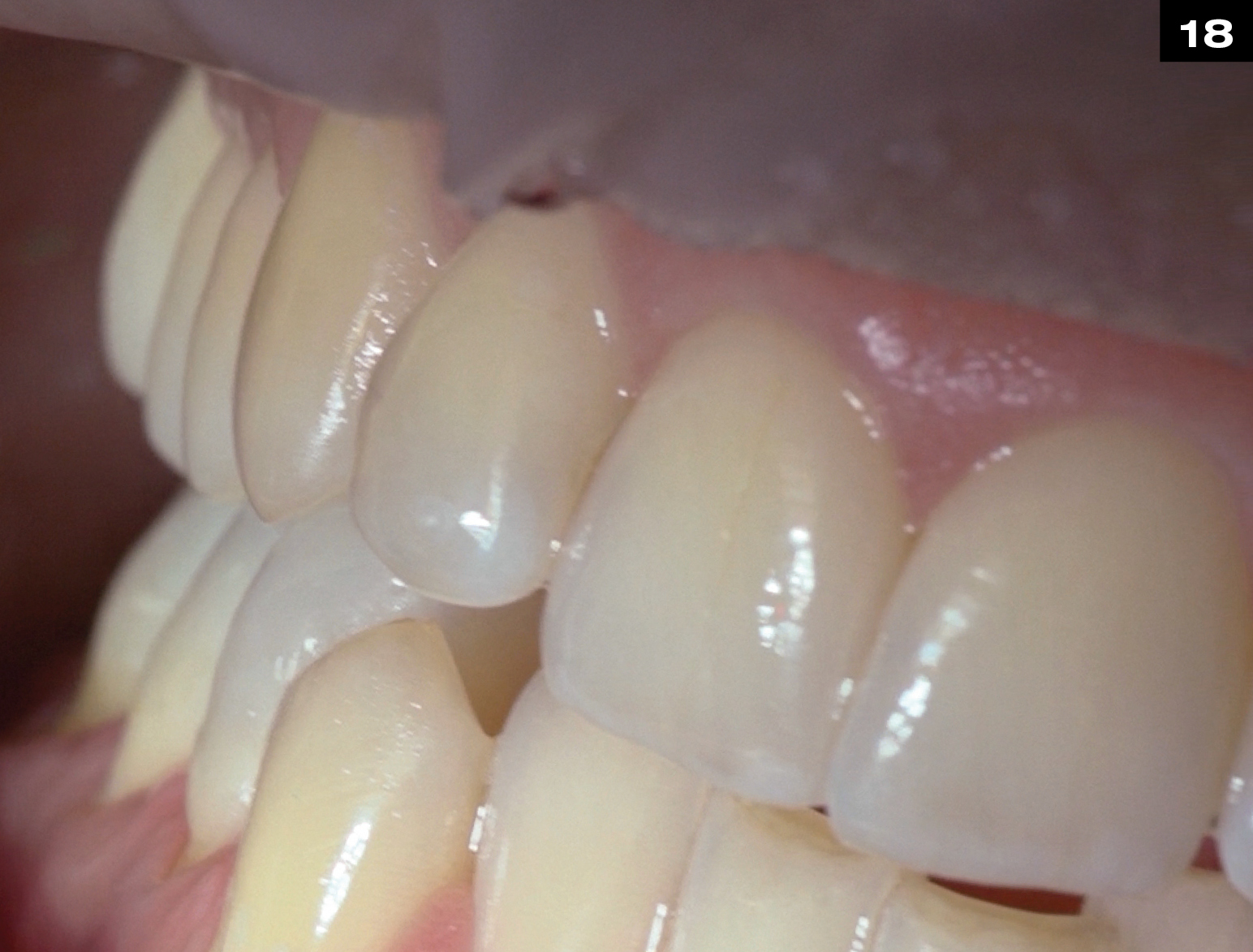
Relined and adapted by the dental technician on stone model
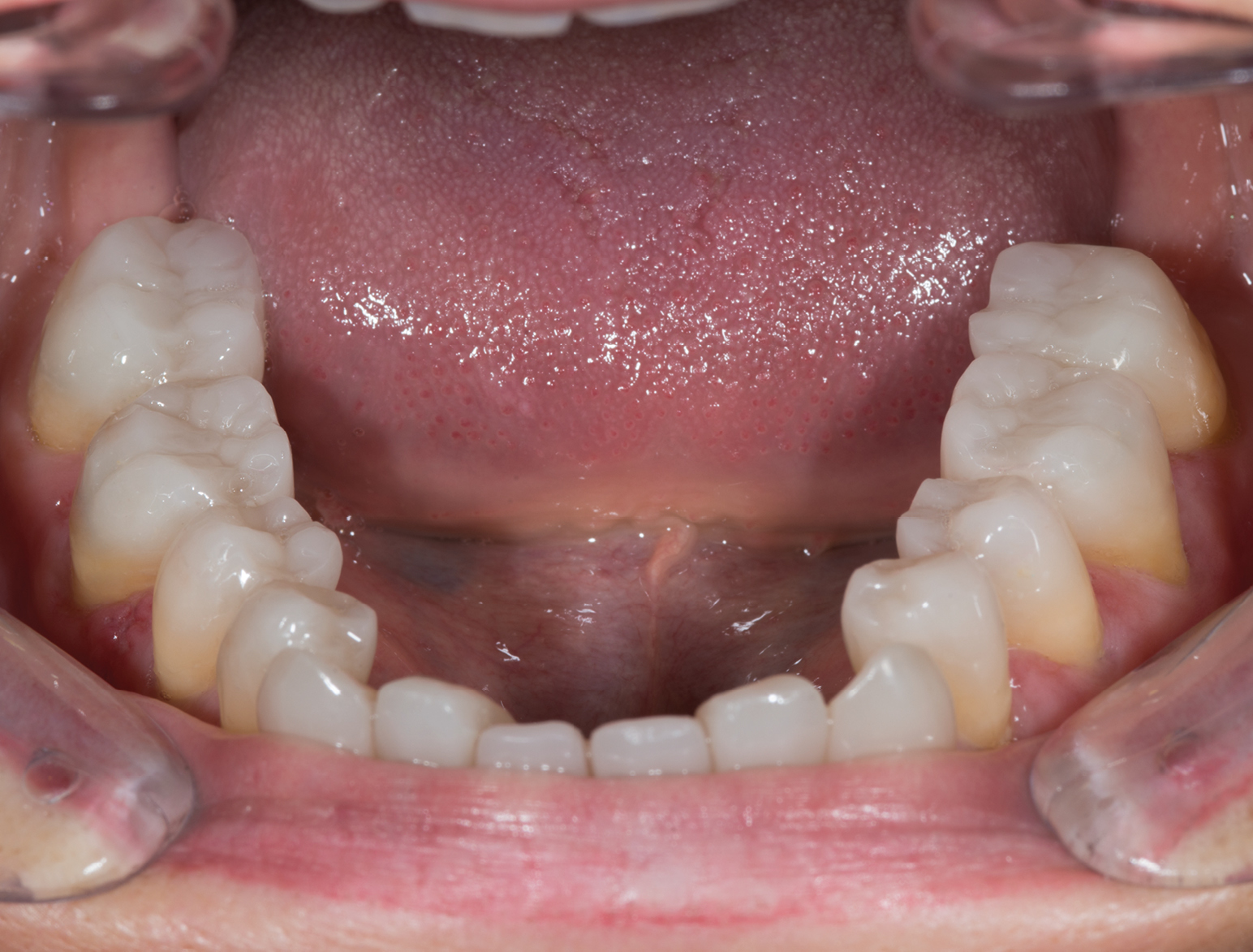
FINISHED OCCLUSIONVD IN FINAL SITUATION
DIRECT PROCEDURE
For advanced professionals: Instead of lining the occlusions on the model in the articulator, a bite registration material (silicone) is used to make an occlusal impression which accurately portrays the clearance between the maxilla and the mandible in the articulator. Using the fixed silicone bite register, direct application of the prefabricated occlusion can be performed. The silicone bite register is in each case placed unilaterally (left or right) on the patient’s occlusion. In other words, when the left quadrant is restored with occlusions, the right quadrant sets the height and position of the bite elevation and thus the final position of the composite-lined and bonded occlusions on the left when biting down (replacing the supporting pin when closing the articulator). Once the left quadrant has been restored, the right quadrant is treated. Now one can optionally prepare a further silicone register from the quadrant already restored with occlusions (left) in combination with the silicone register (right) already prepared with the articulator, which additionally guides and sets the already attained occlusional relationship between the maxilla and the mandible (left) during biting. Practised users can dispense with this silicone register (for example, on the left) as the patient now already bites on the newly gained occlusion or bite elevation during biting. After setting all occlusions, re-occlusion is performed until the desired contact points have been attained.
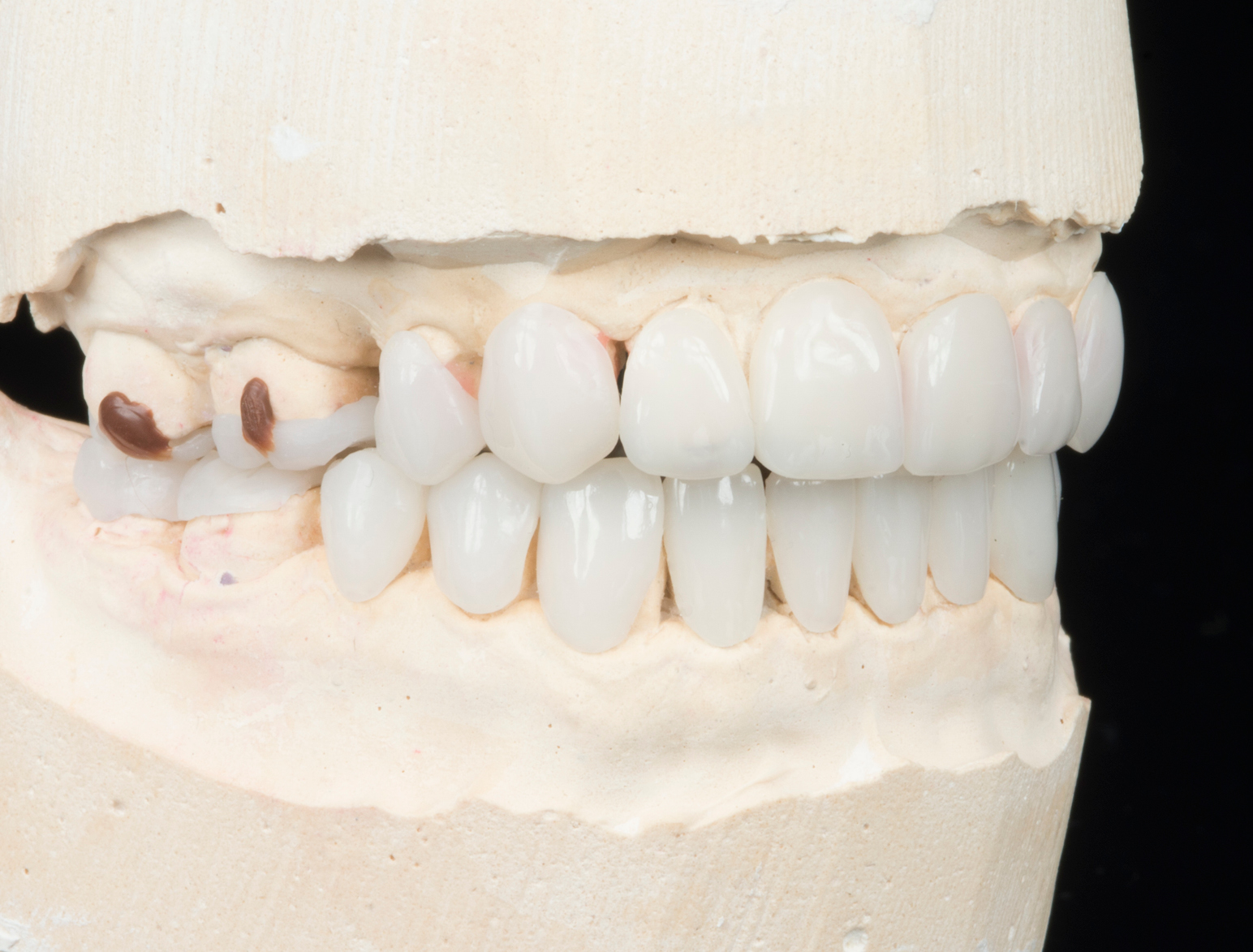
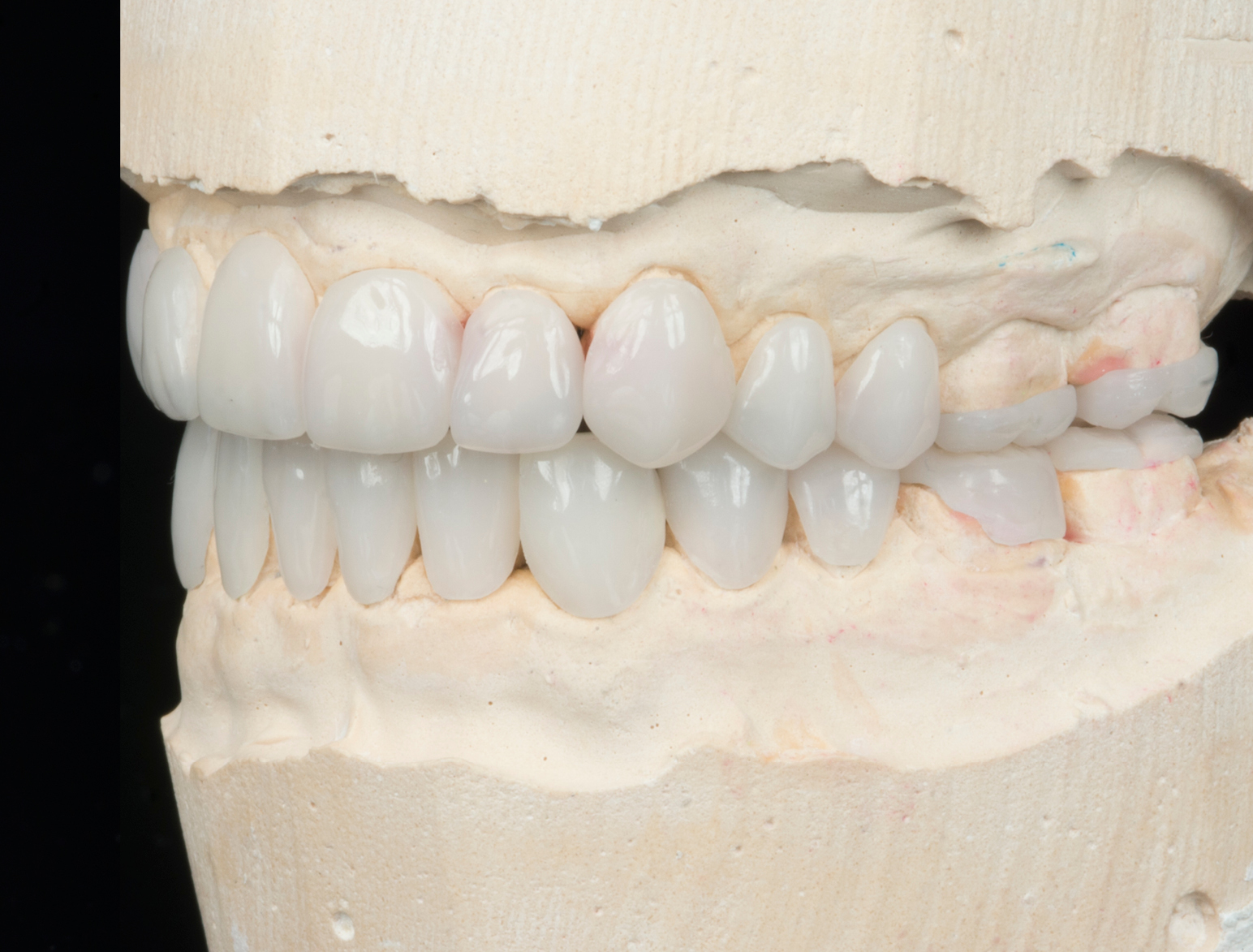
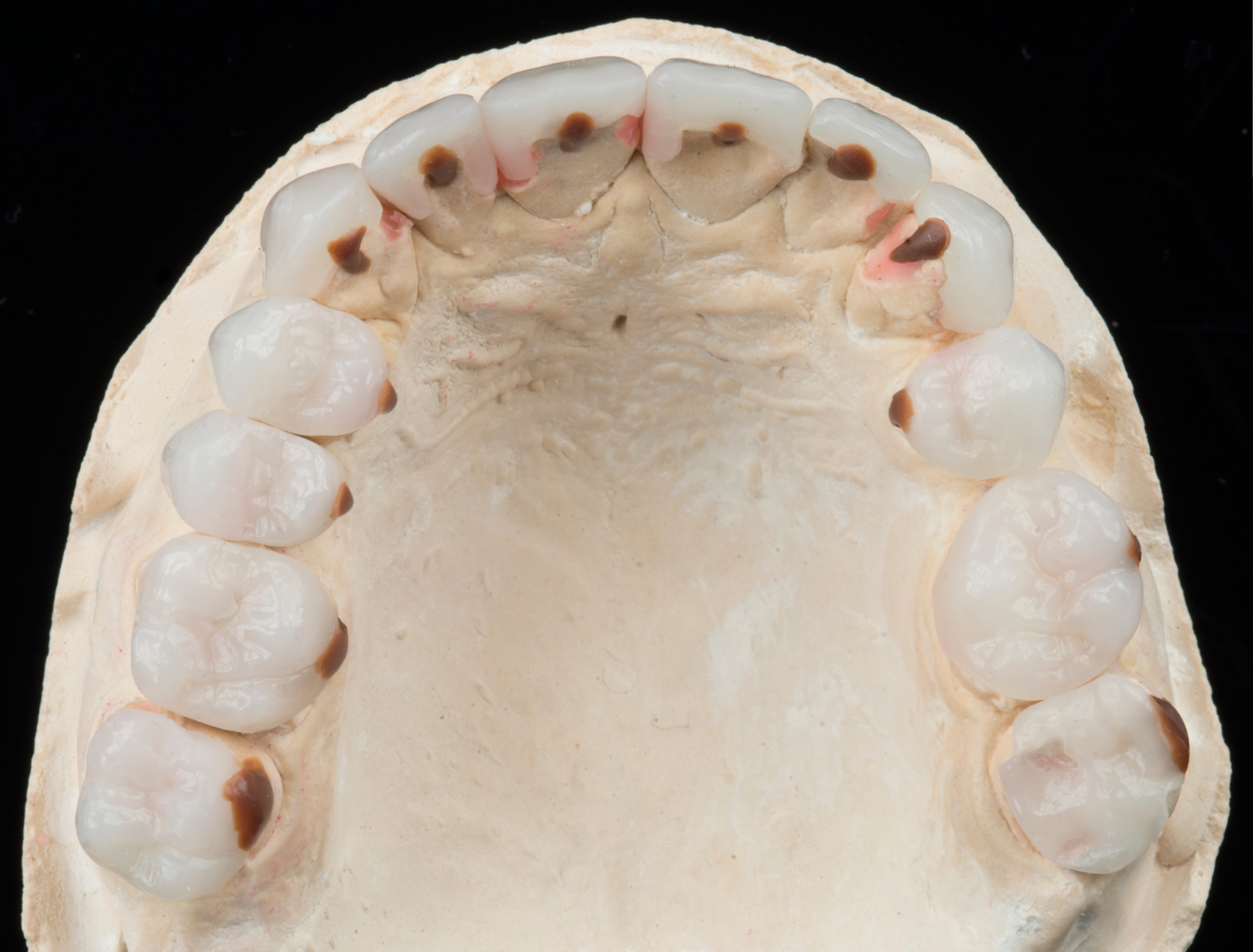
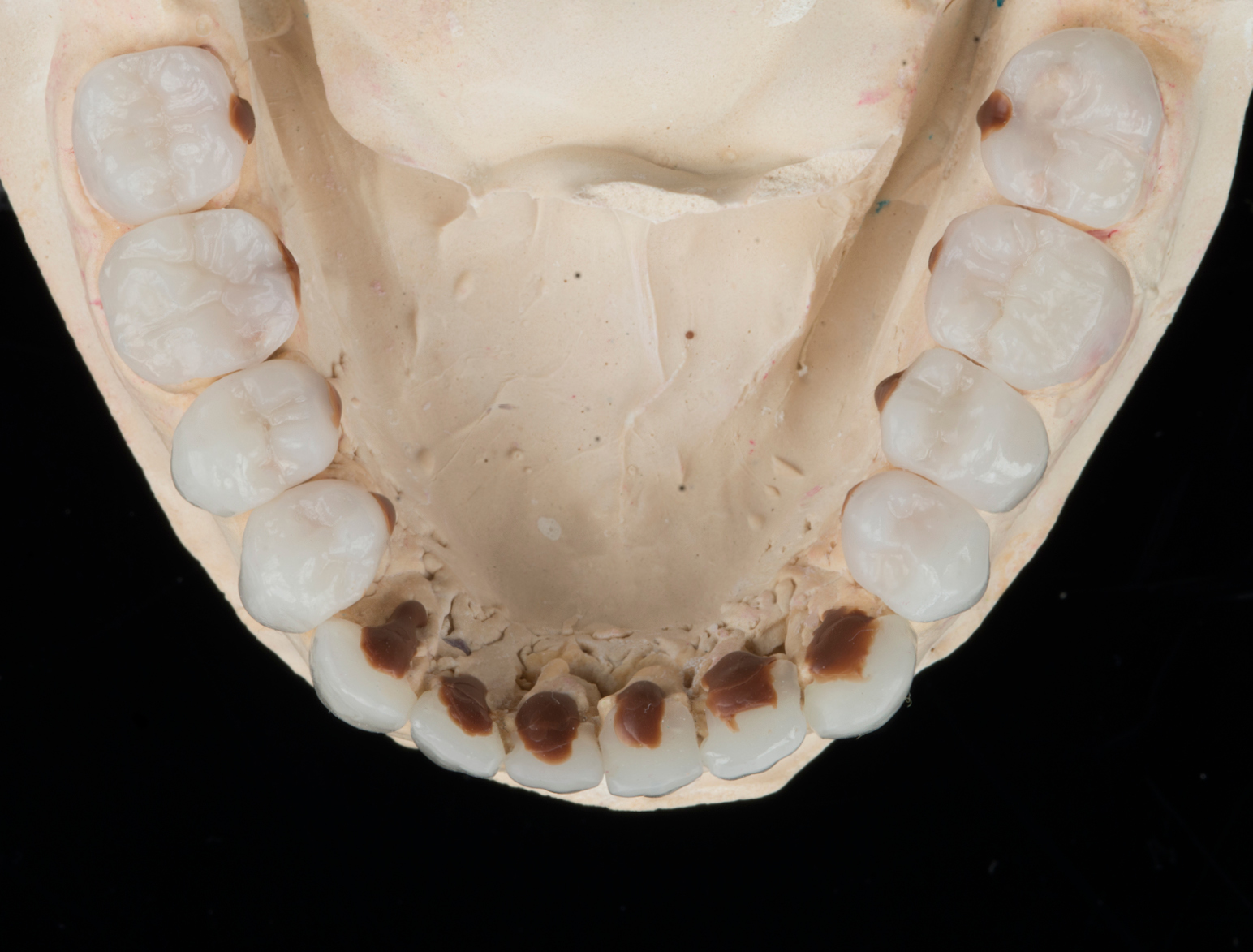
Clinical Cases
CONGENITAL AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA HYPOMATURATION
BEFORE & AFTER / STEP BY STEP
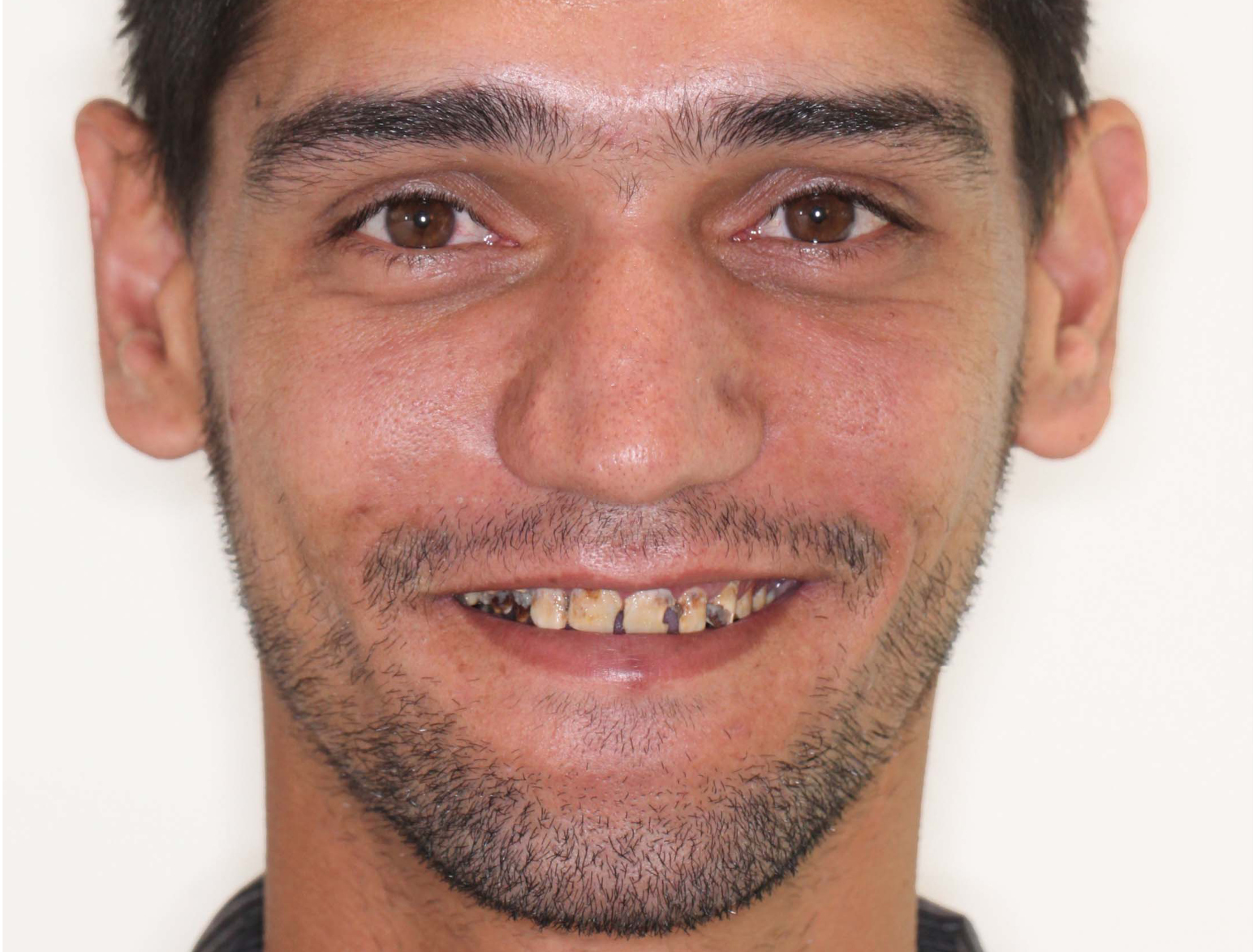

BEFORE
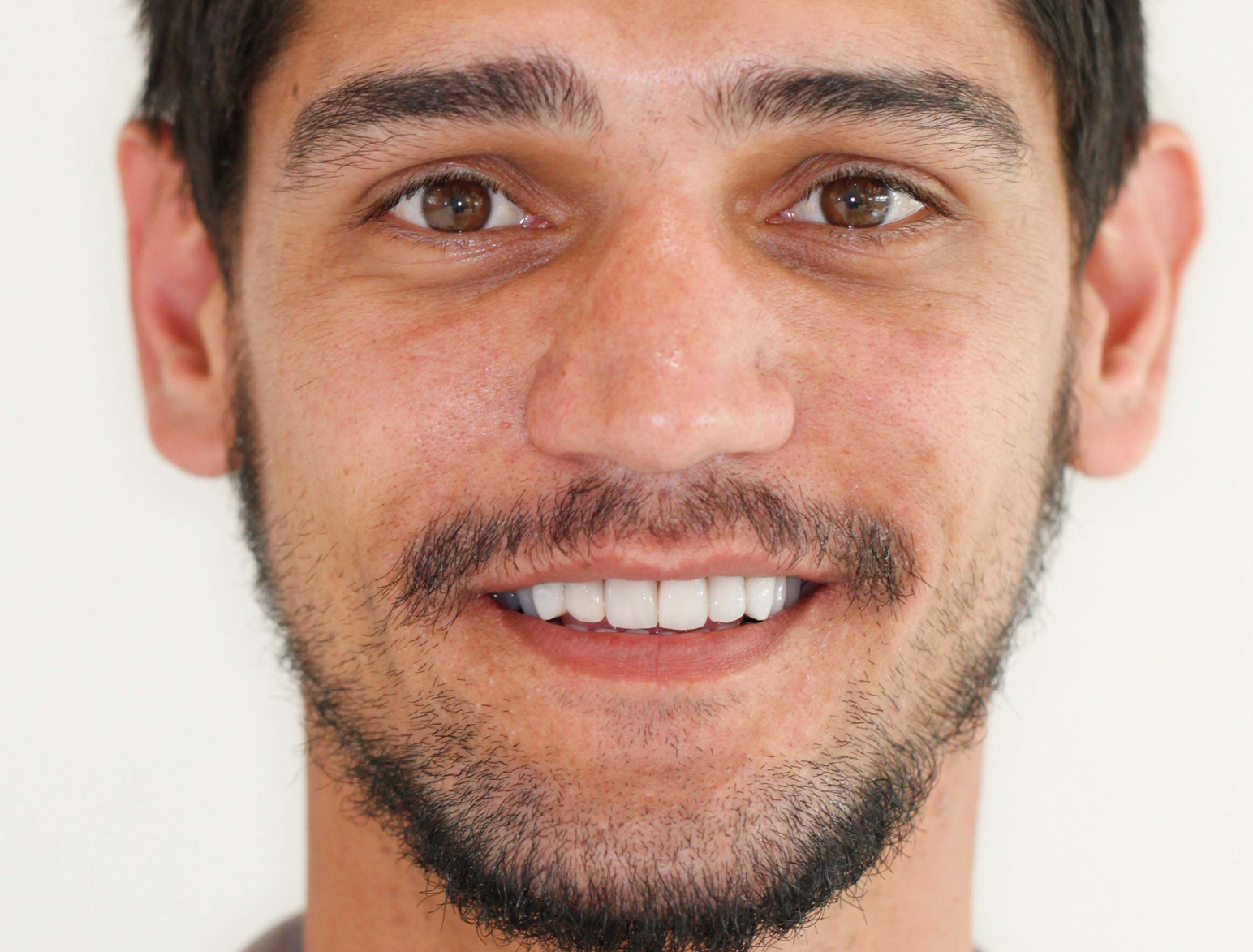

AFTER
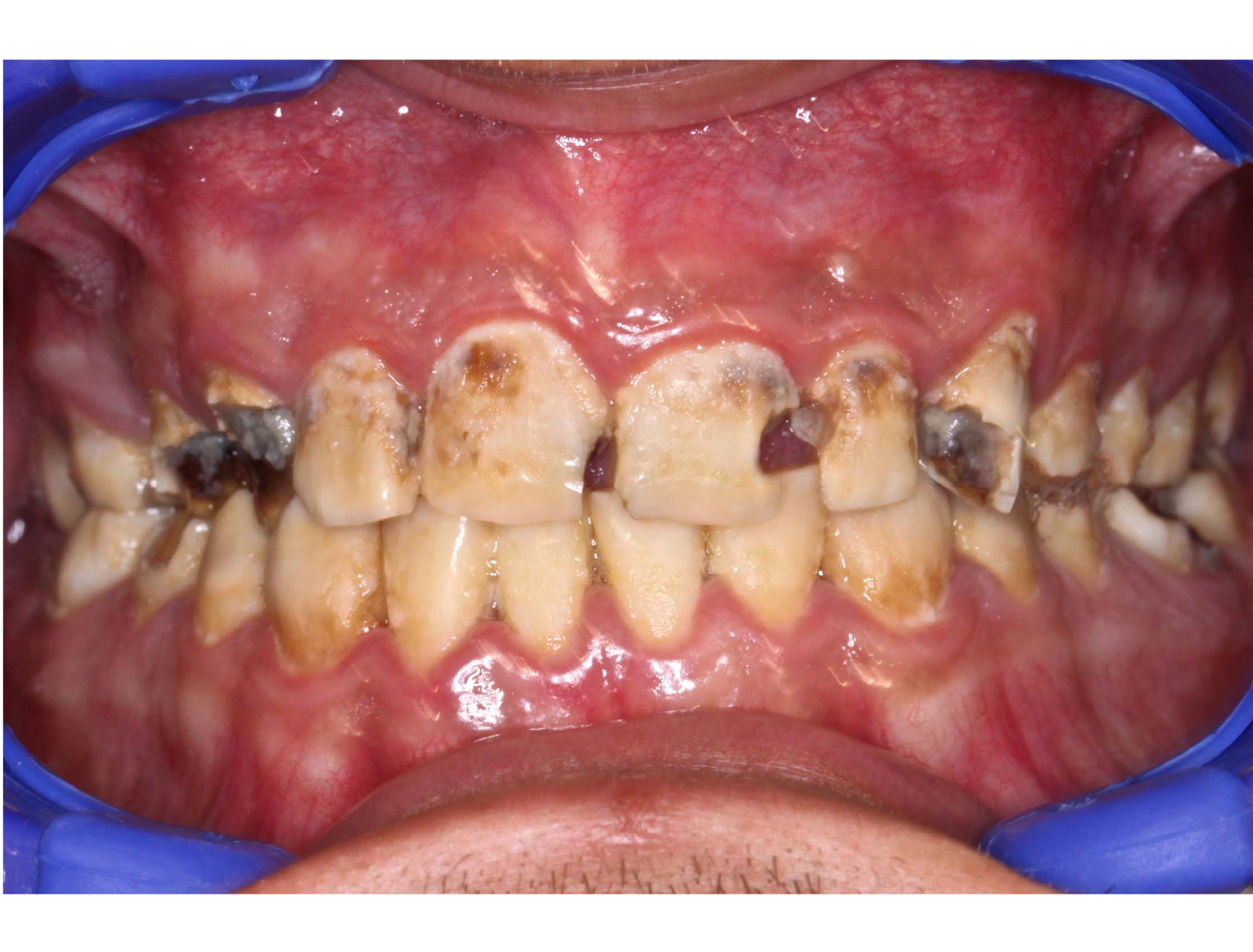
BEFORE
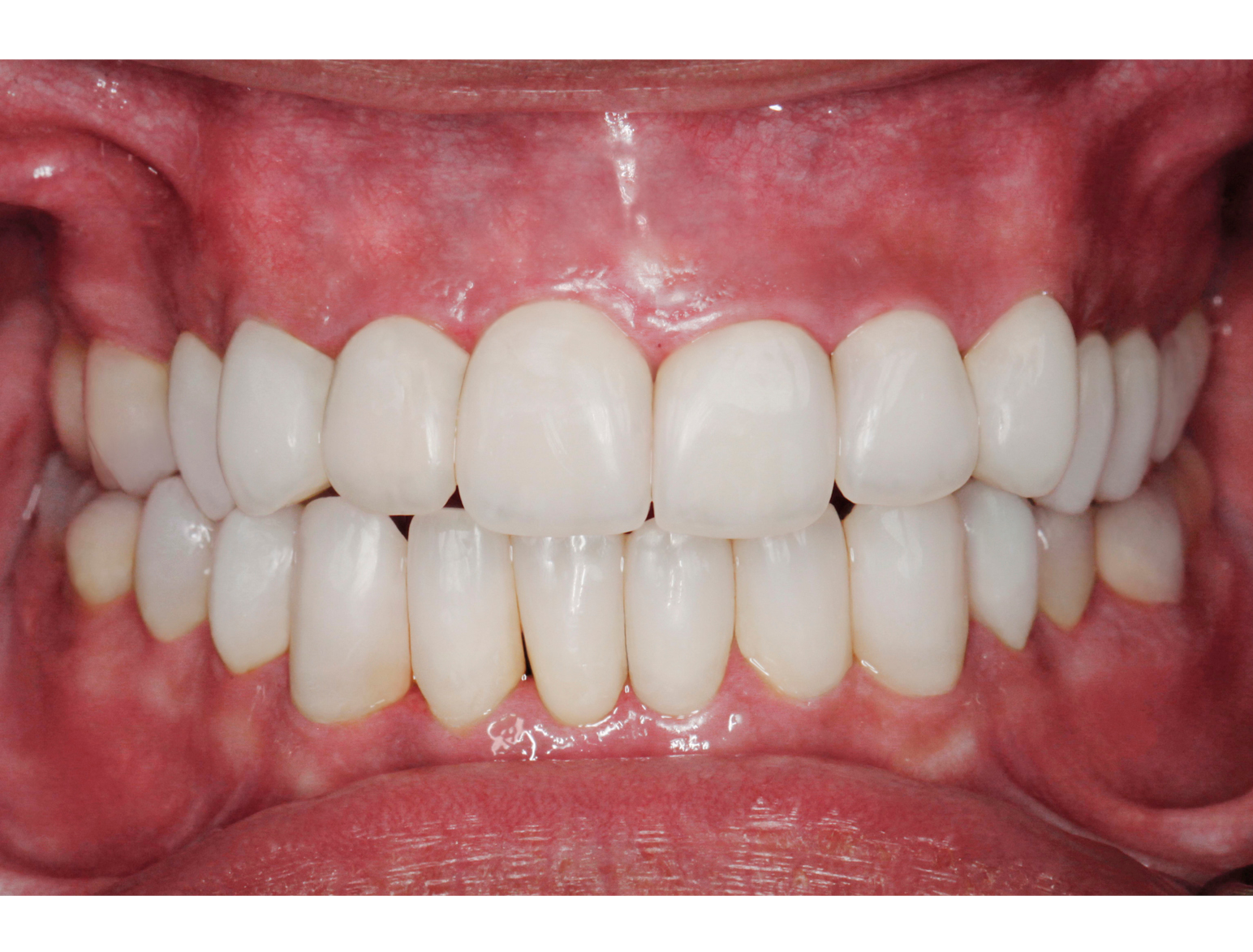
AFTER
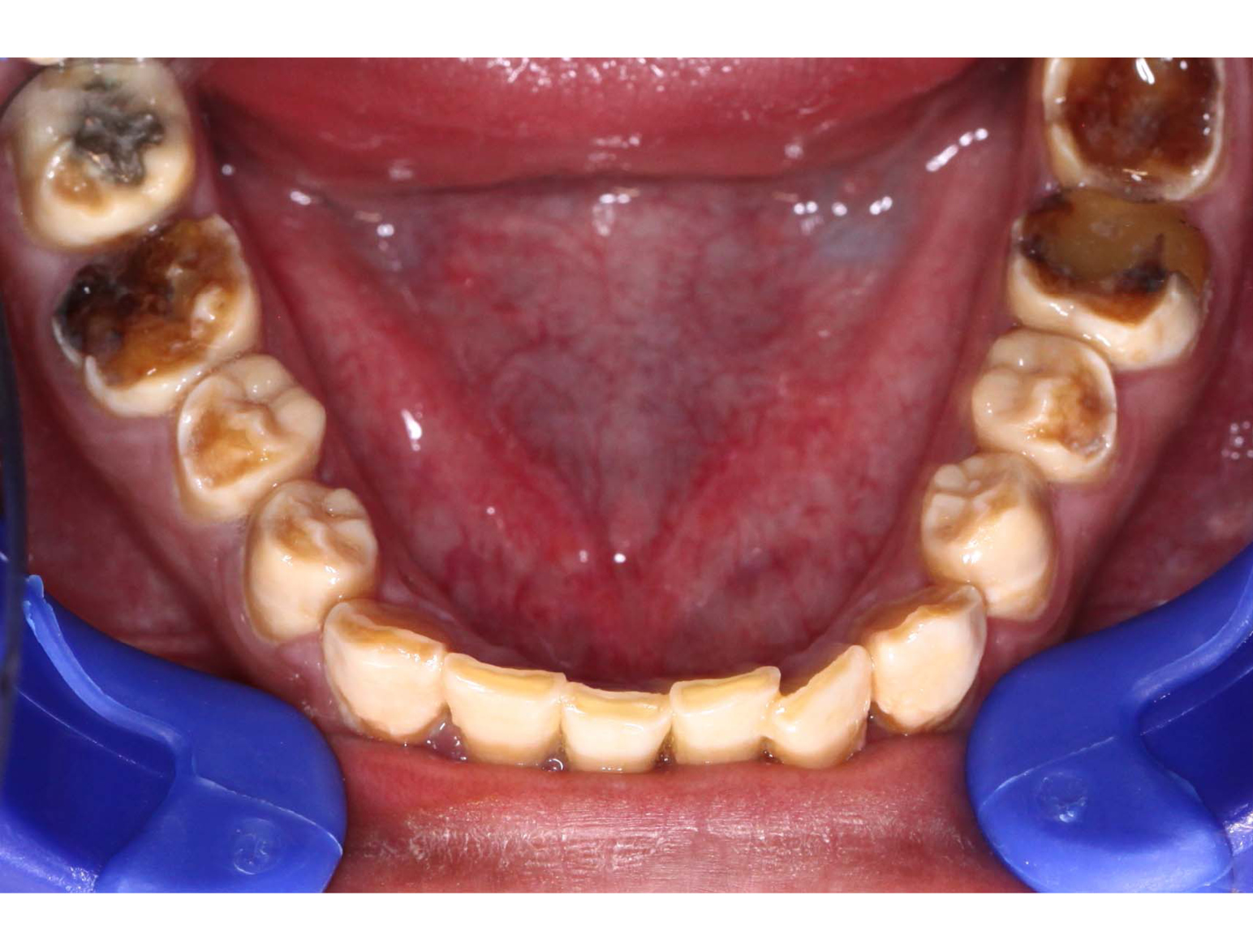
BEFORE
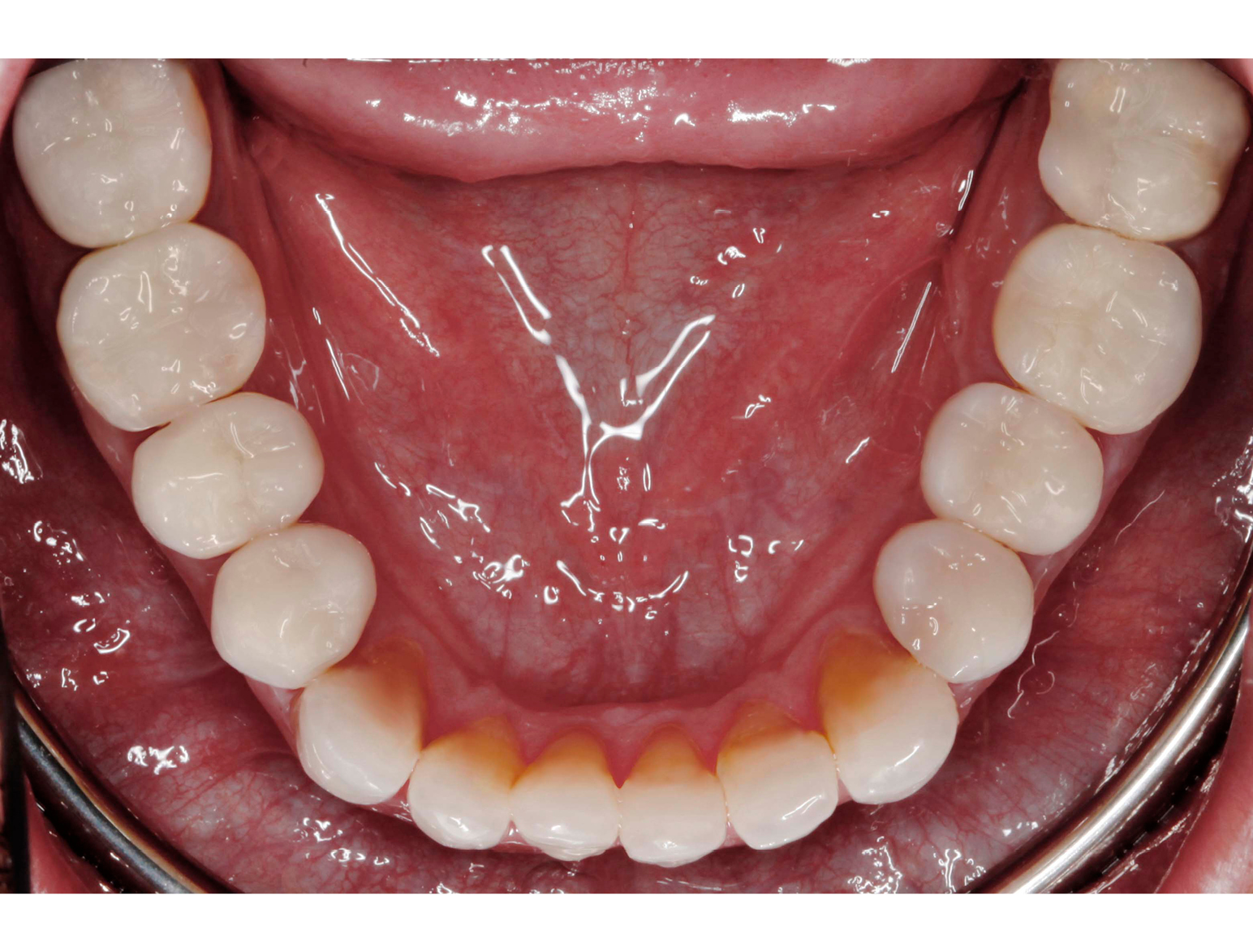
AFTER
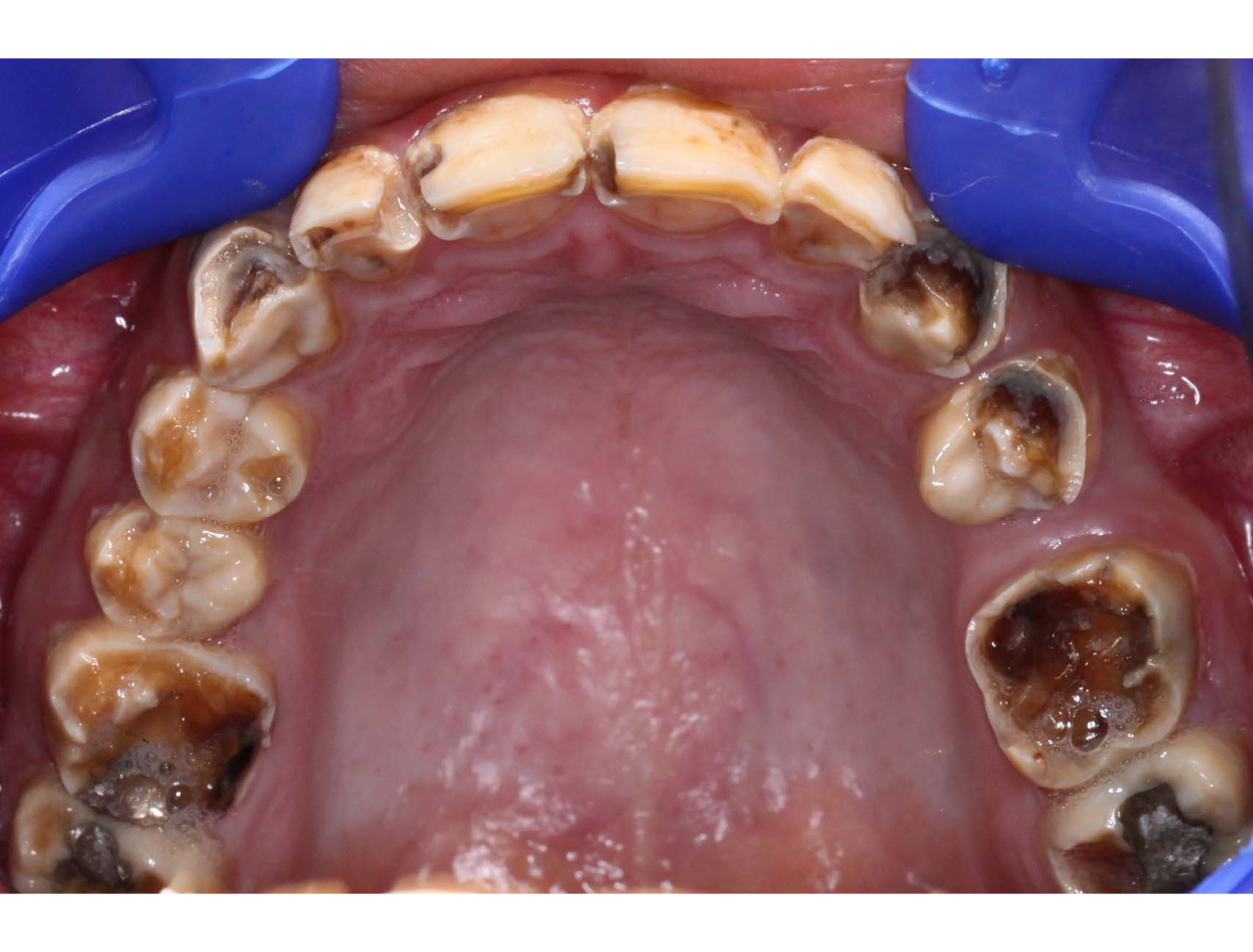
BEFORE
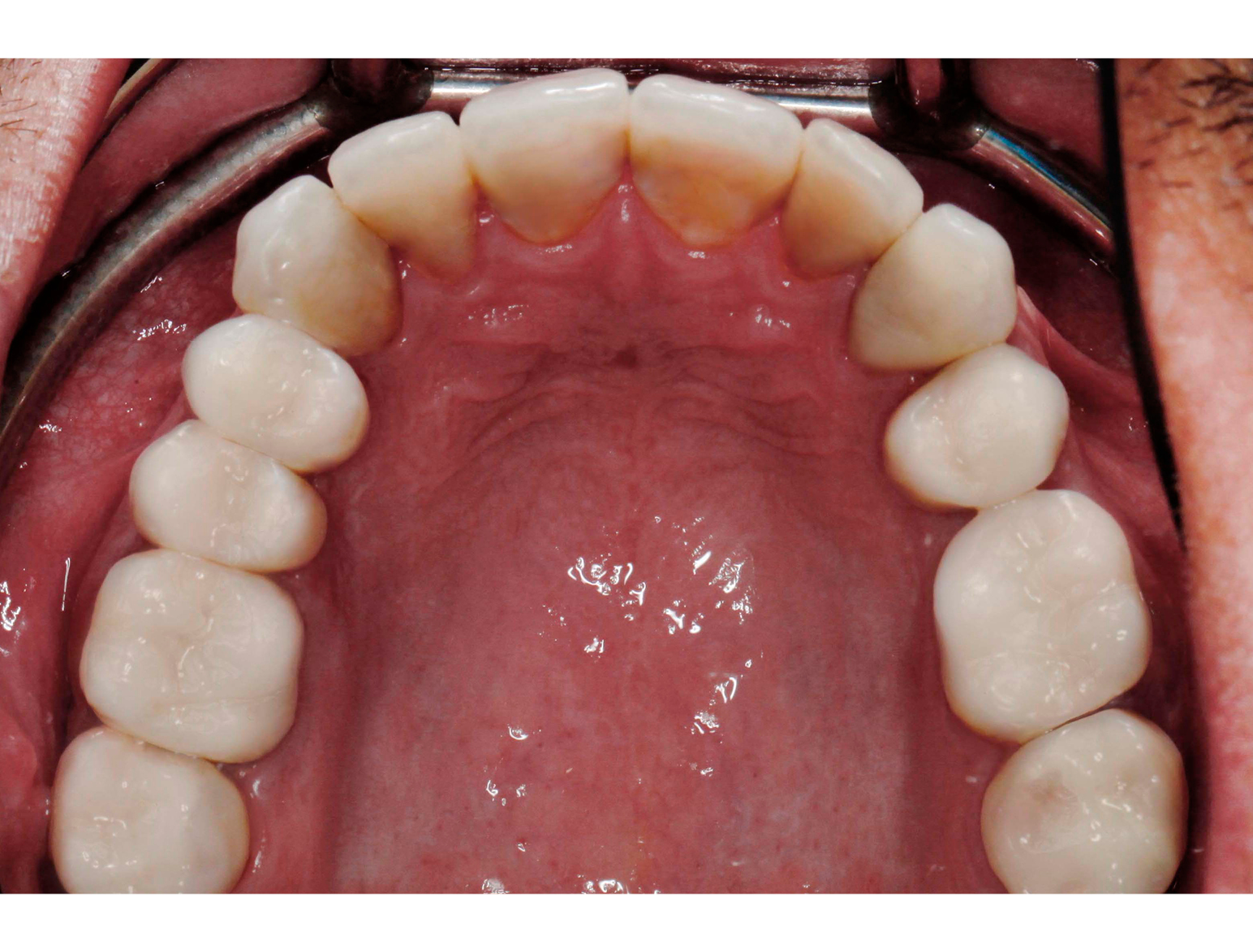
AFTER
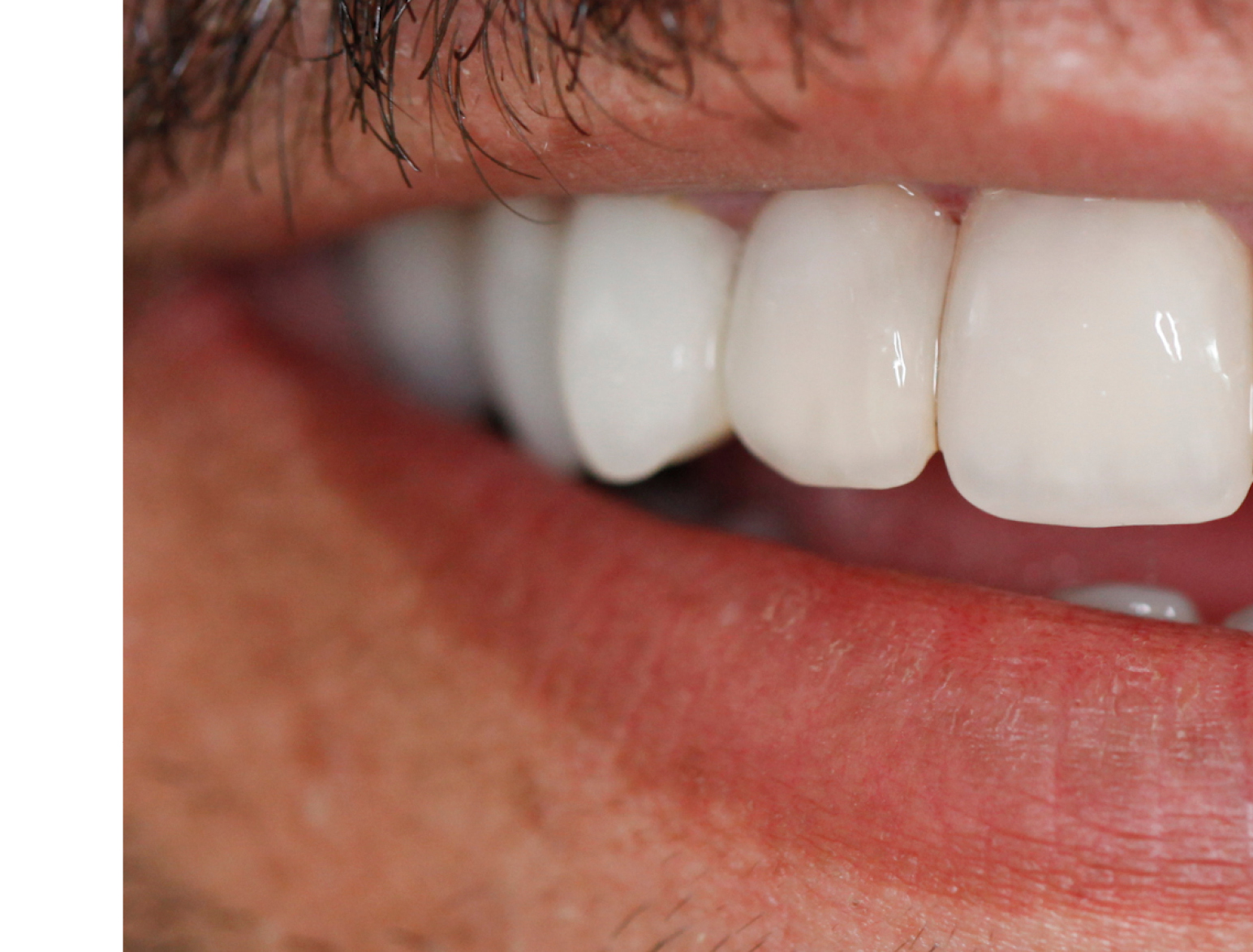
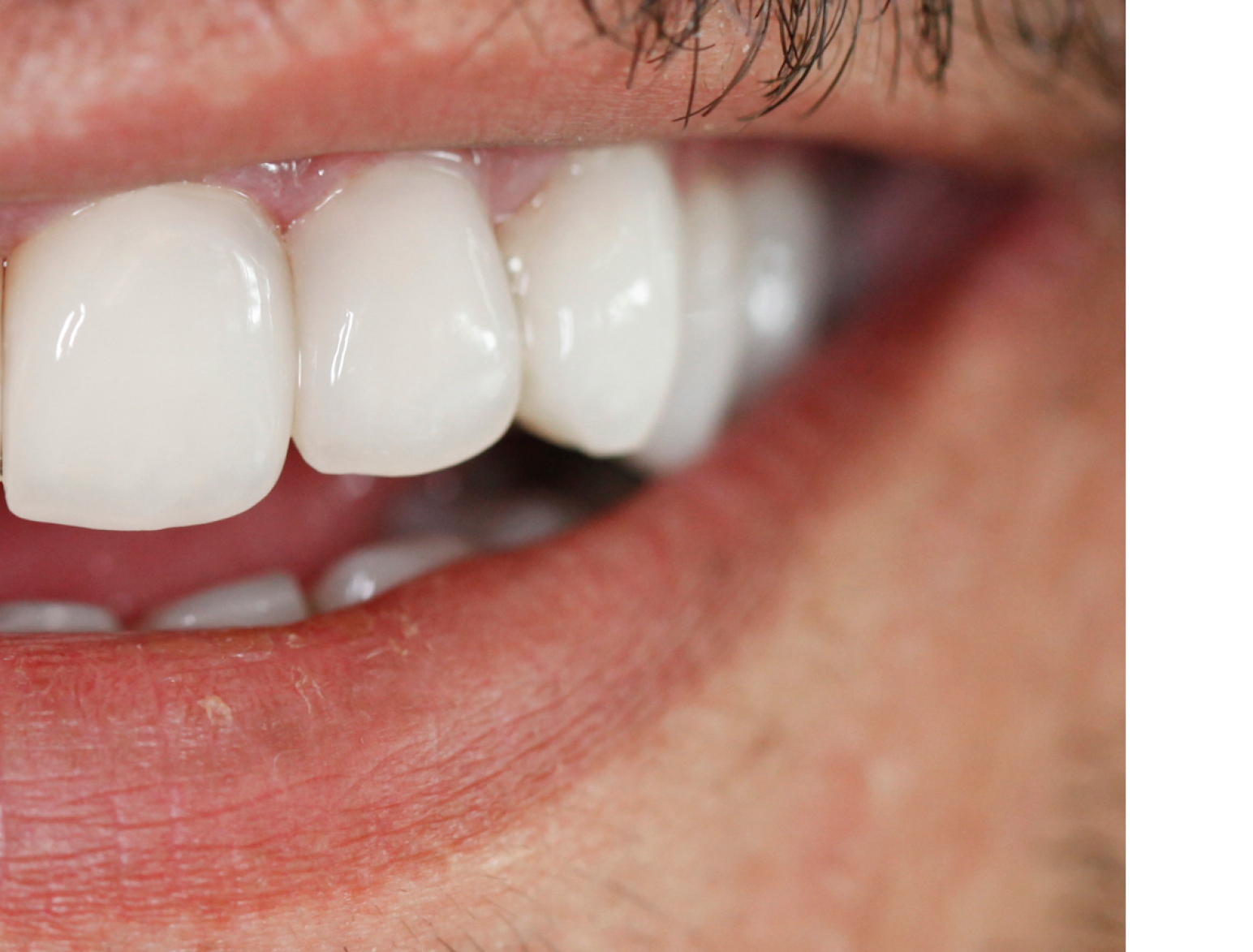
POSTERIOR RESTORATIONS
BEFORE & AFTER / STEP BY STEP
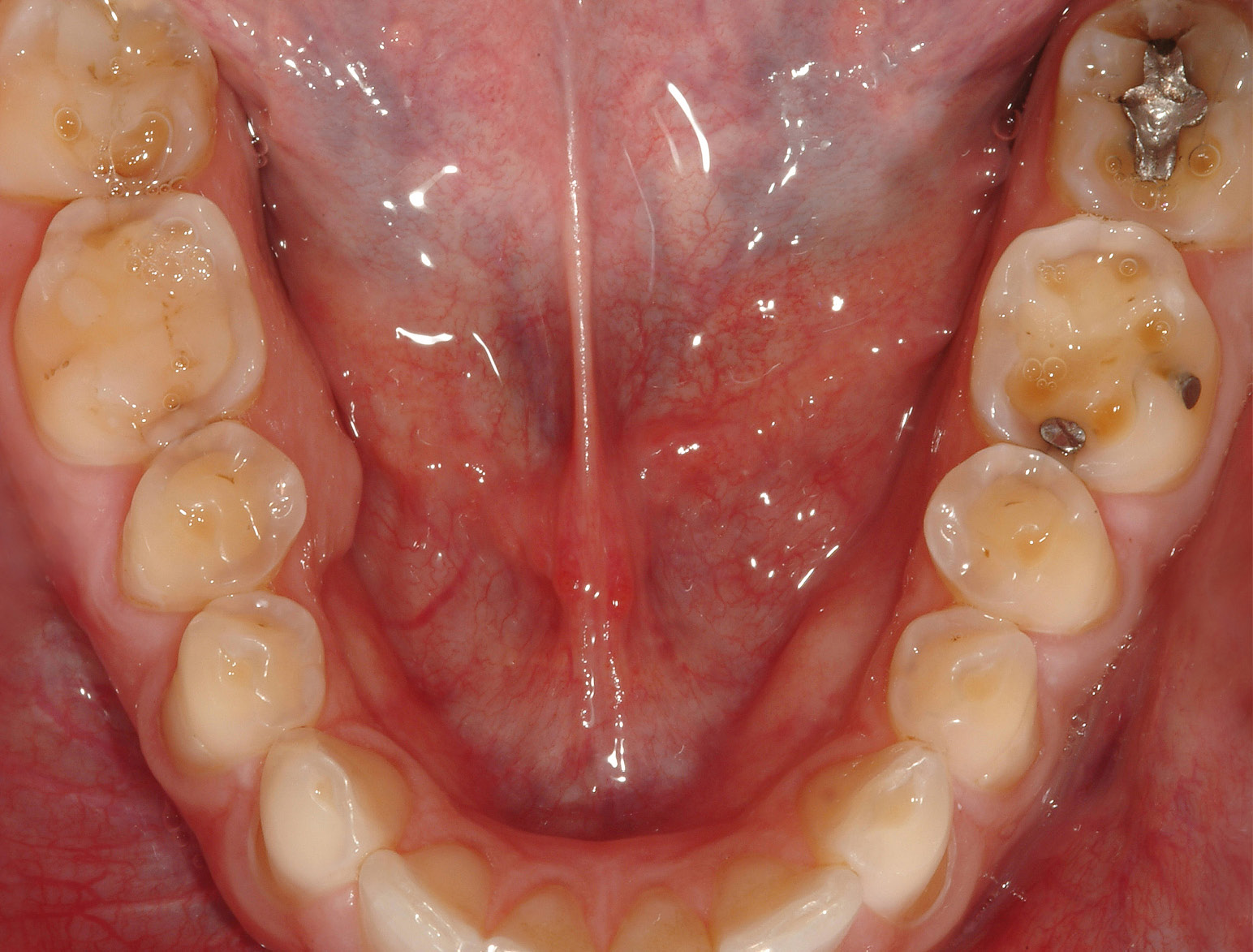
BEFORE
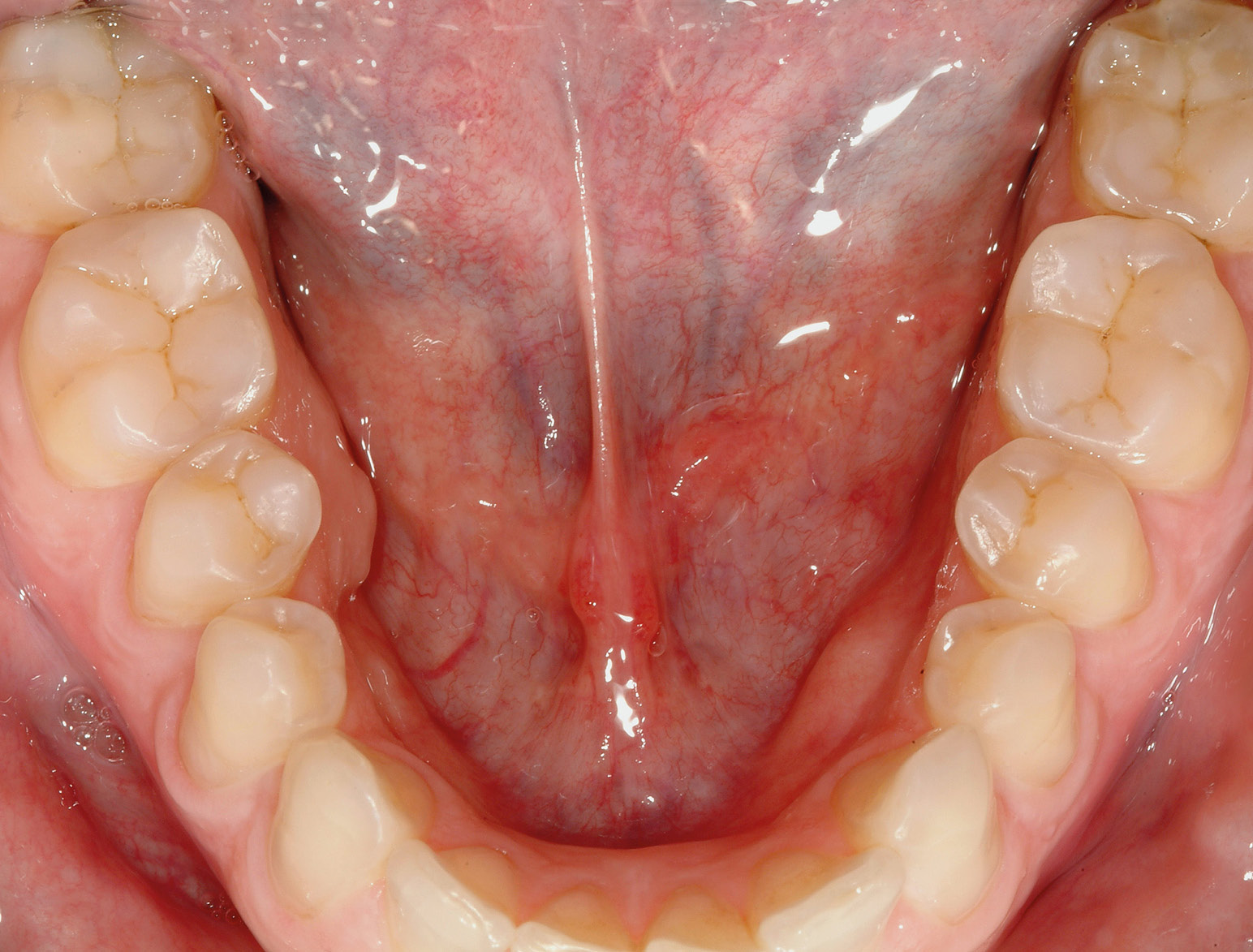
AFTER
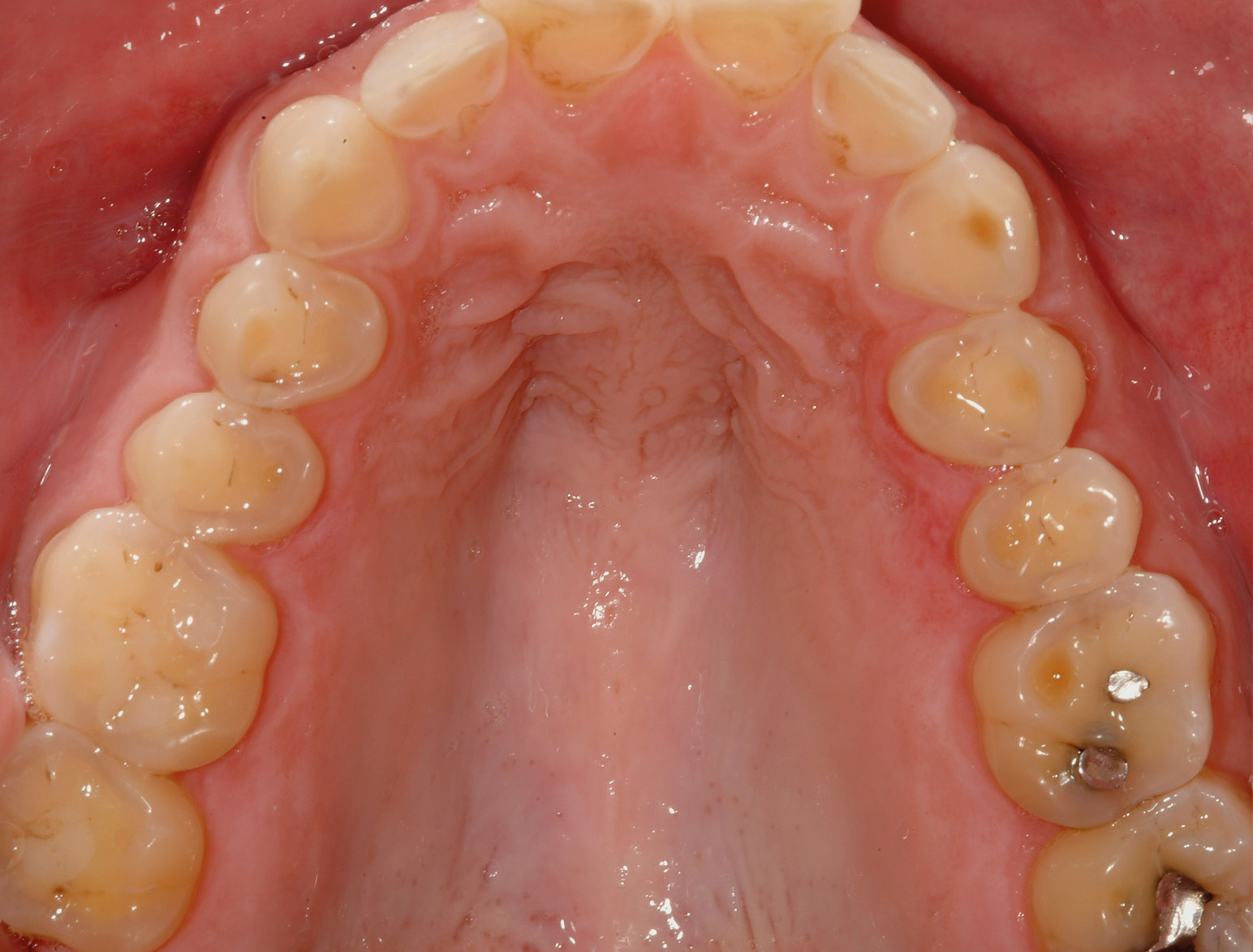
BEFORE
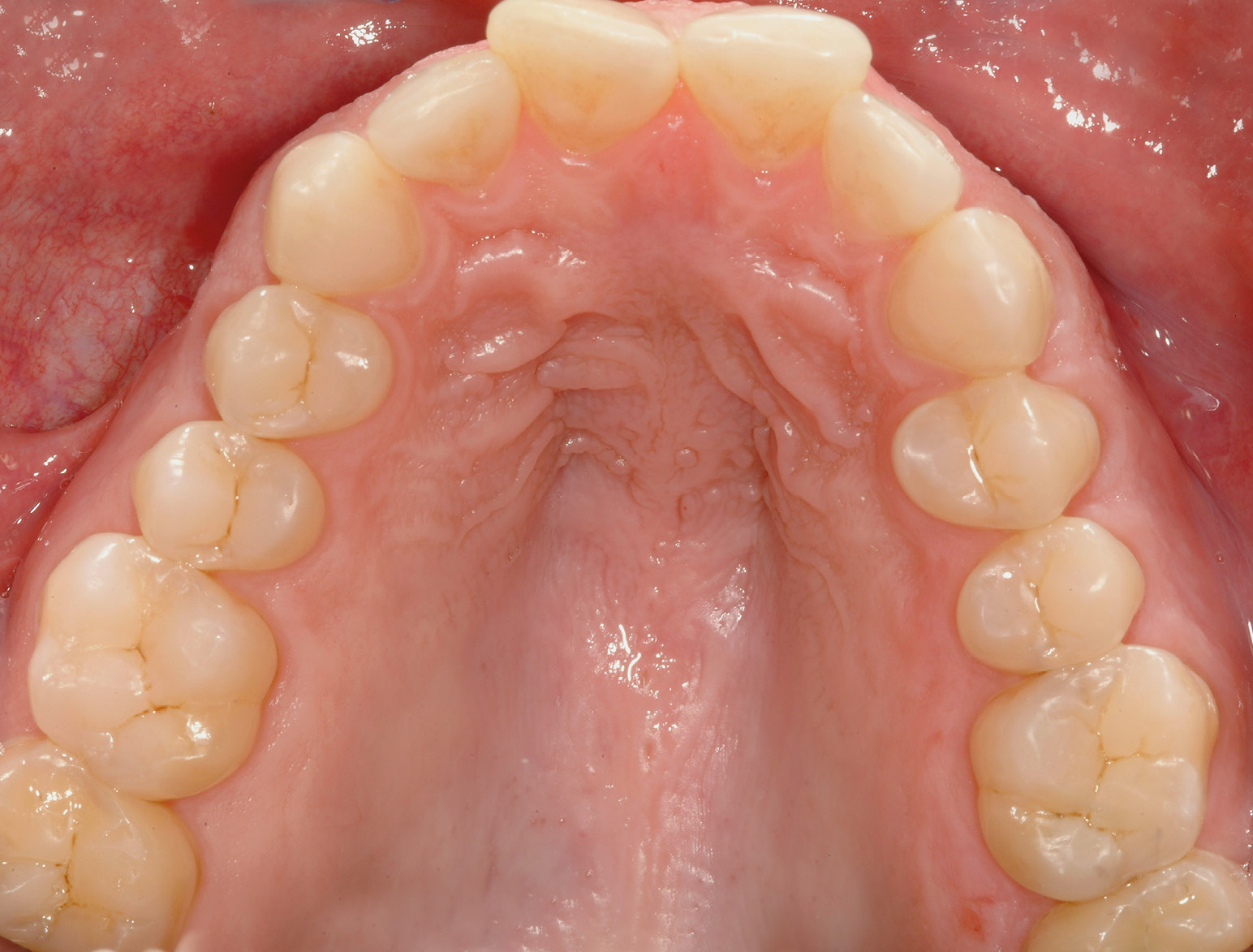
AFTER
FULL MOUTH REHABILITATION
BEFORE & AFTER / STEP BY STEP

BEFORE

AFTER
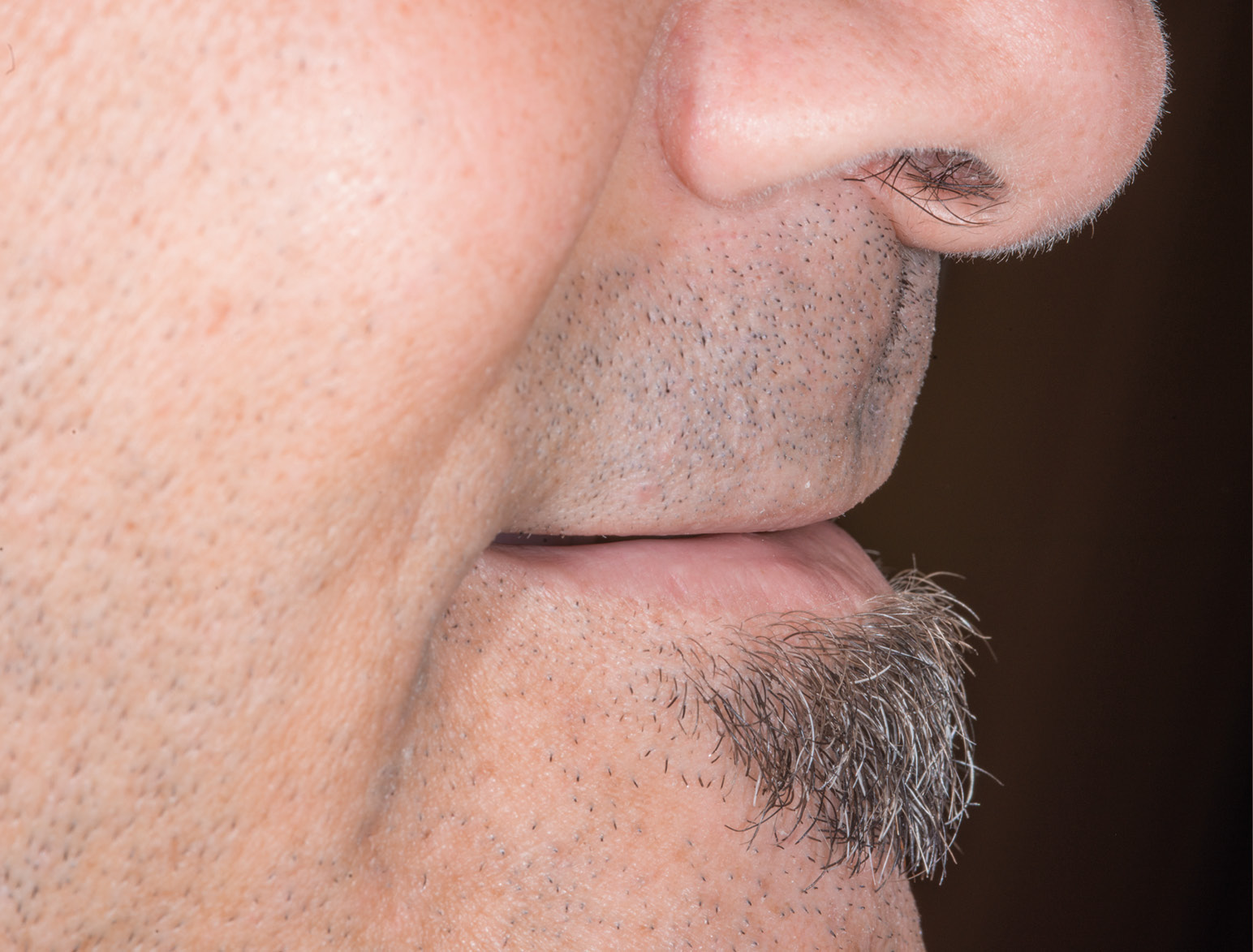
BEFORE
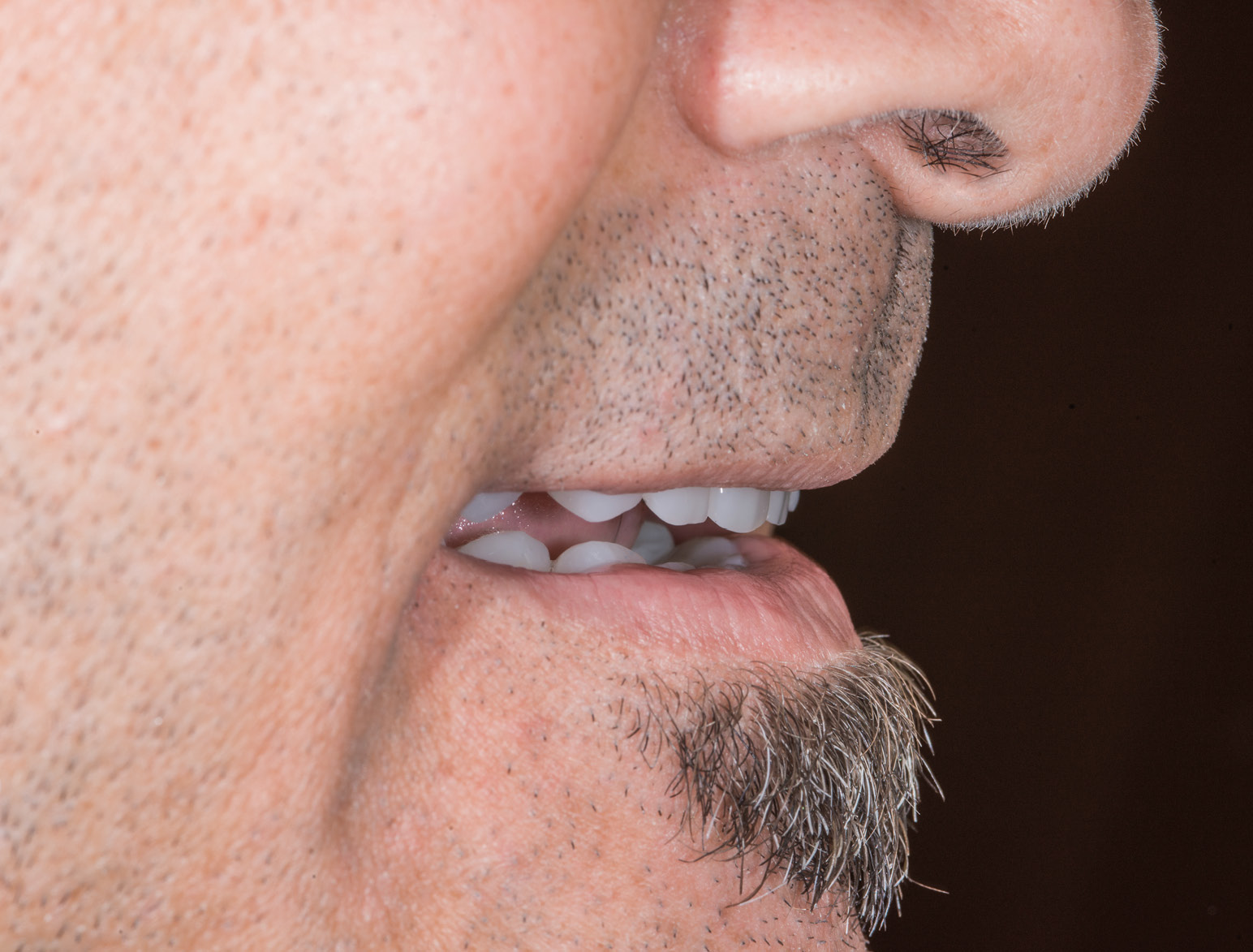
AFTER
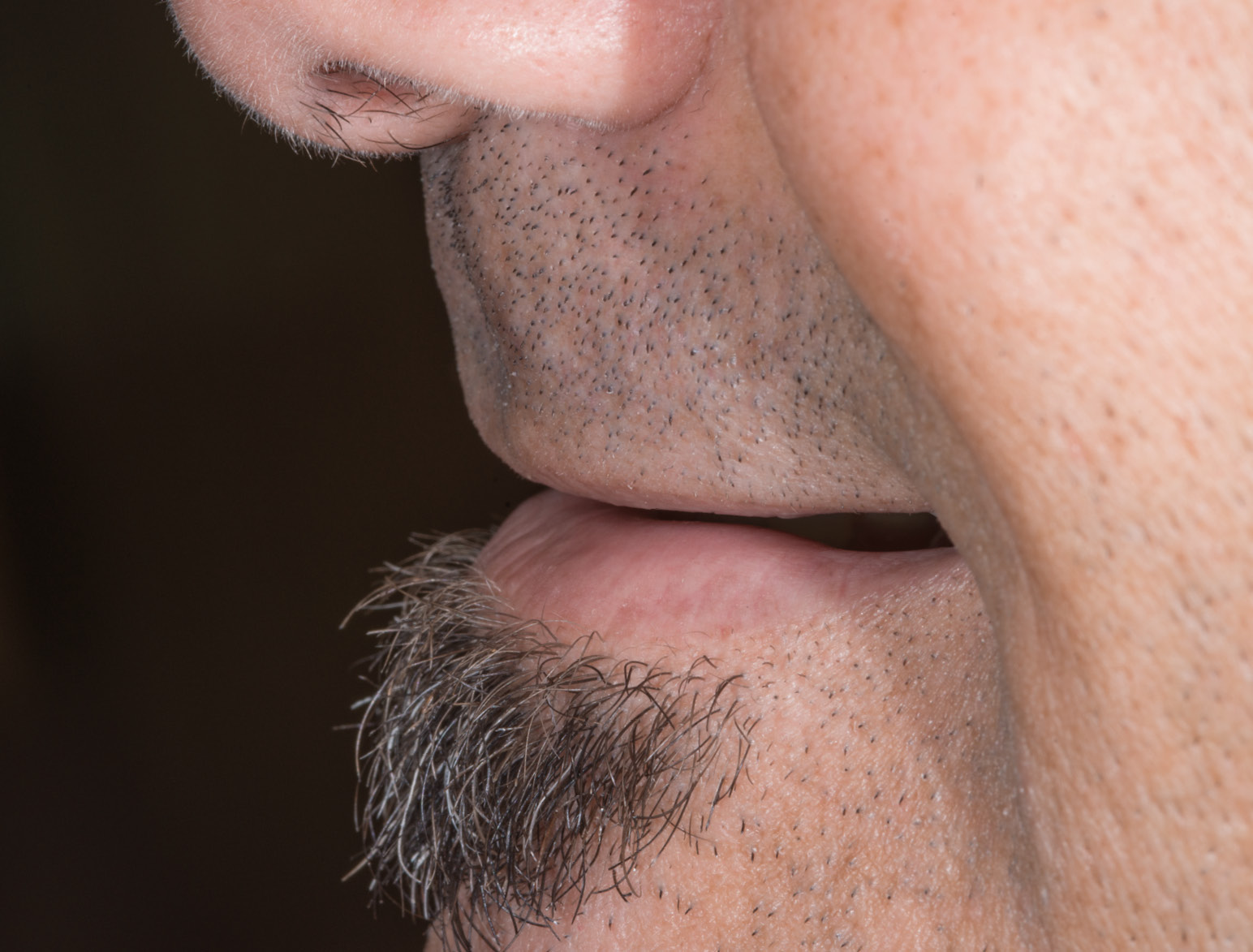
BEFORE
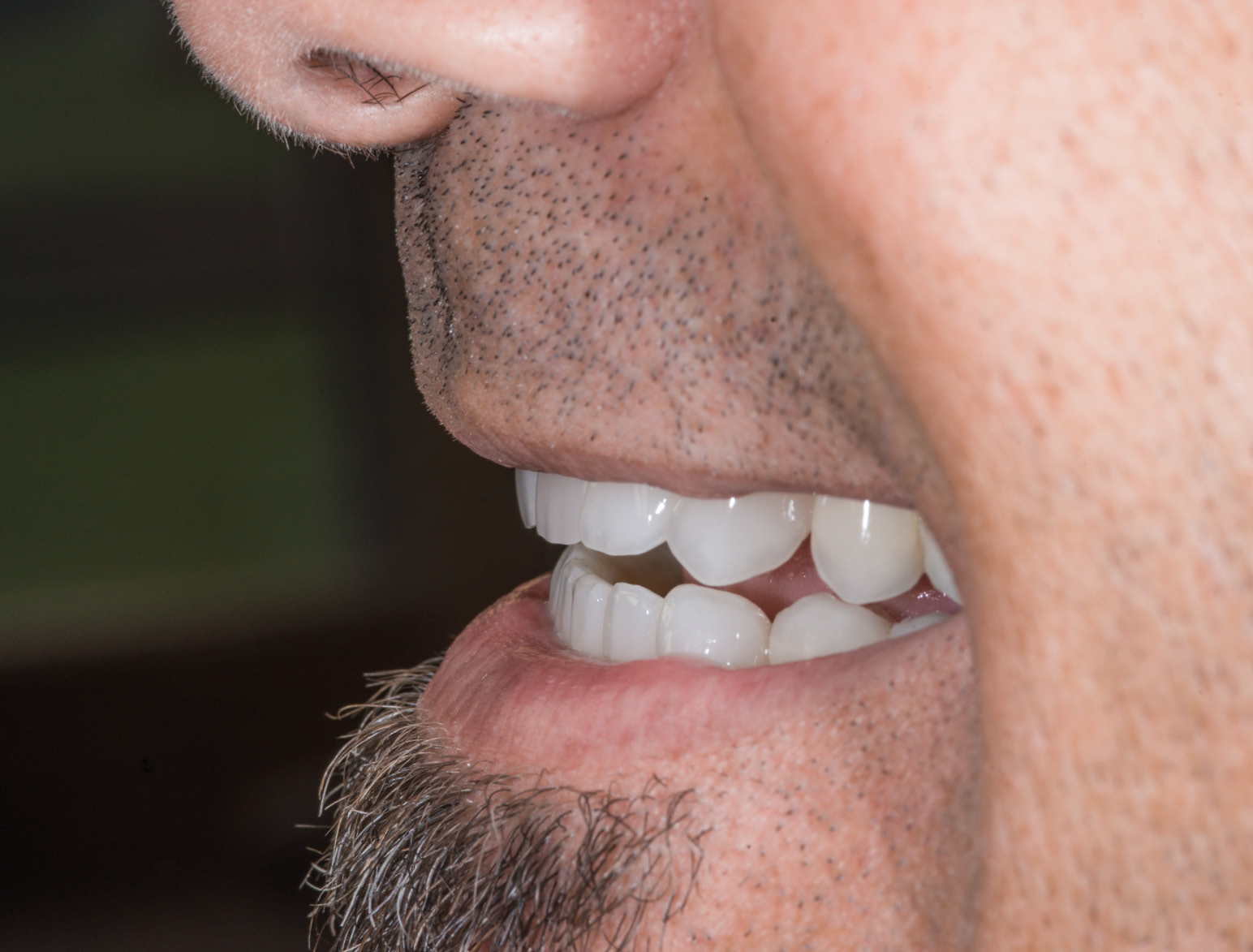
AFTER
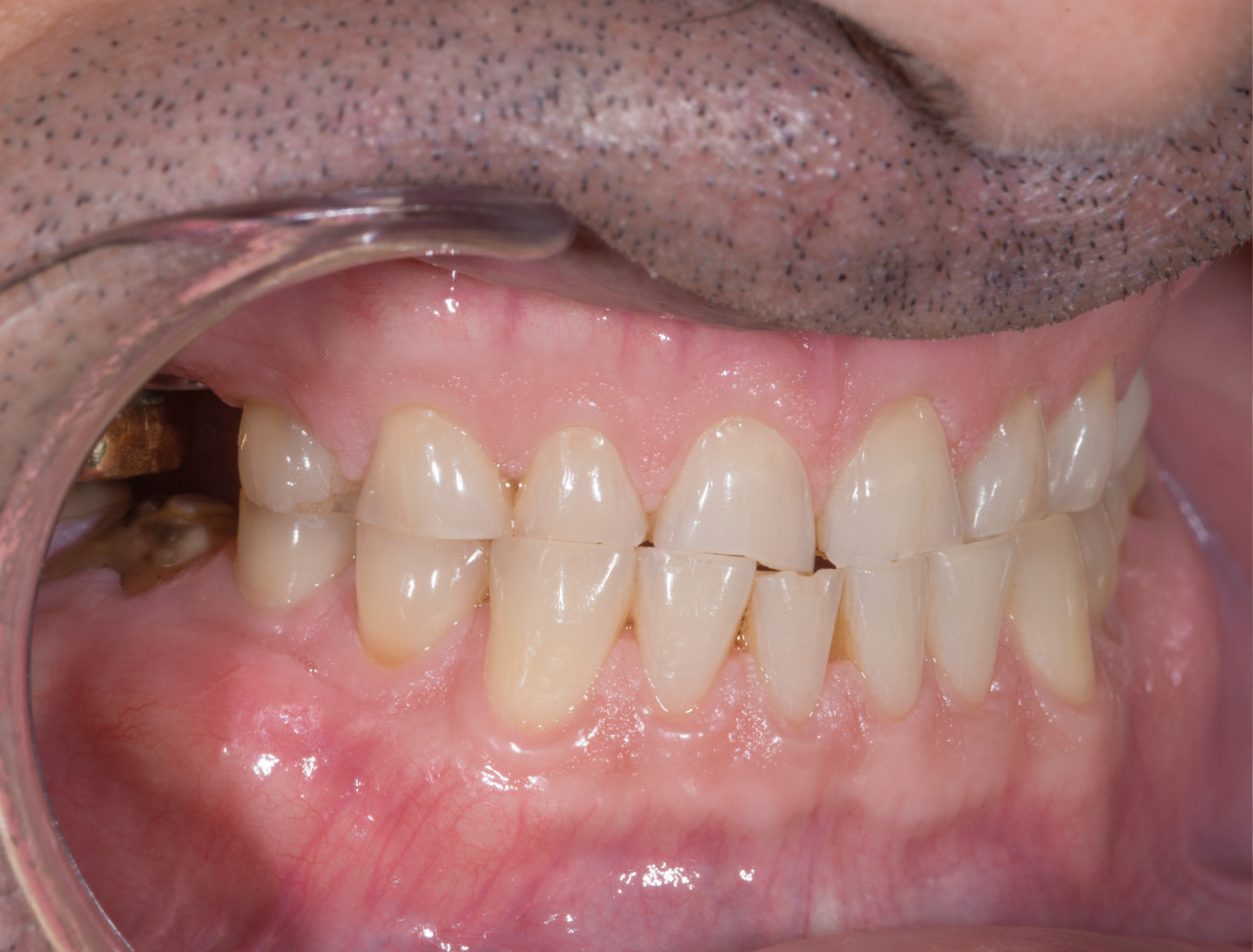
BEFORE
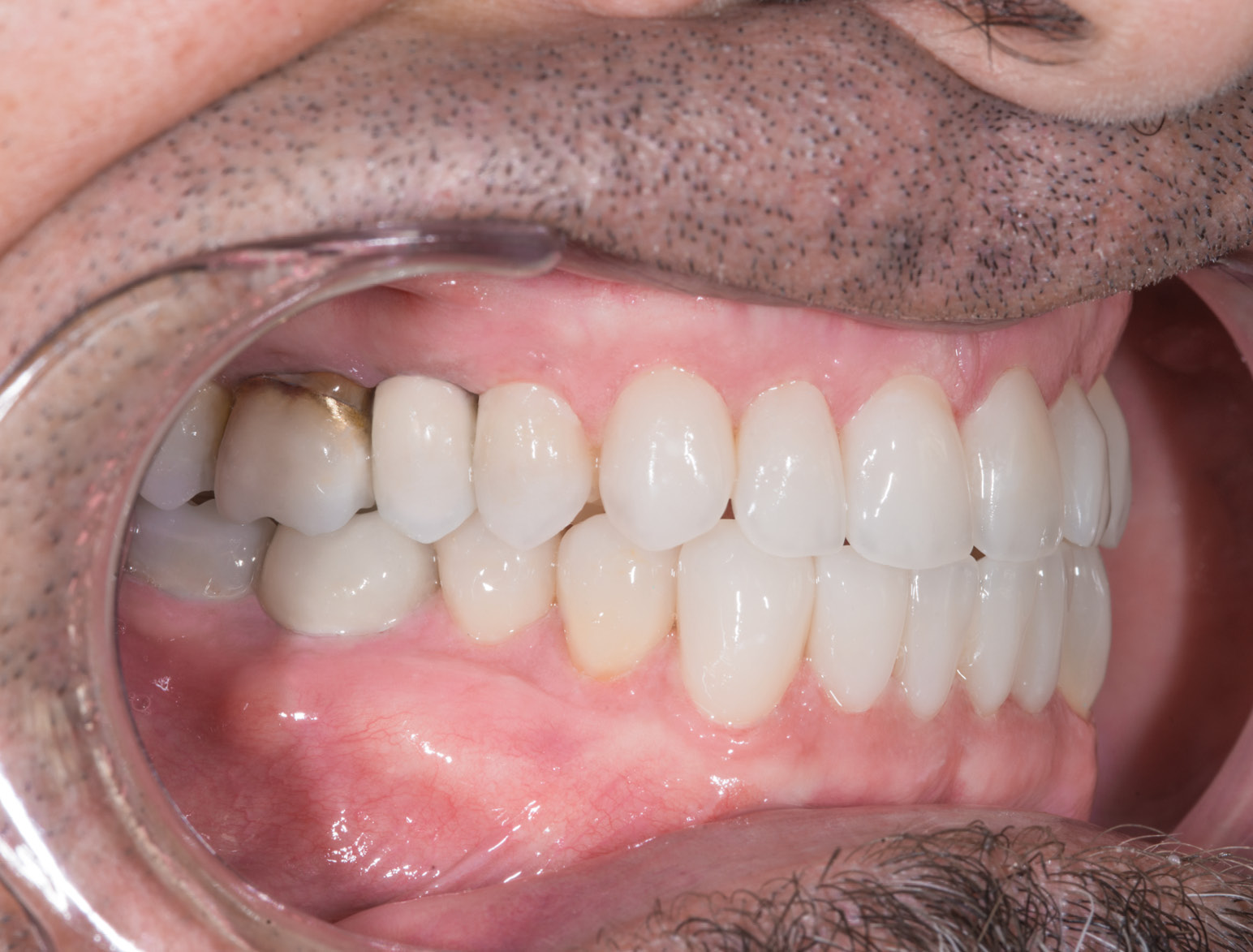
AFTER
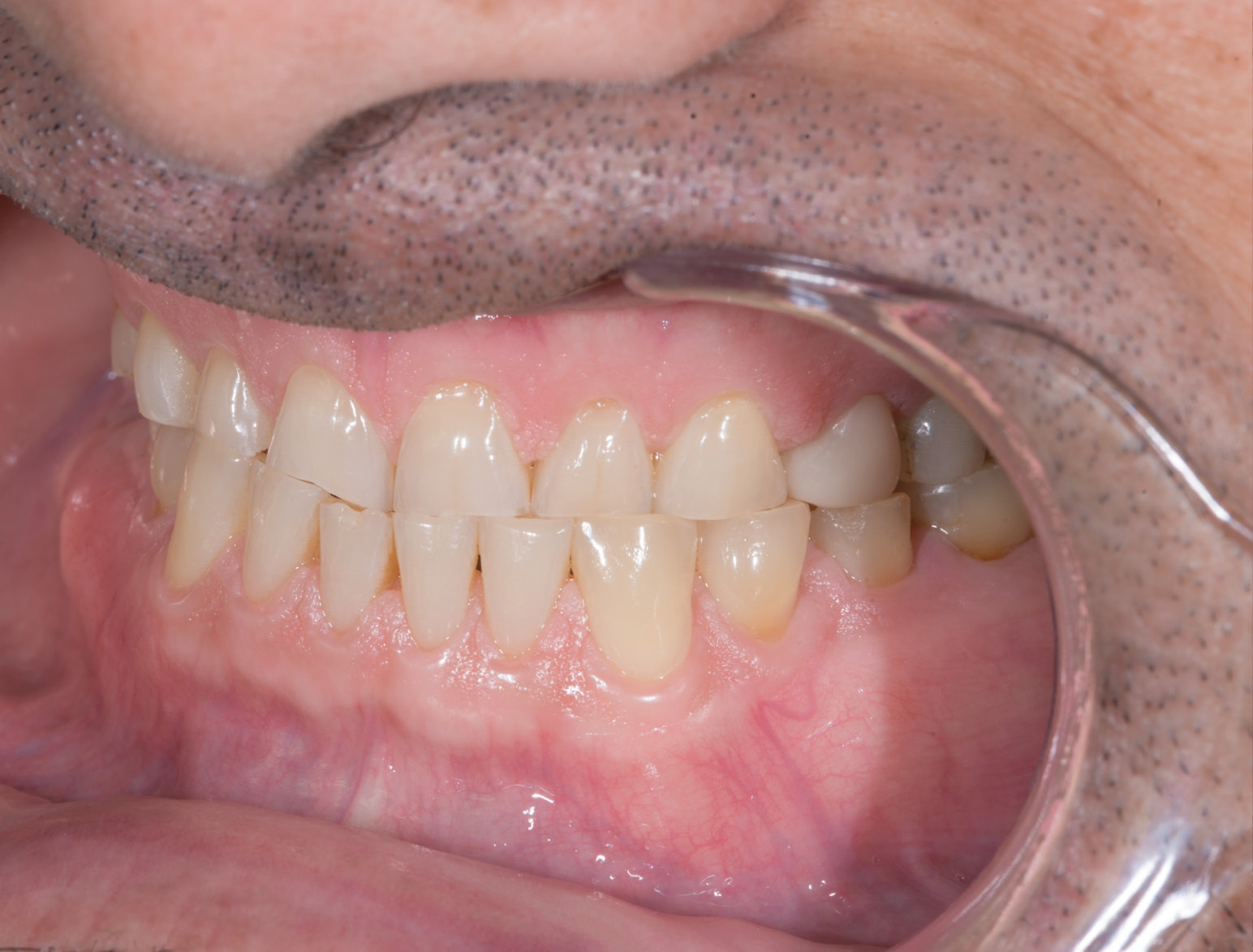
BEFORE
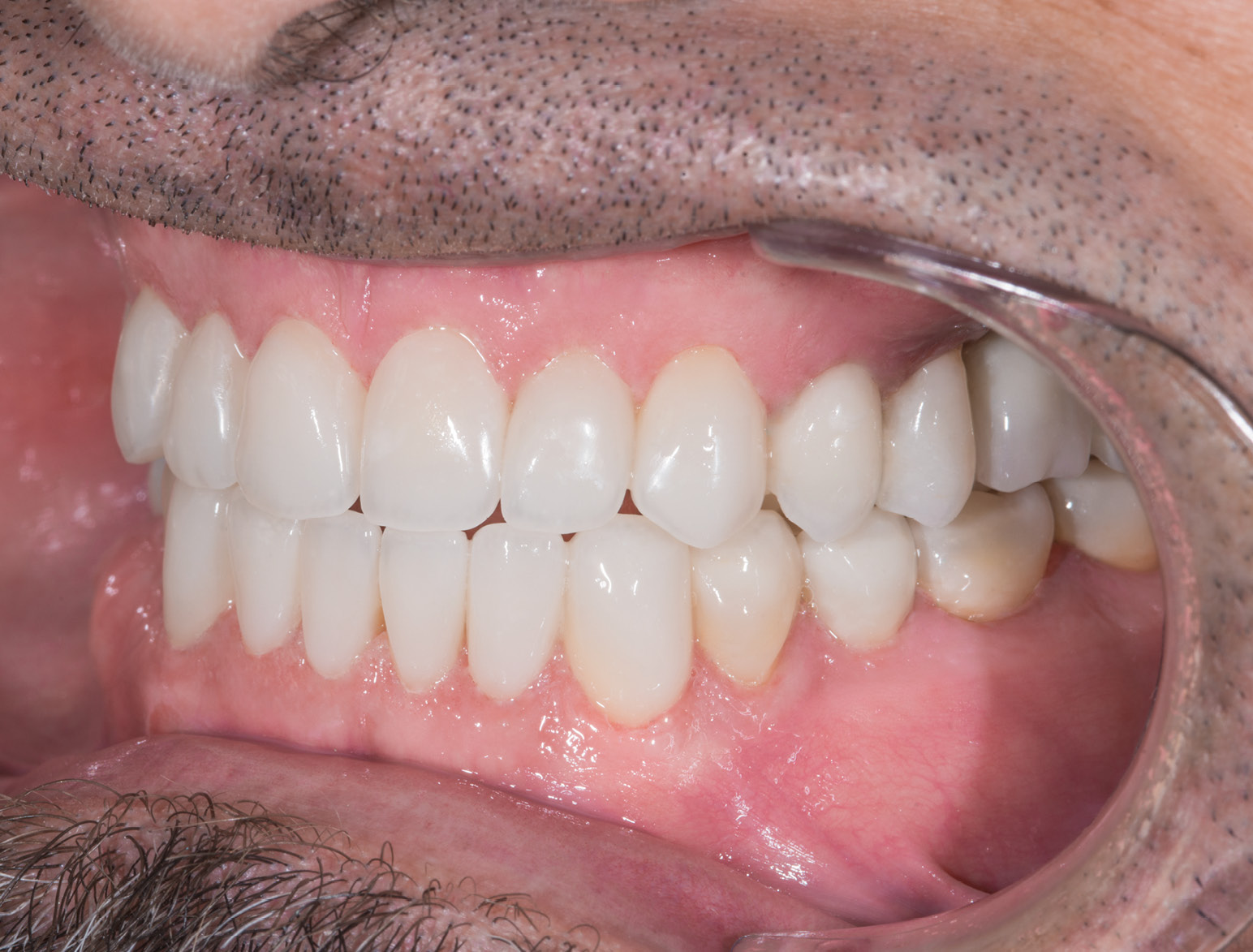
AFTER
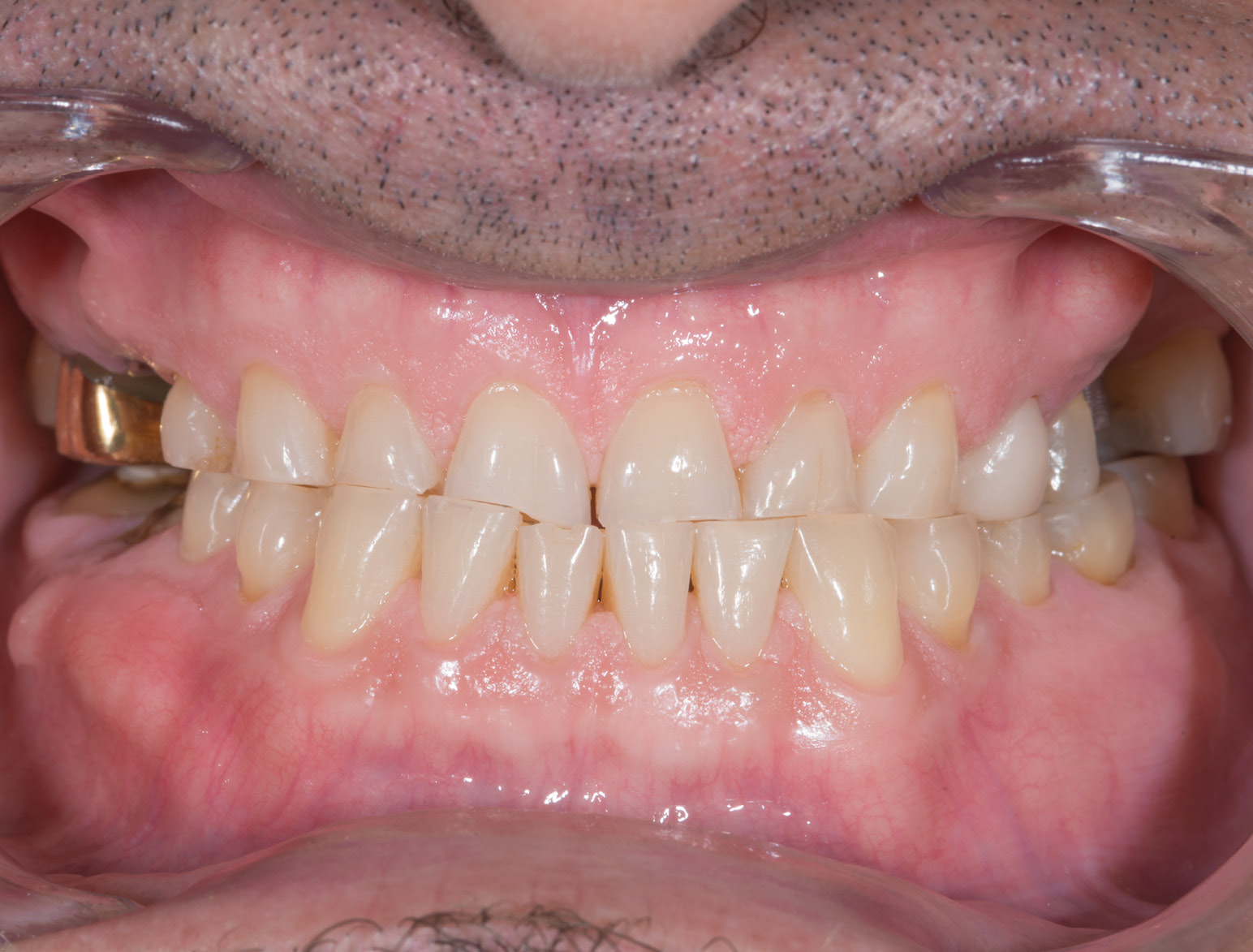
BEFORE
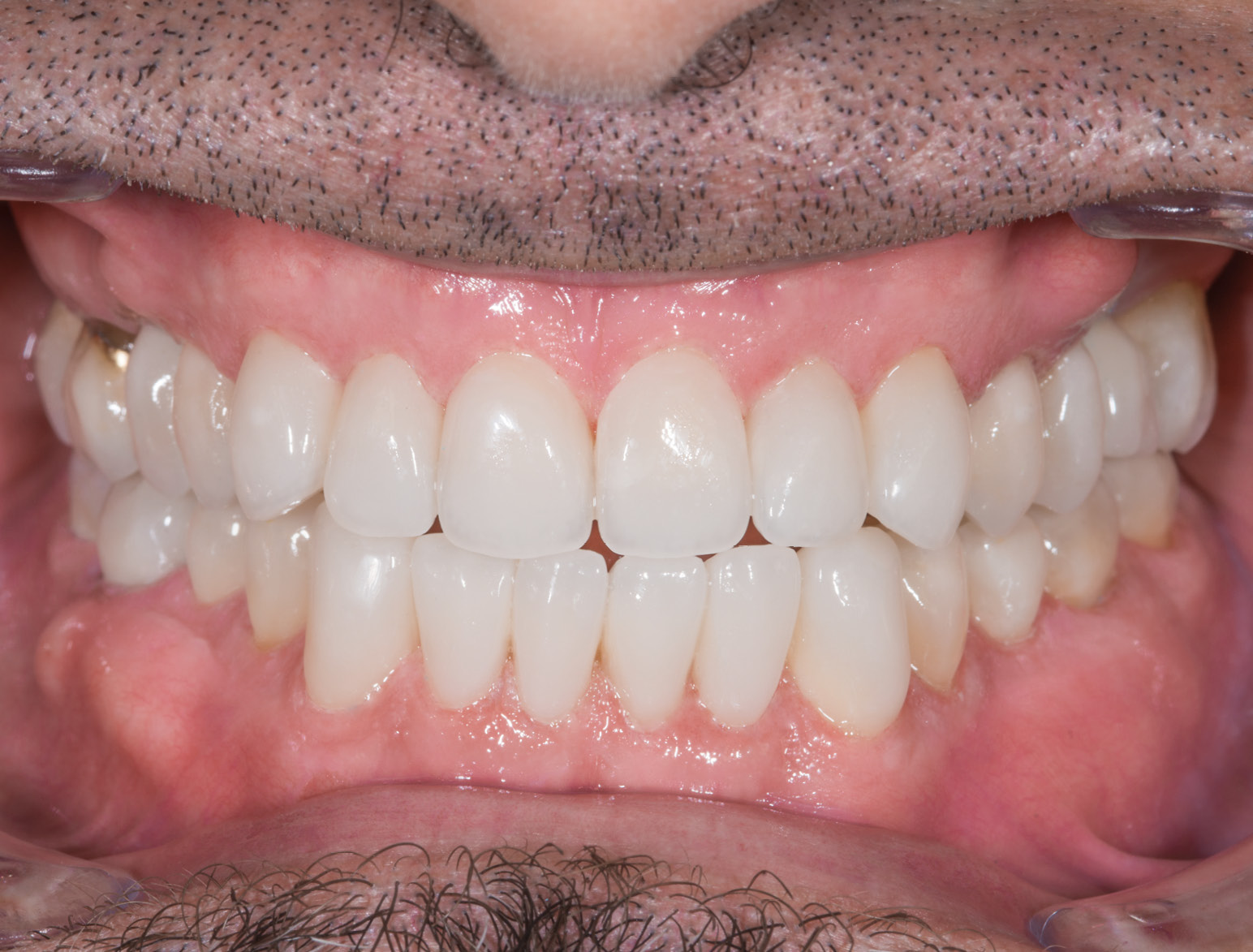
AFTER
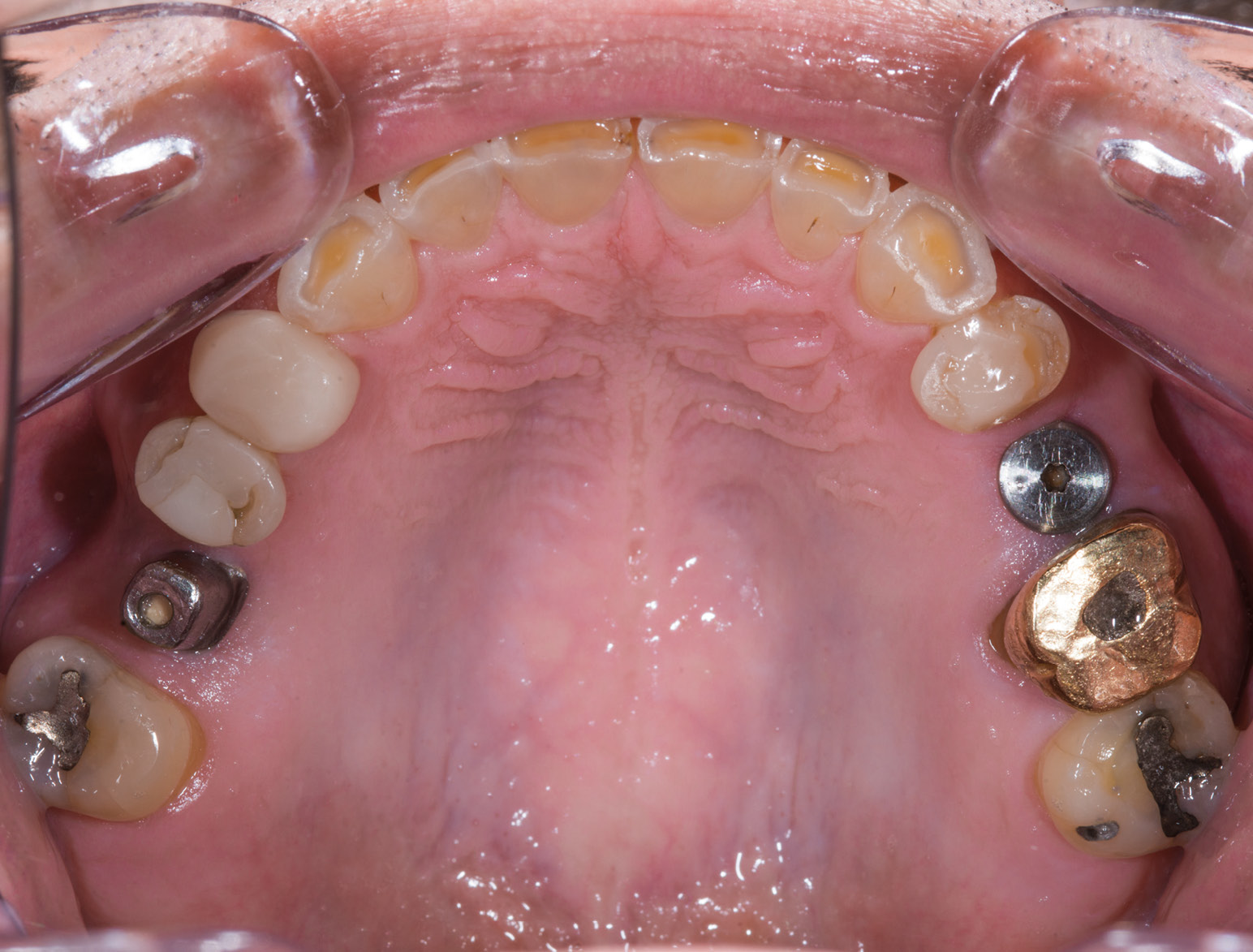
BEFORE
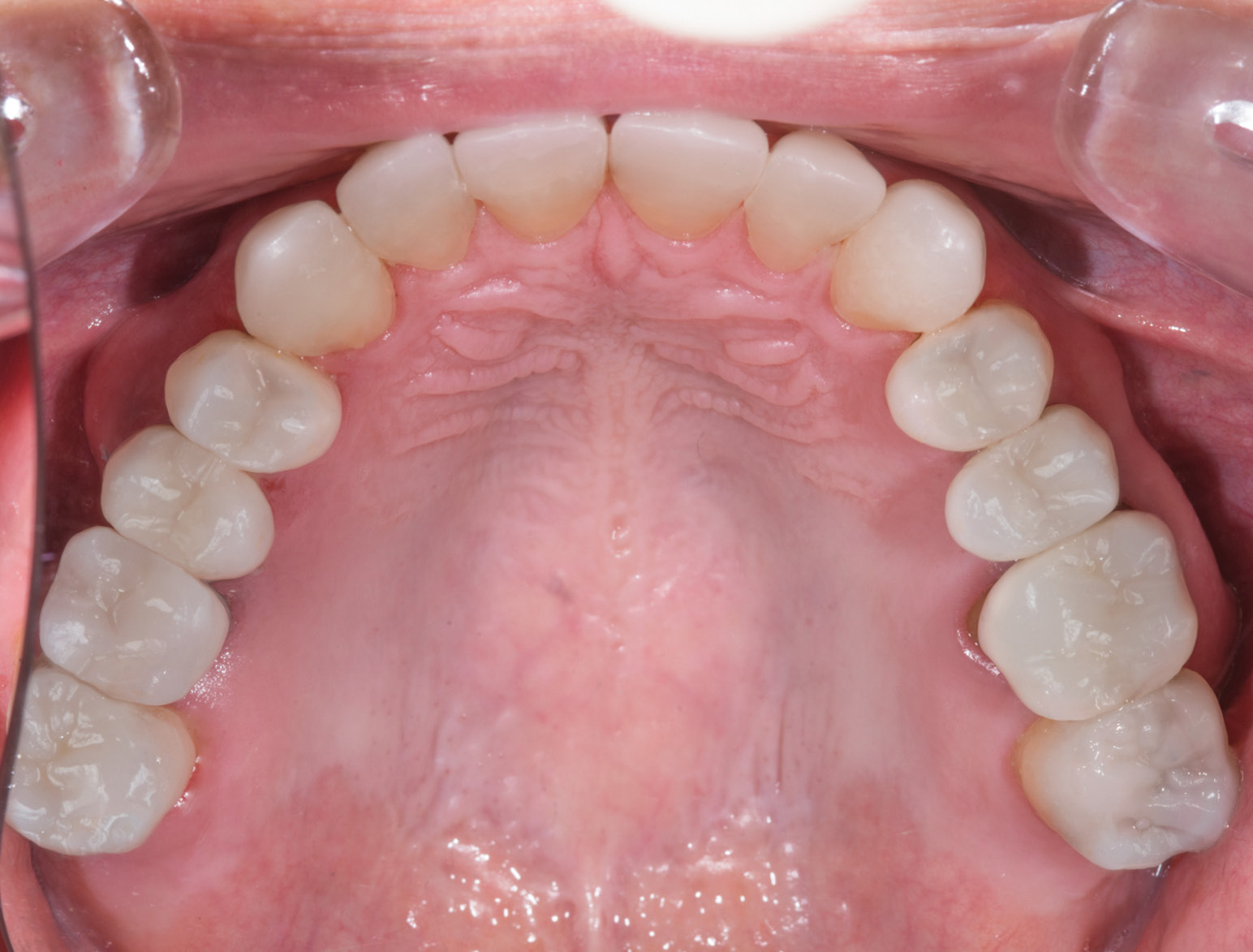
AFTER
BEFORE
AFTER
LIFTING THE VERTICAL DIMENSION
BEFORE & AFTER / STEP BY STEP

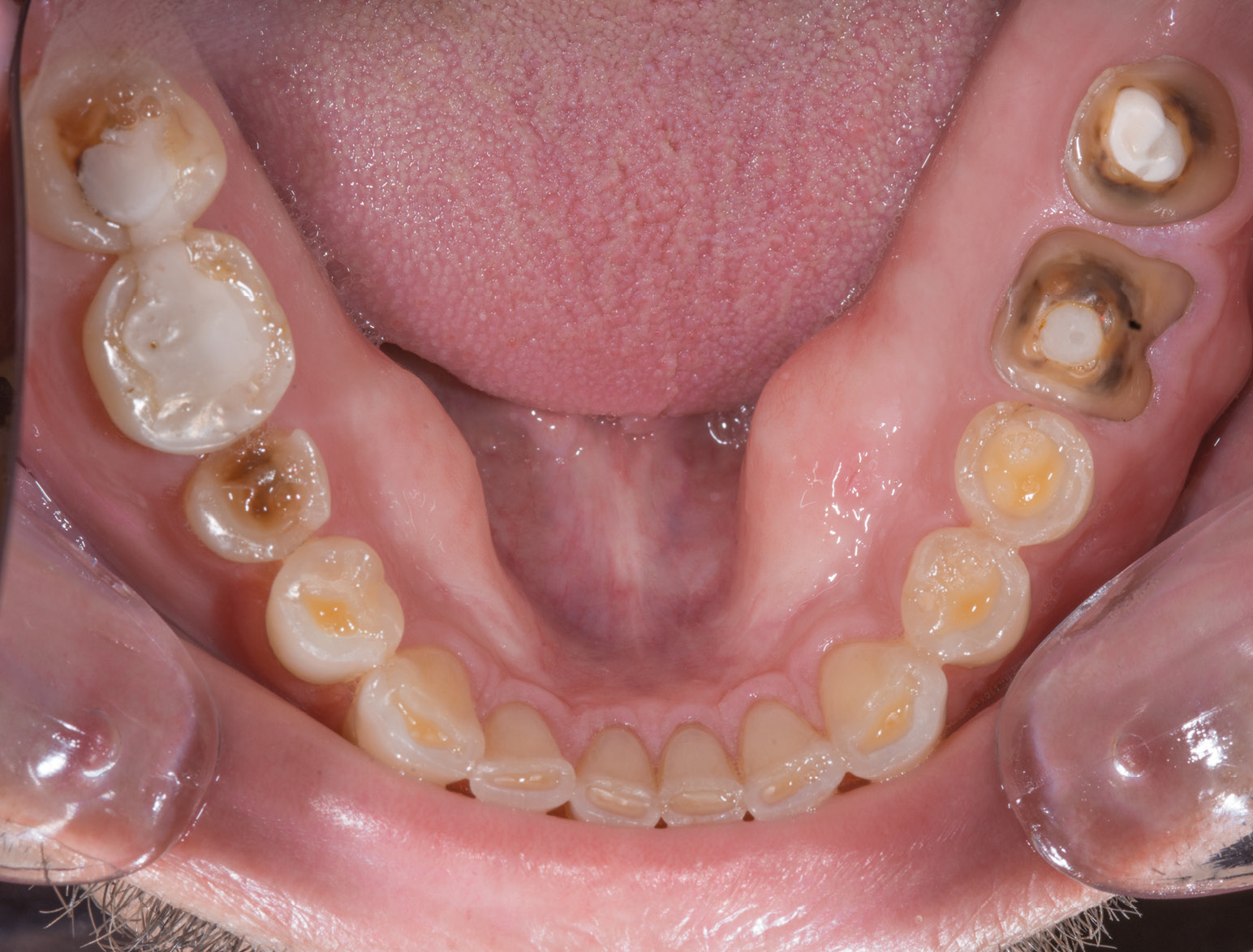
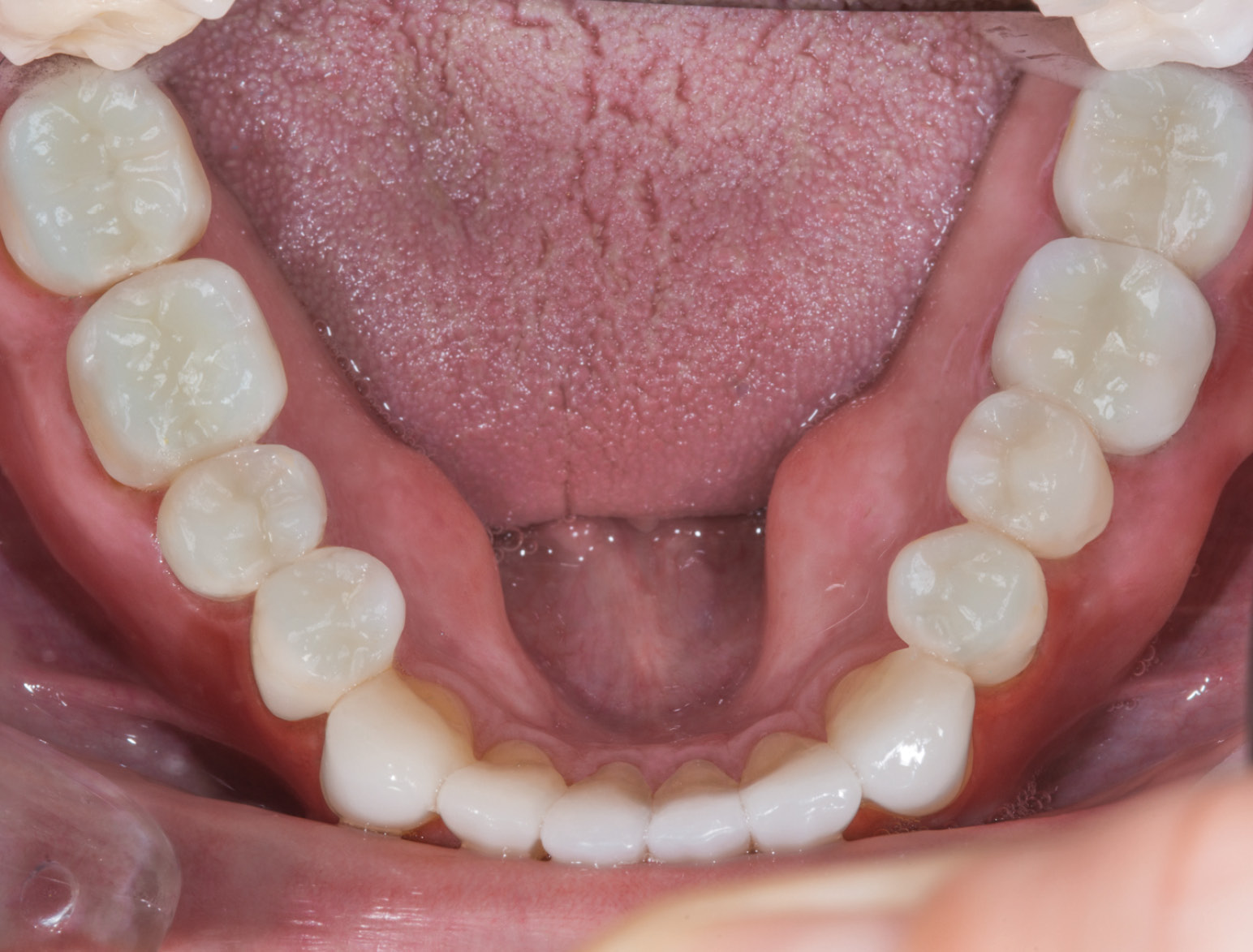
BEFORE

AFTER
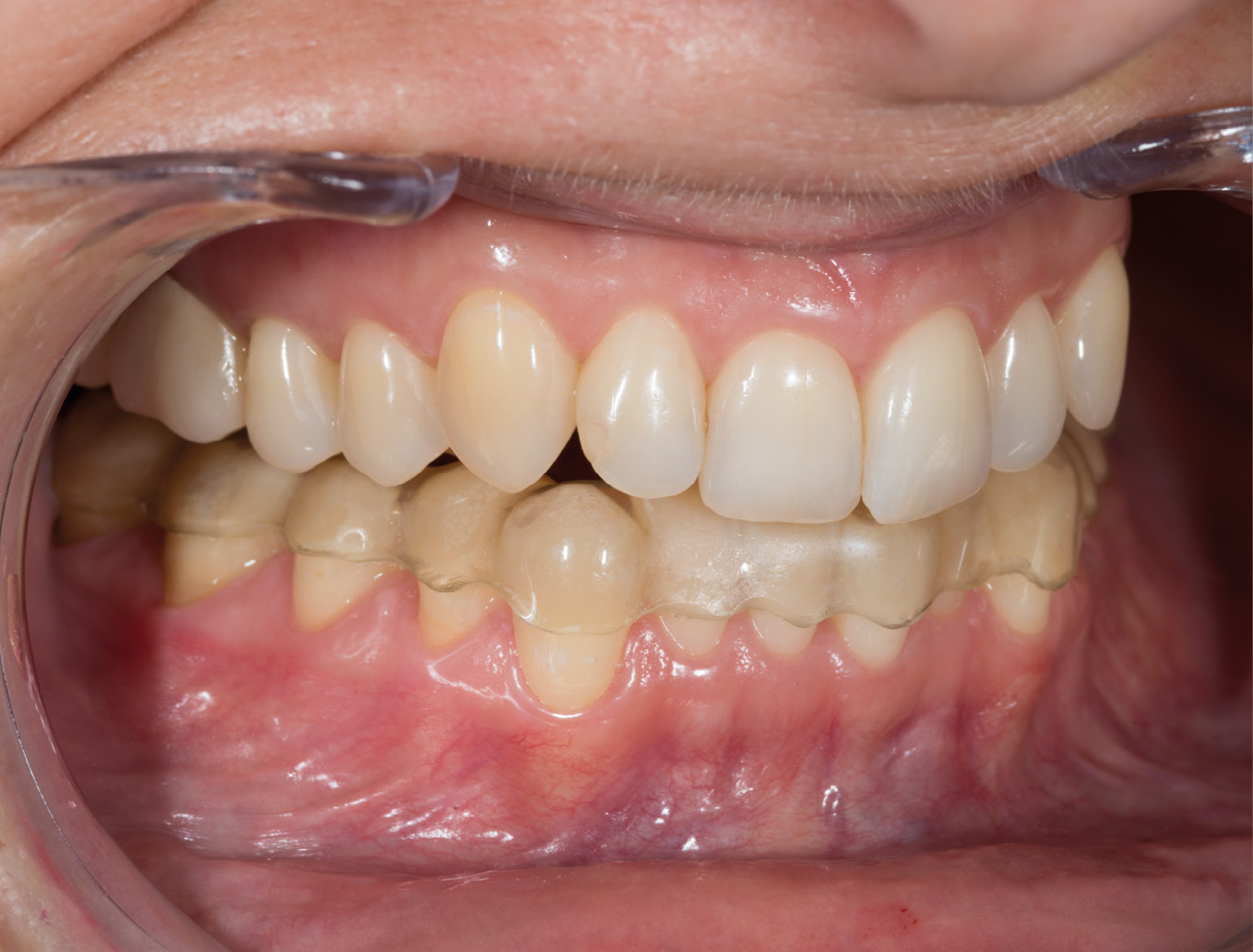
BEFORE
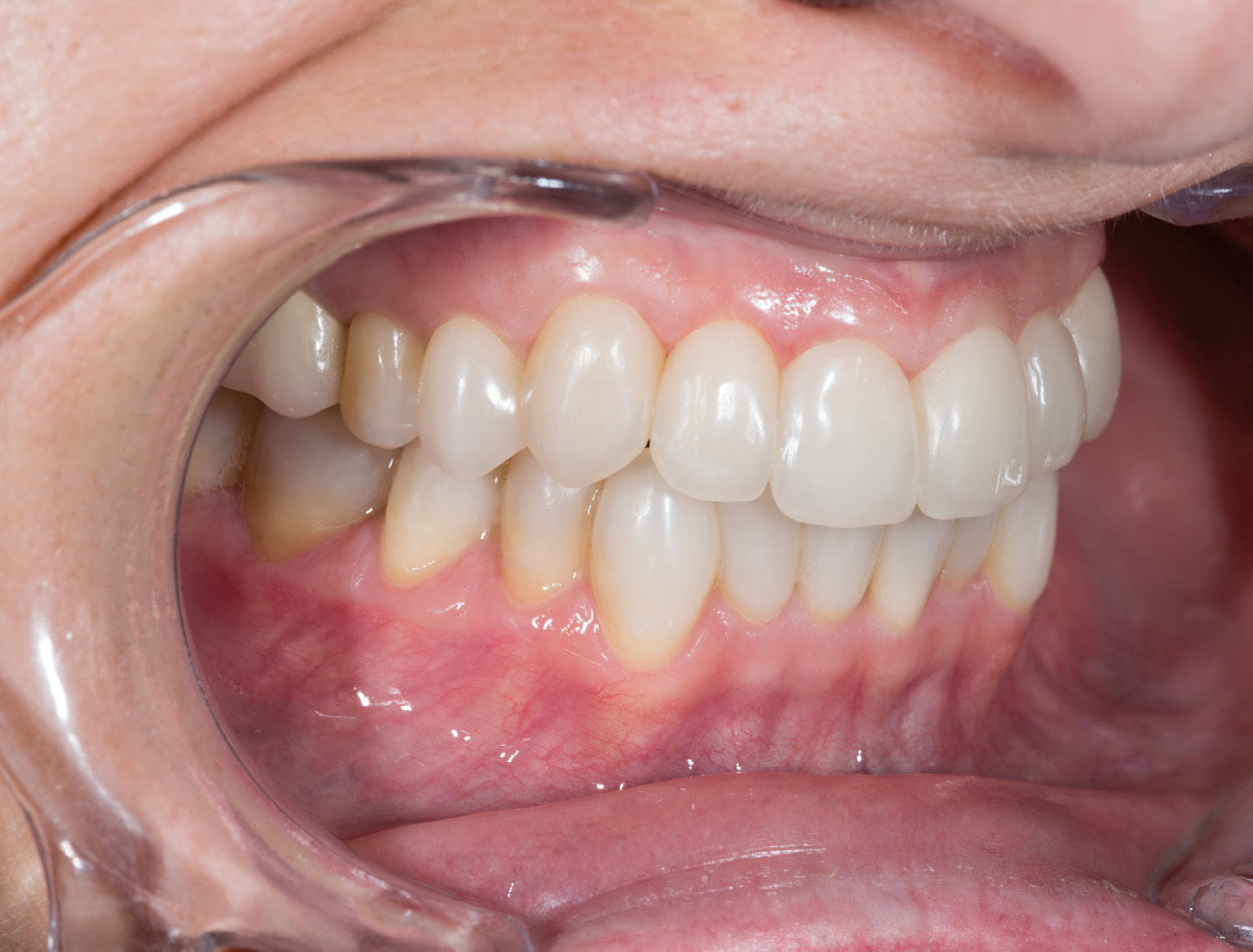
AFTER
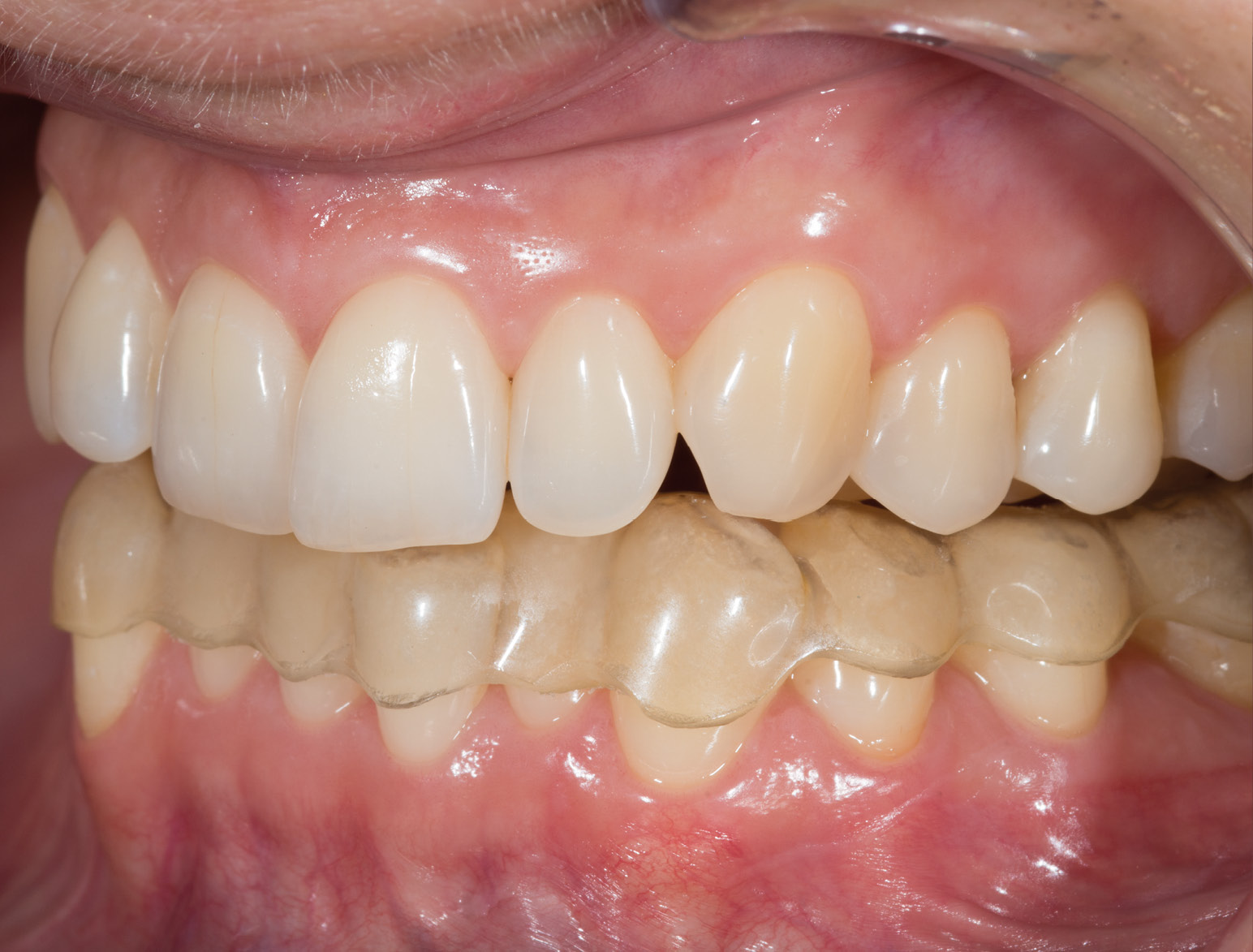
BEFORE
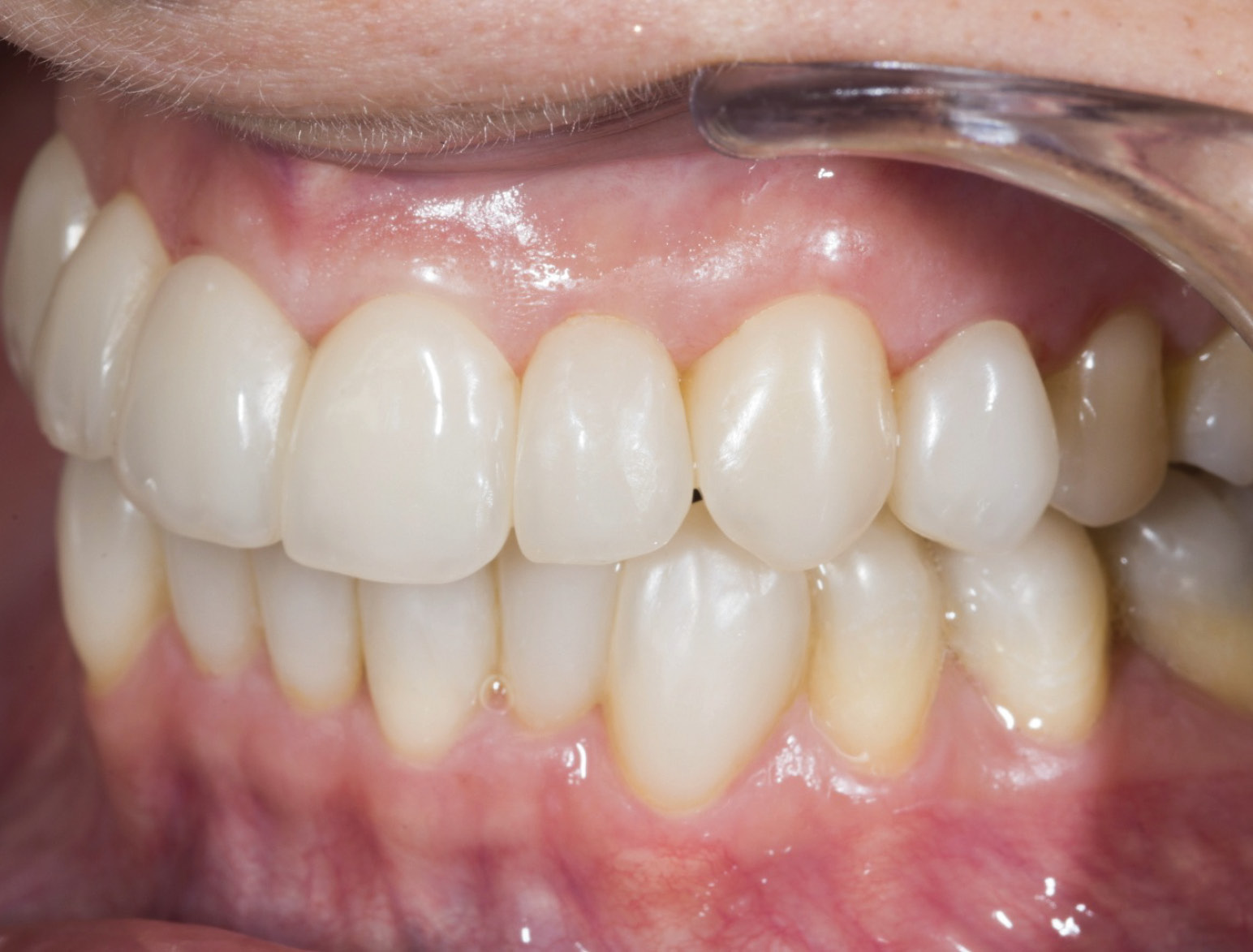
AFTER
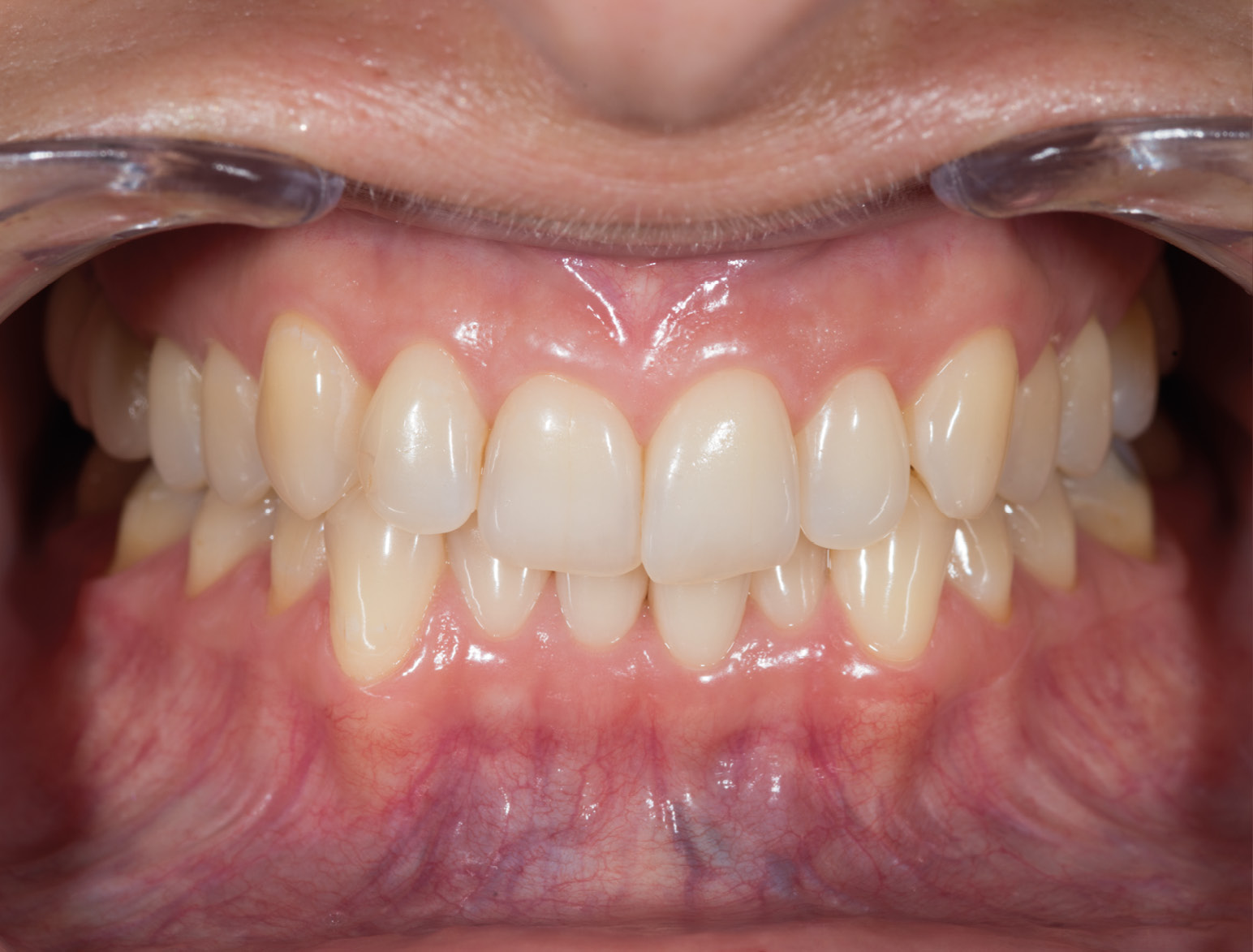
BEFORE
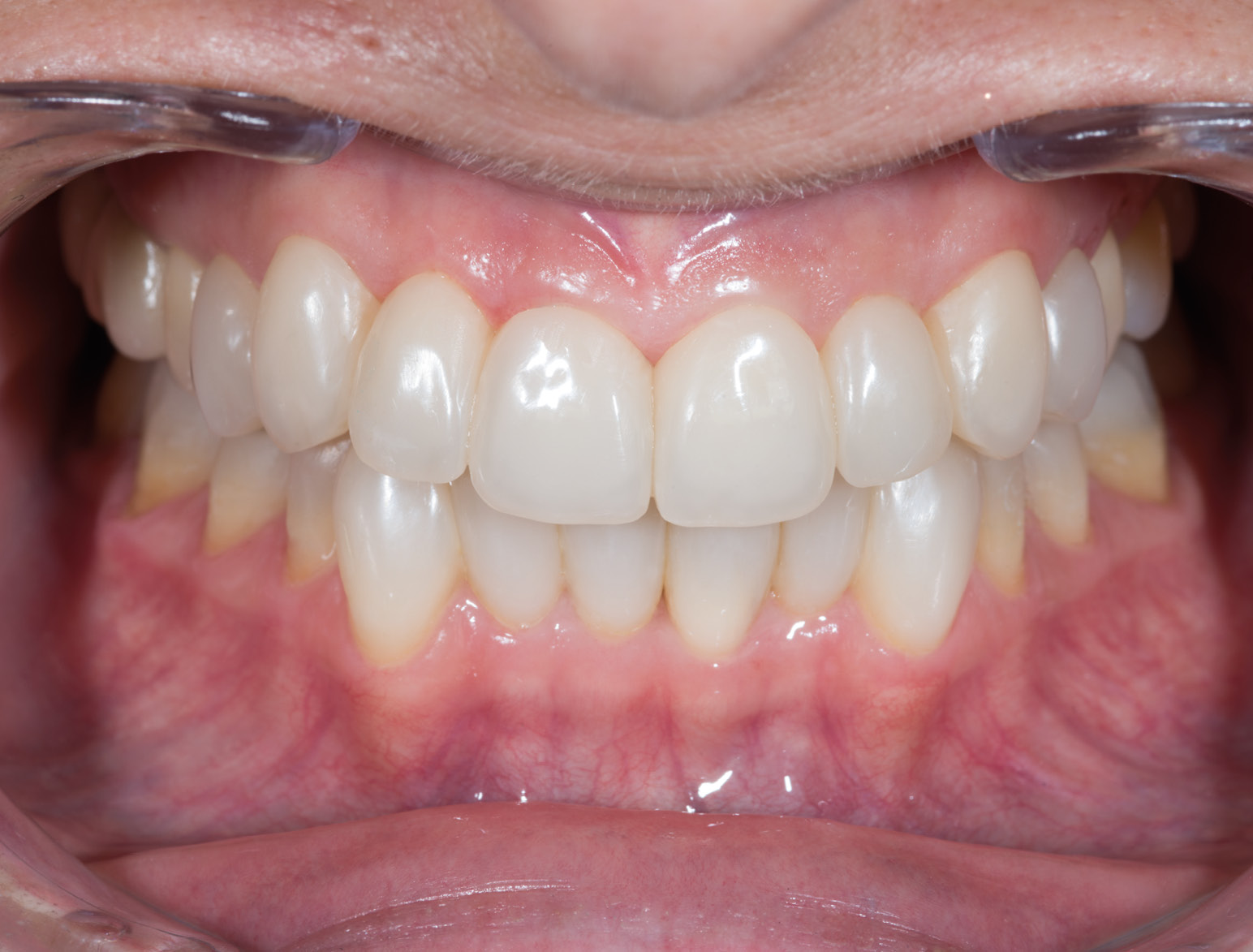
AFTER
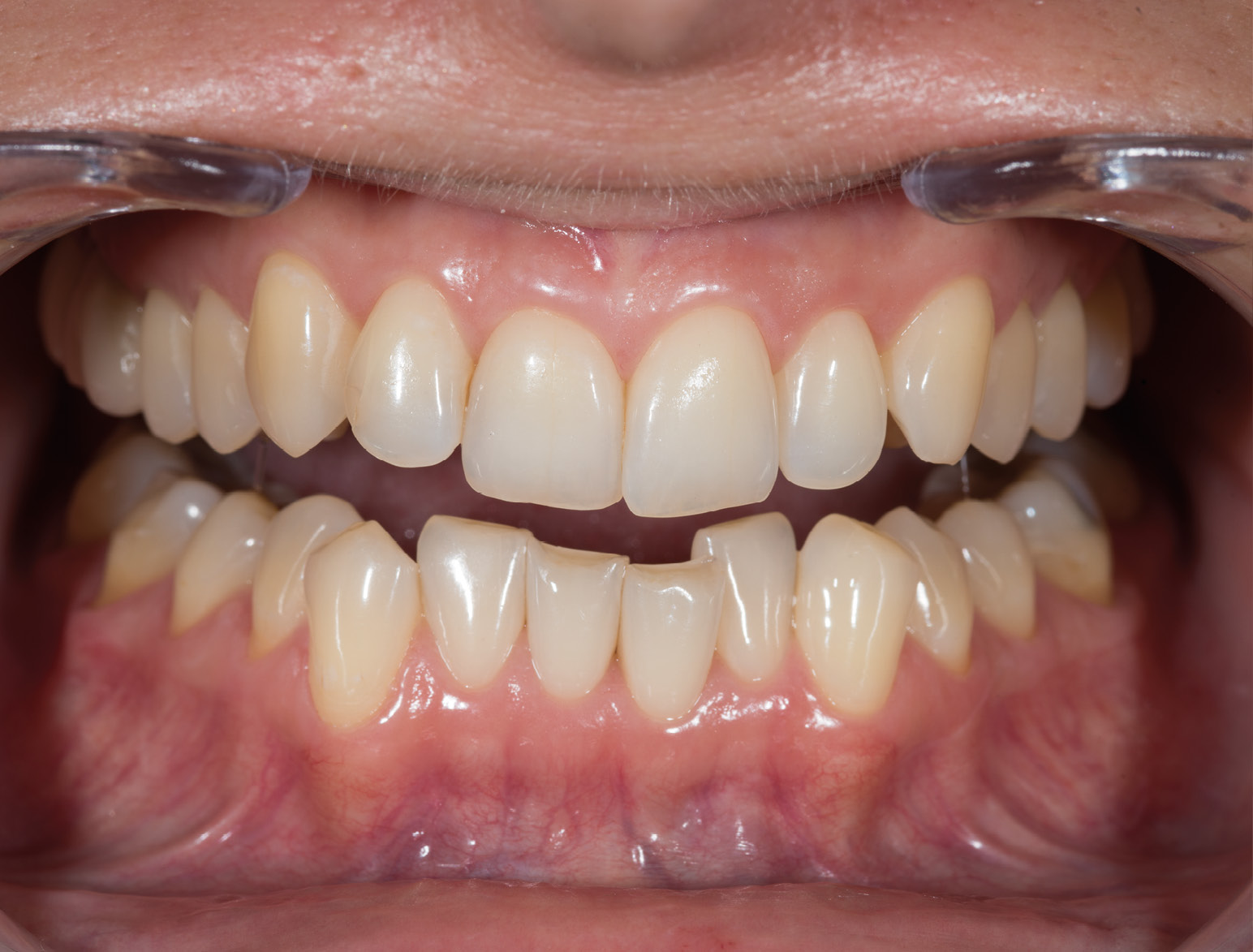
BEFORE
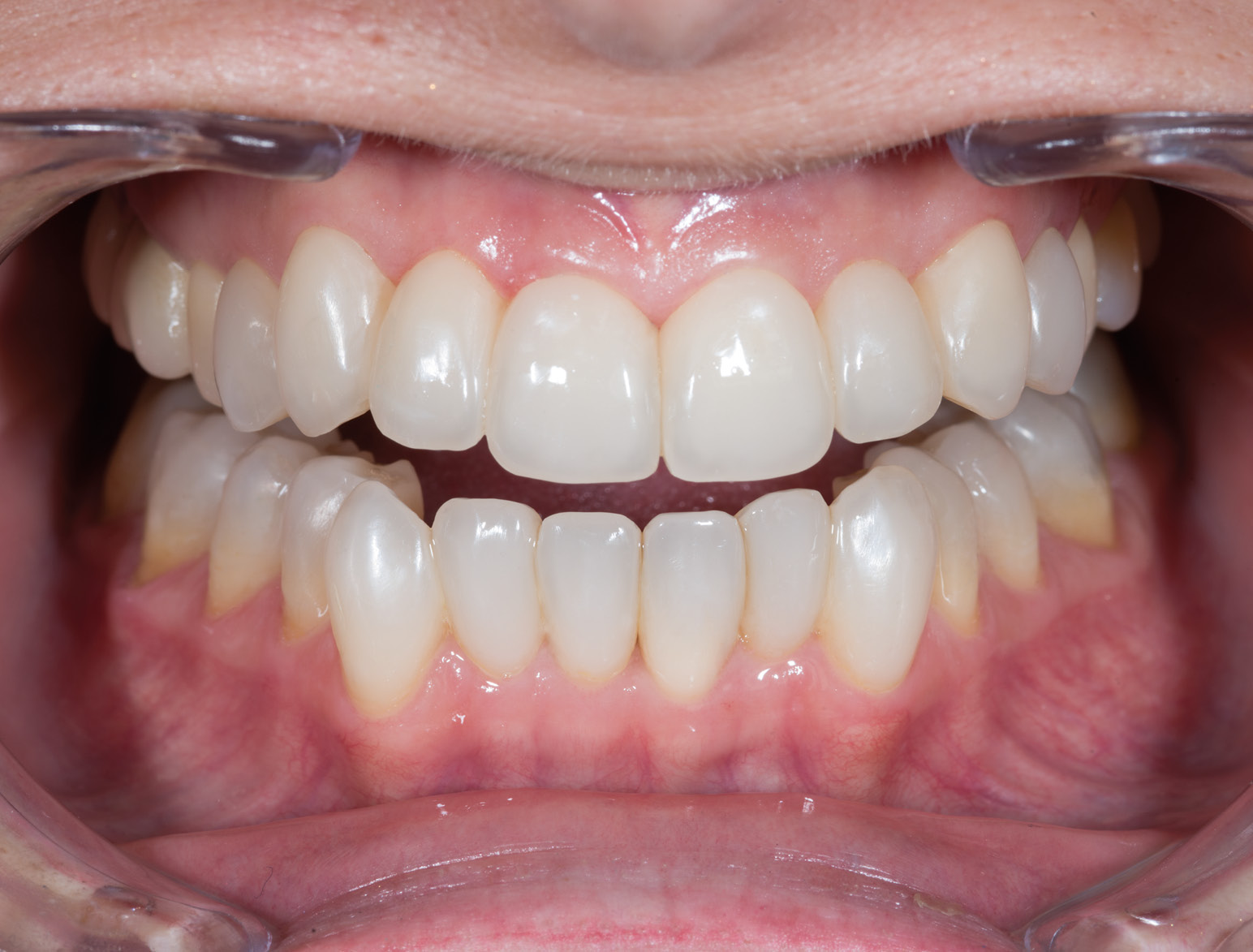
AFTER
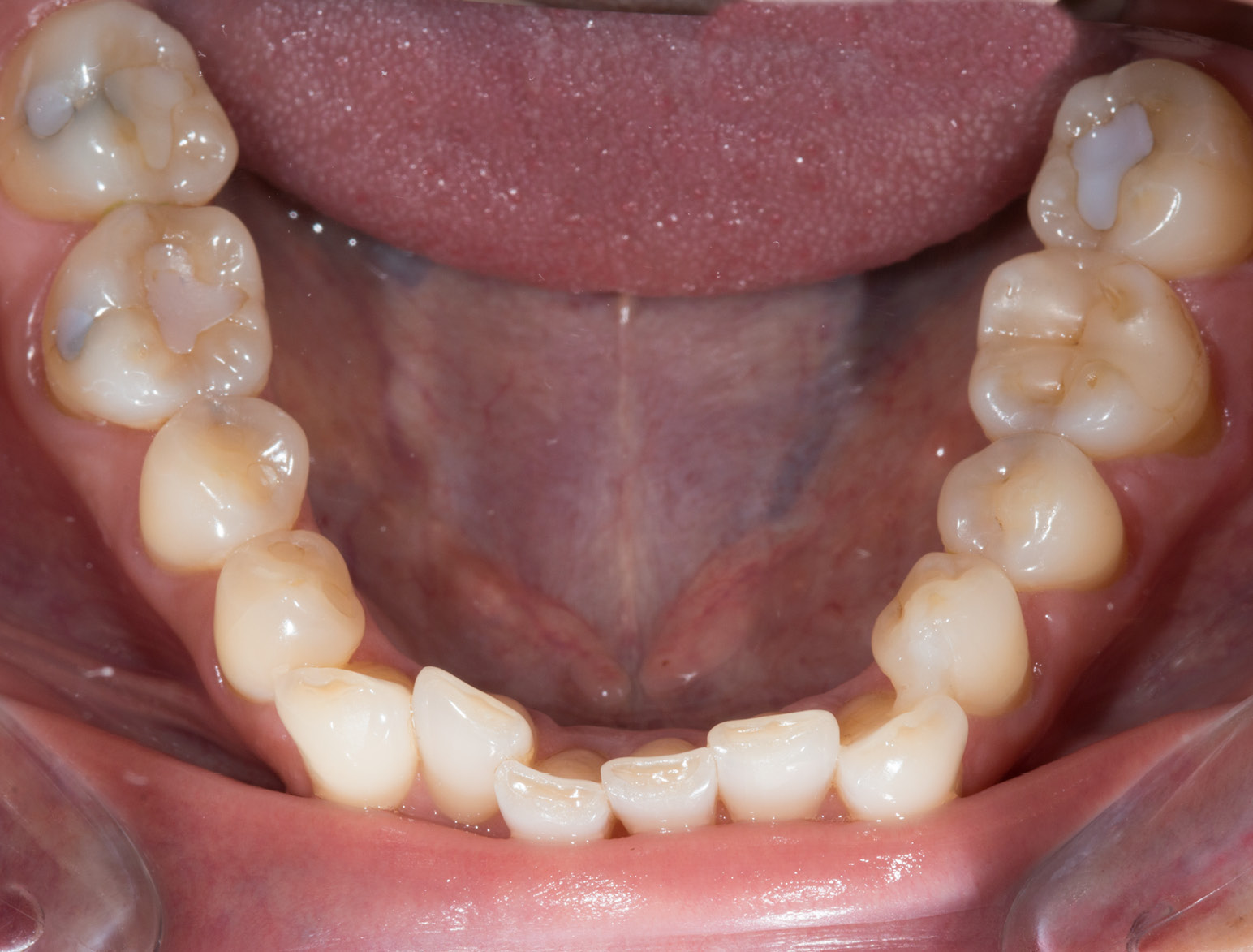
BEFORE
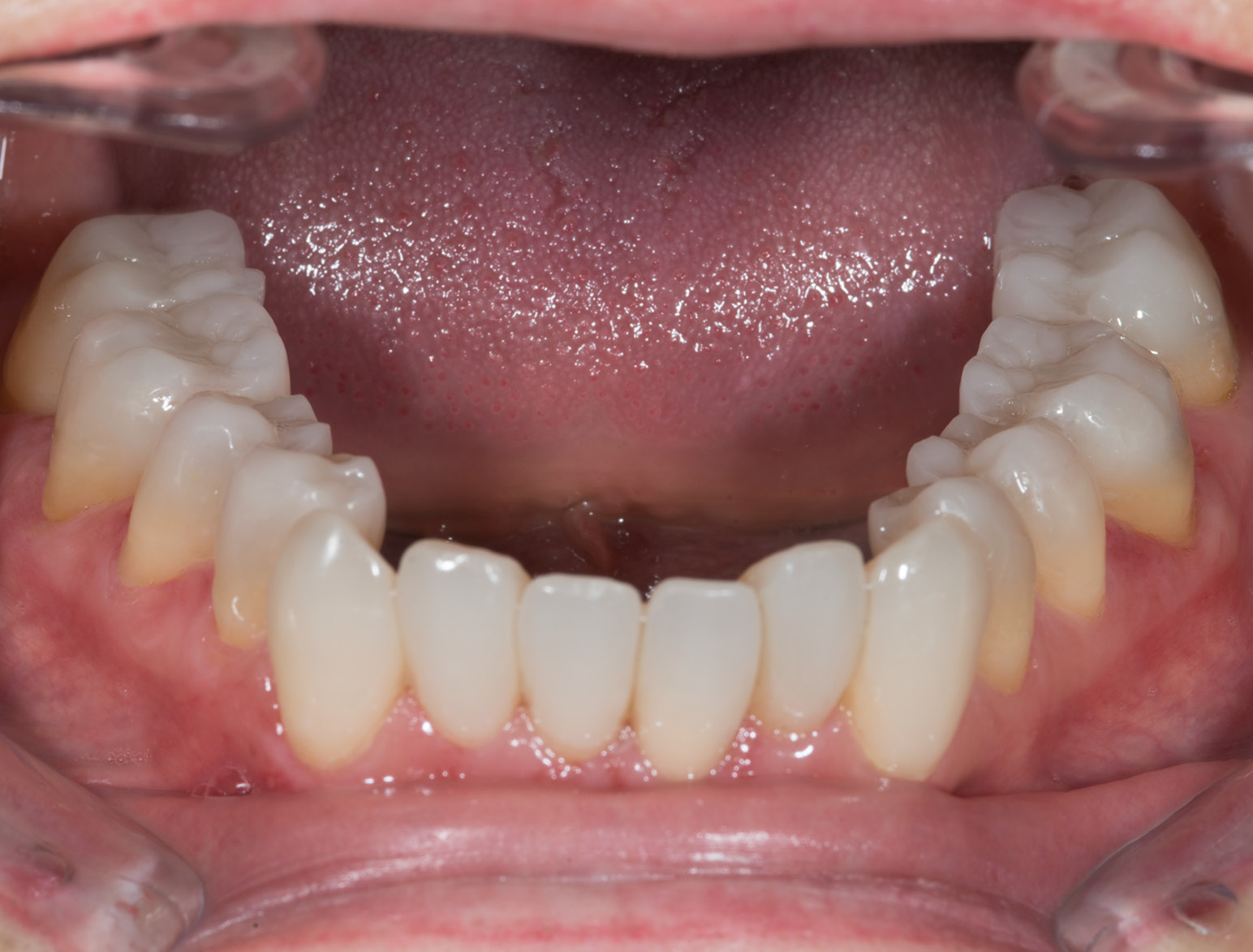
AFTER
Sizes
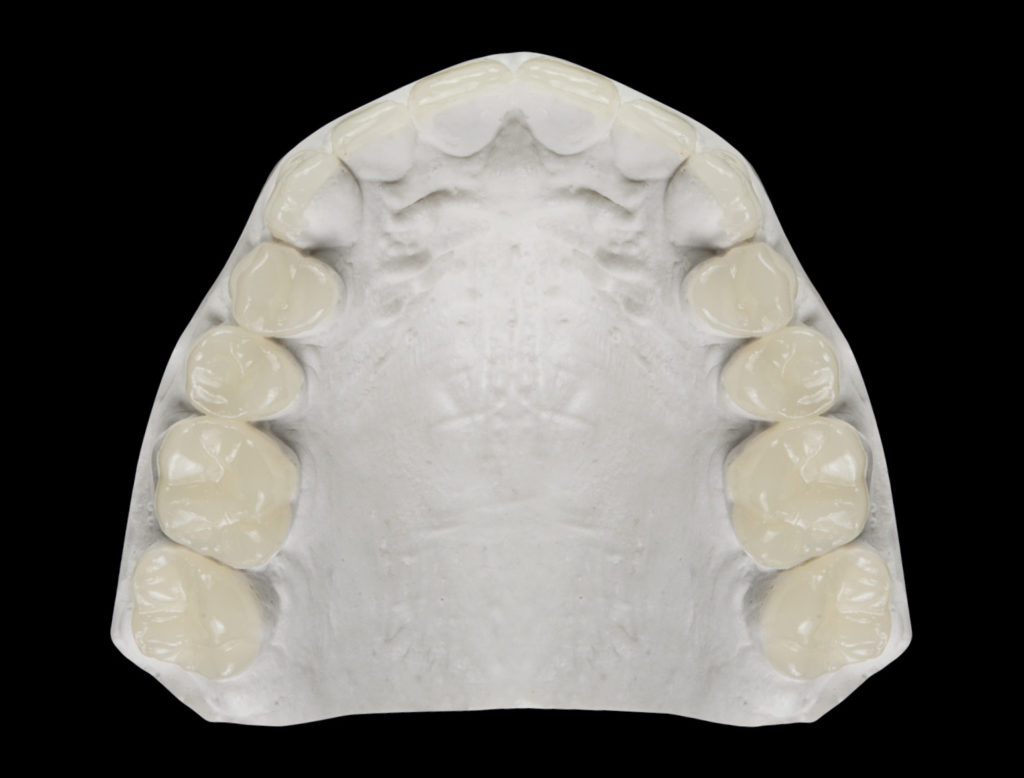
One size for all
Based on a study of all shape and size variations of natural tooth anatomy, prefabricated and contourable universal occlusion shapes for the upper and lower arches were developed.
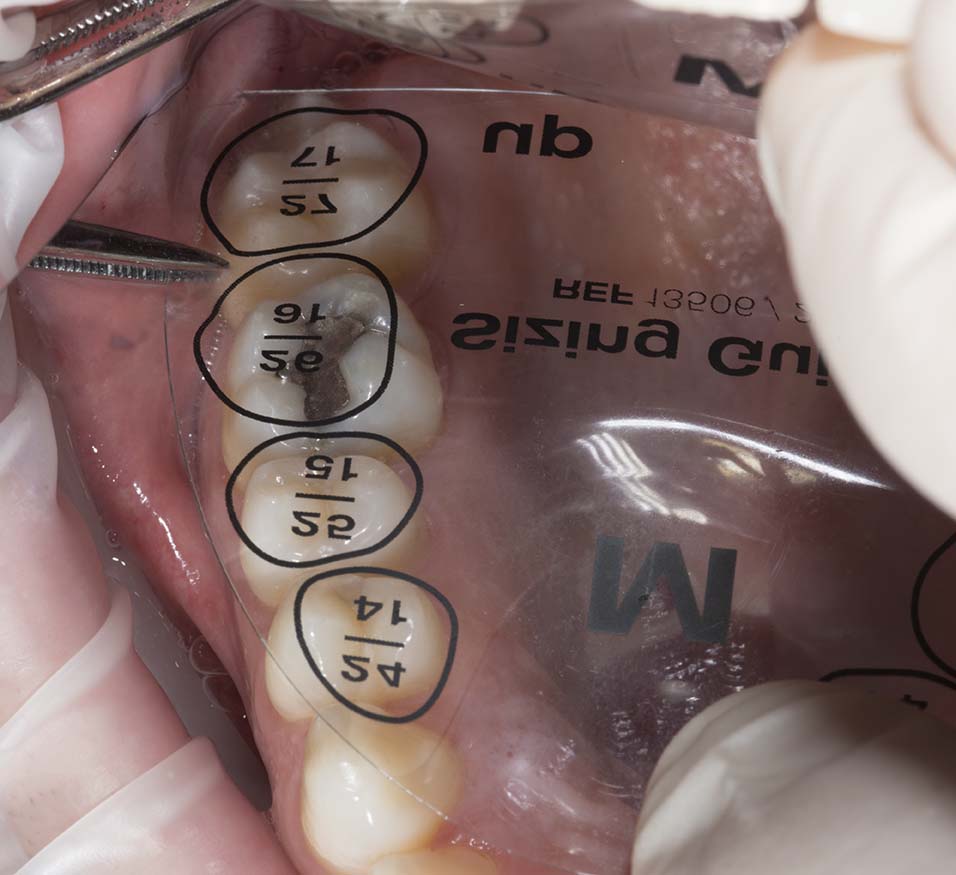
SIZE SELECTION
The selection of the tooth shape is made using the available sizing guide. (OCCLUSIONVD - Sizing Guide). The sizing guide is positioned over the teeth to be restored, and the outline allows for proper selection of the best-fitting occlusion.
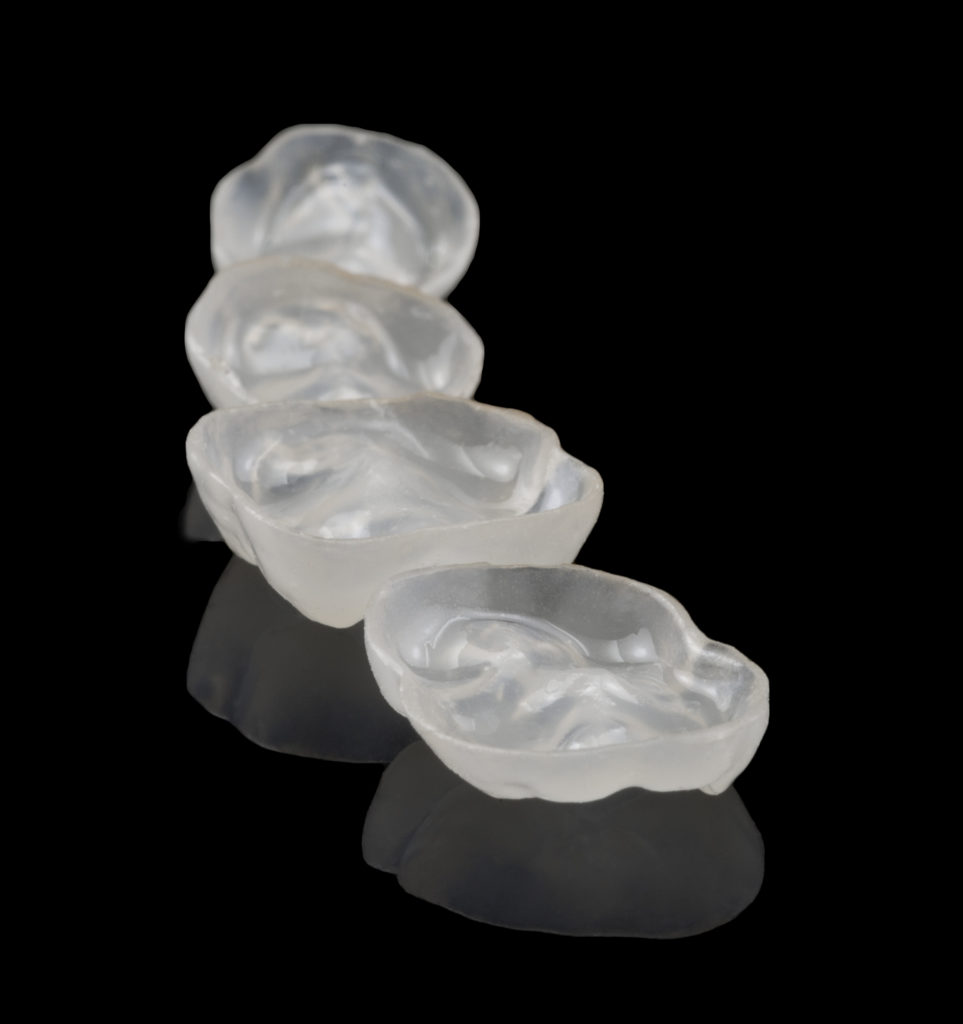

MORPHOLOGY
Ultra-thin, anatomical occlusions in three sizes (S, M & L). The glass component in the composite filler and laser treatment of the surface give the material nature-like mechanical properties (biomechanics), and the material is also biocompatible (biology). Due to the natural morphology, the prefabricated edelweiss Occlusions are very easy to incorporate into an existing occlusion.
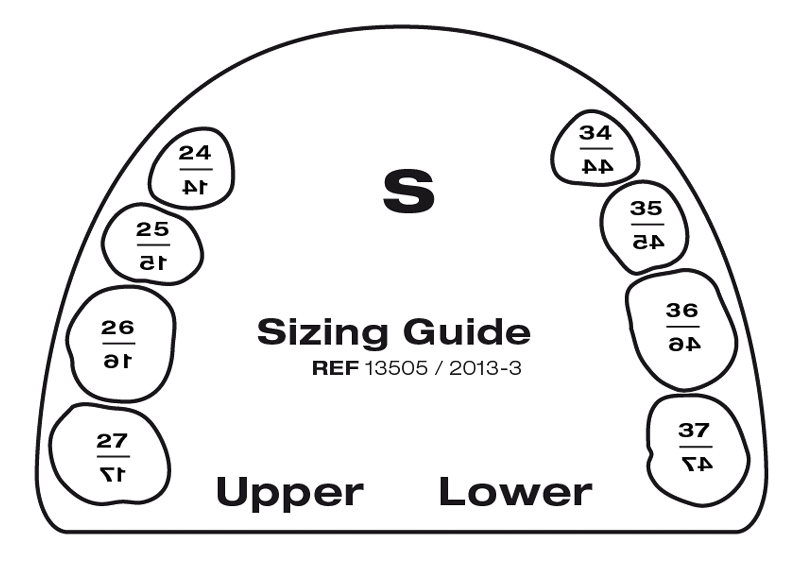
SIZING GUIDE
Small
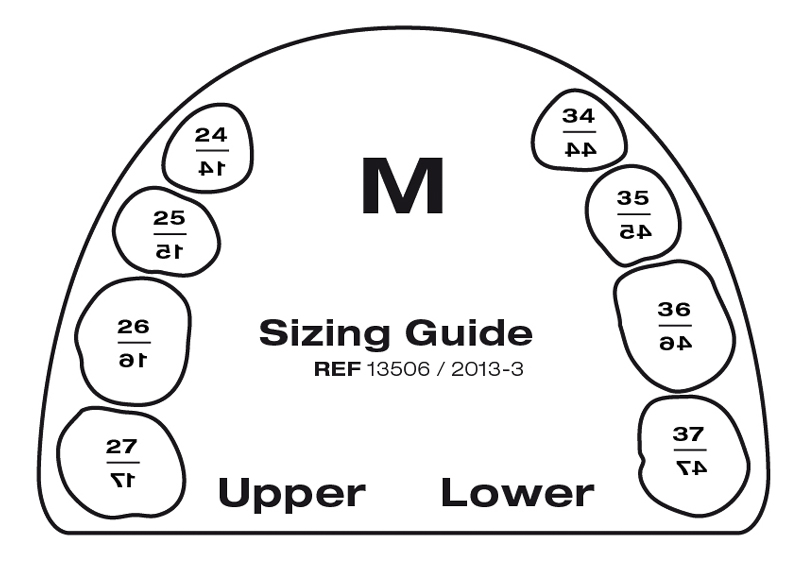
SIZING GUIDE
Medium
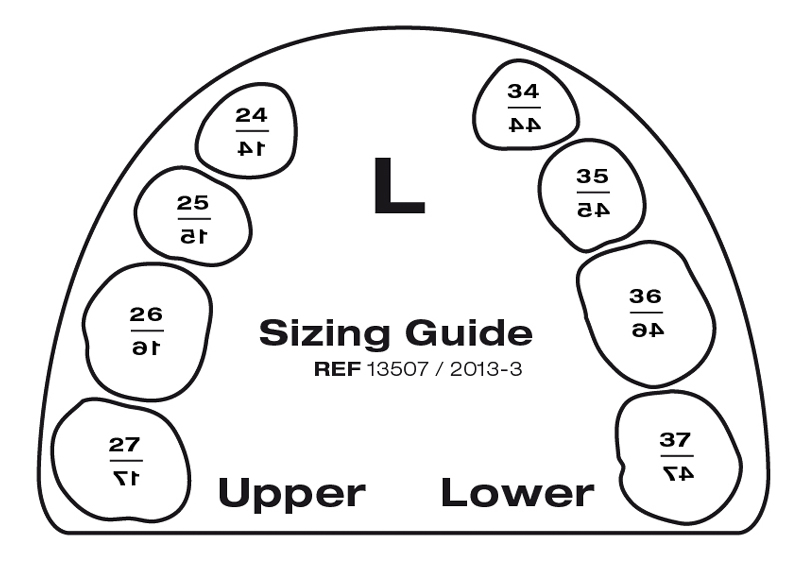
SIZING GUIDE
Large
Shade Range
EDELWEISS SHADE GUIDE
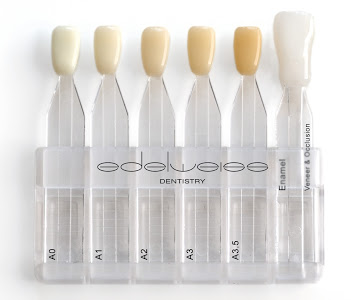
edelweiss dentin and enamel shades based on the natural layering technique.
EDELWEISS SHADE SELECTION
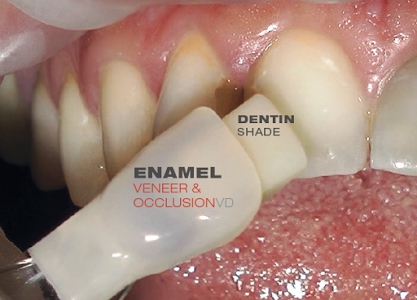
Placing the enamel VENEER shell over the dentin core. For light refraction place glycerine within enamel shell first.
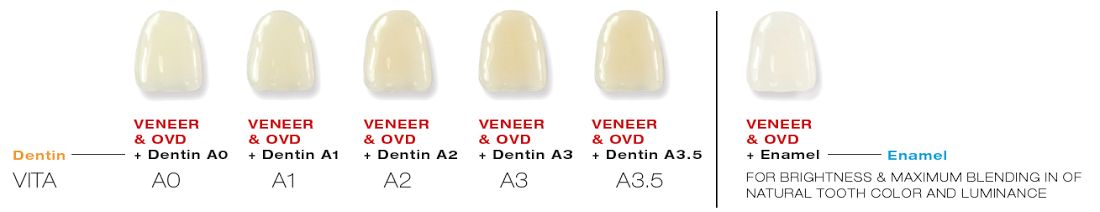
EDELWEISS SHADE SYSTEM
edelweiss VENEERs consist of the shade Enamel – Vita Enamel AO. The respective dentin and enamel shades used to cement the VENEER will determine the final shade tone of the restoration.
Example:
edelweiss VENEER (Vita Enamel Shade AO) cemented with Dentin Shade A3 (Vita Dentin Shade A3) will result in the Vita Dentin Shade A3.
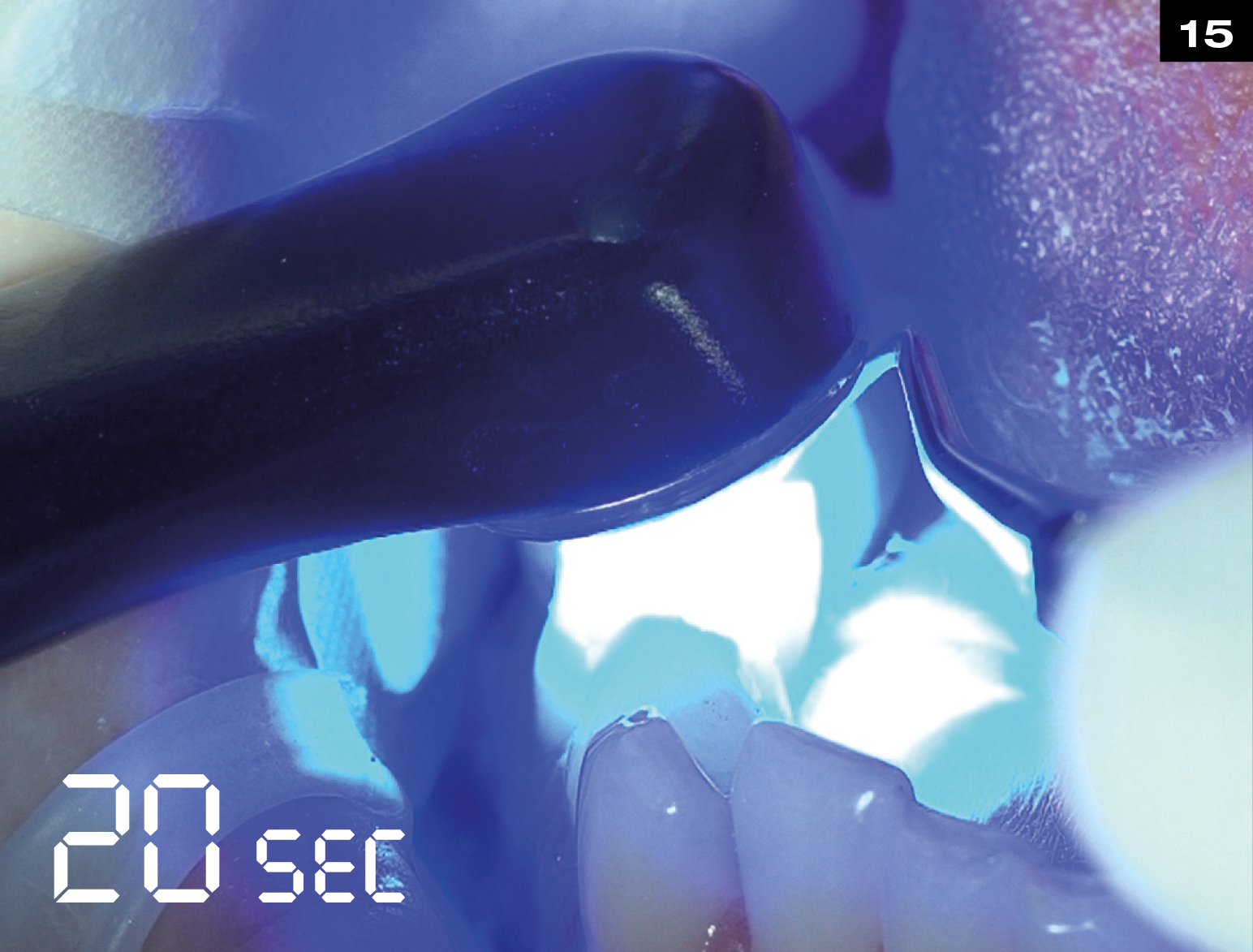
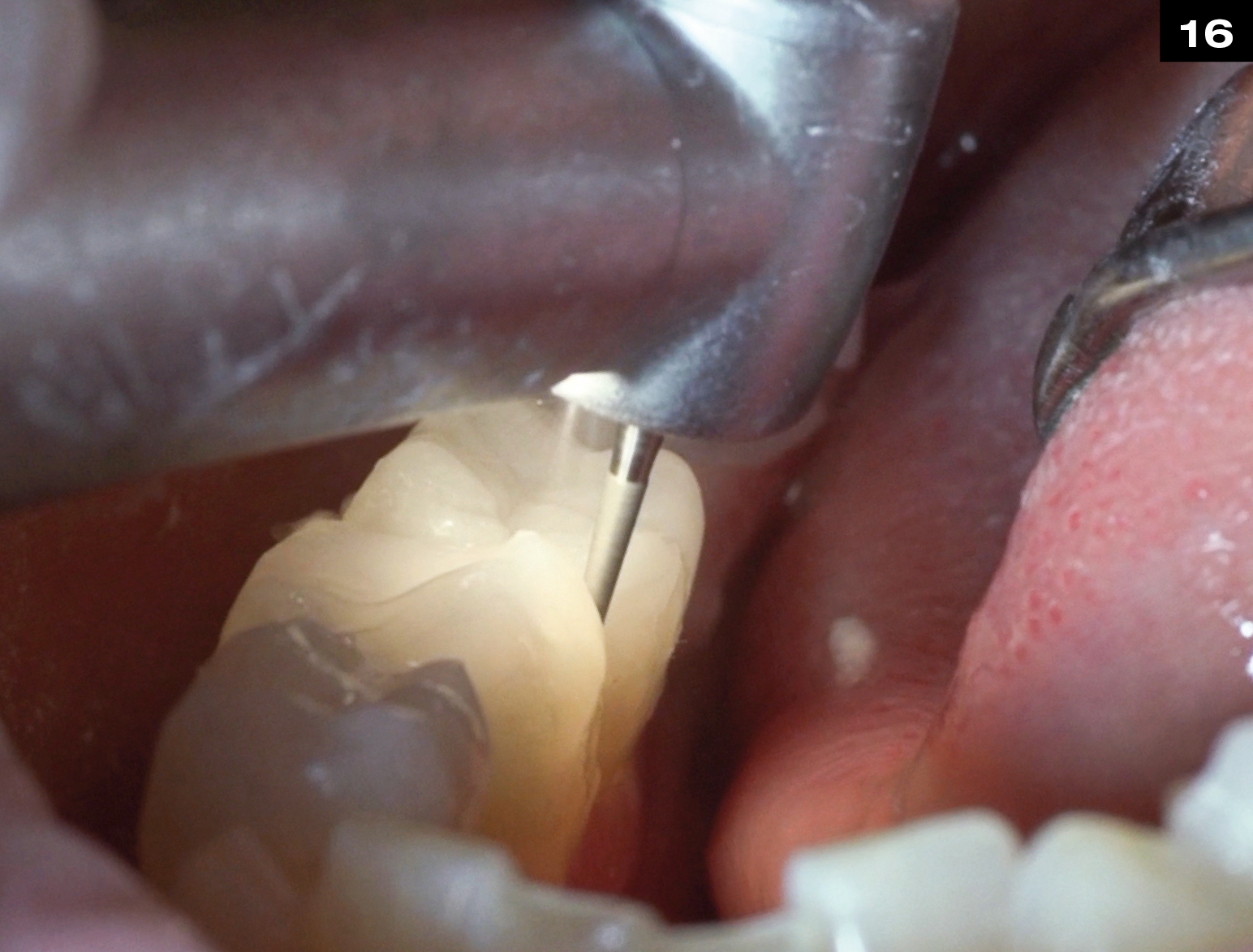
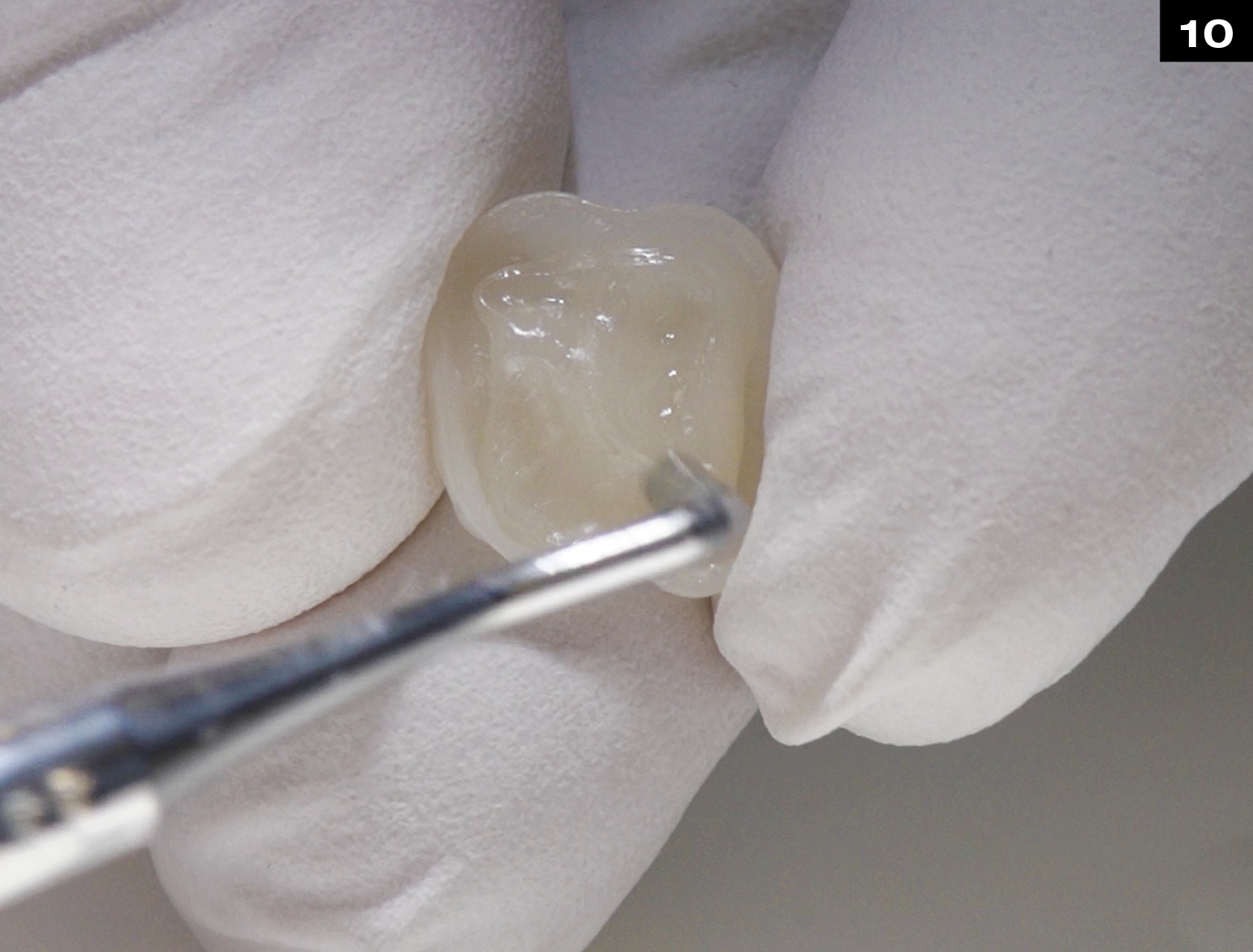
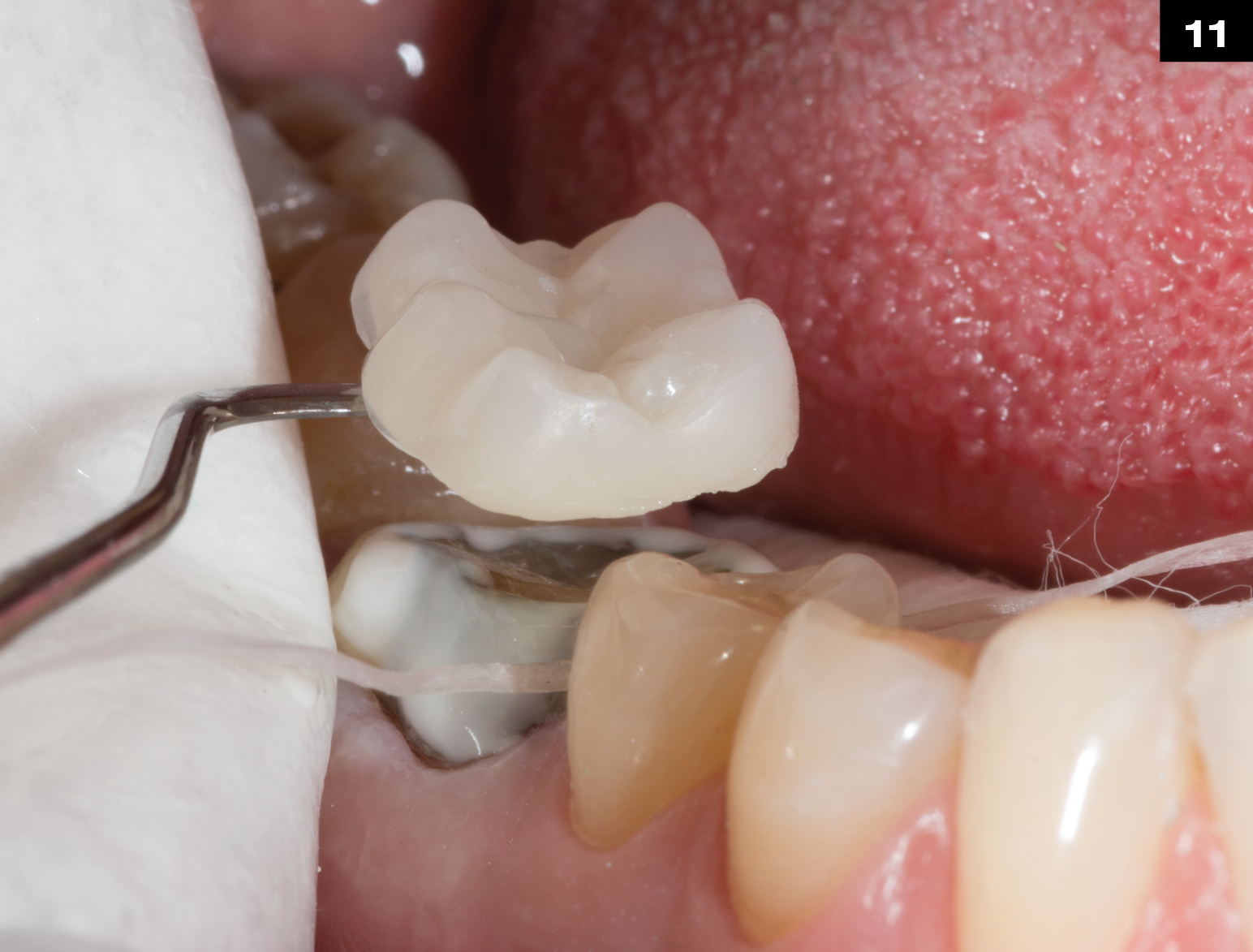
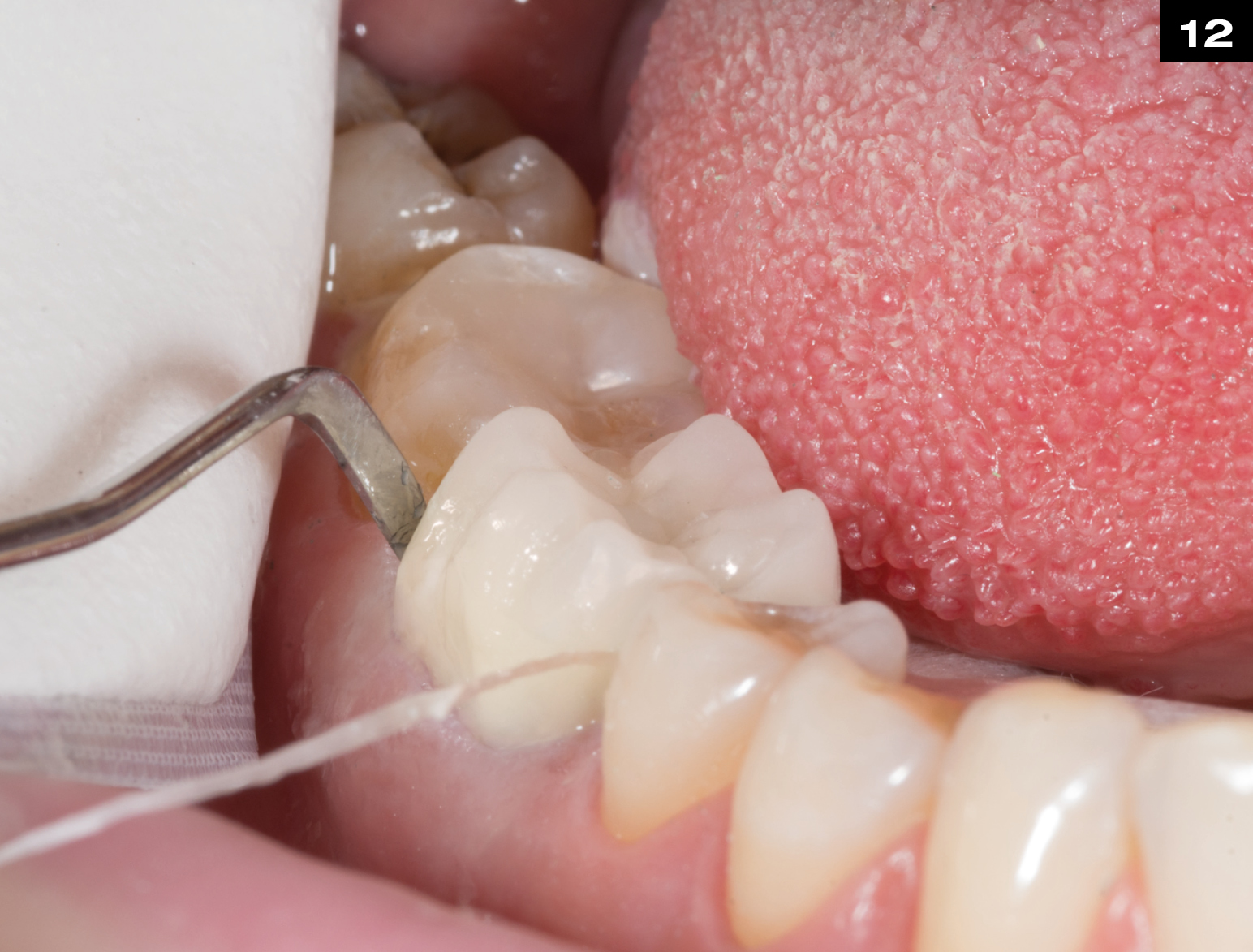
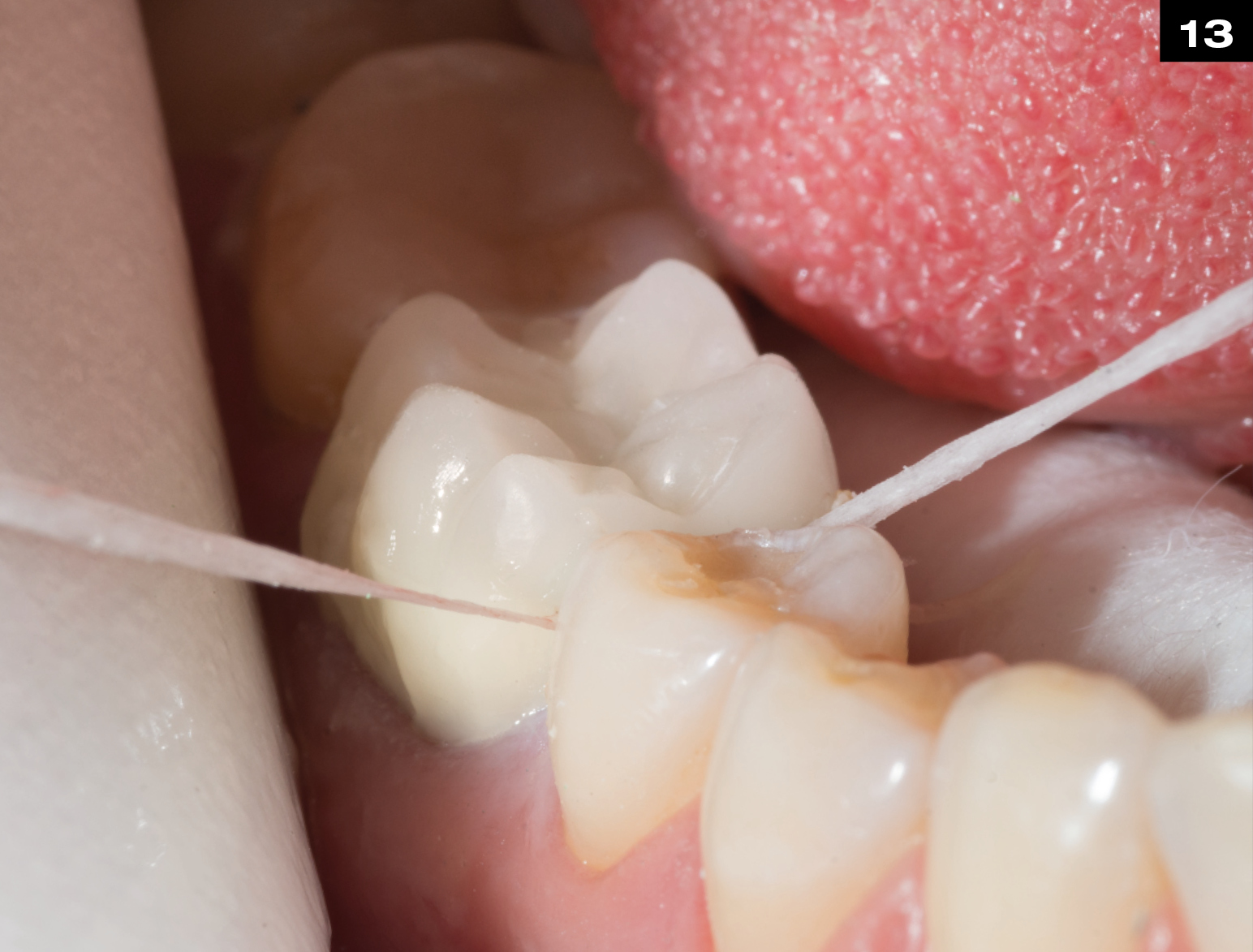
Step by Step
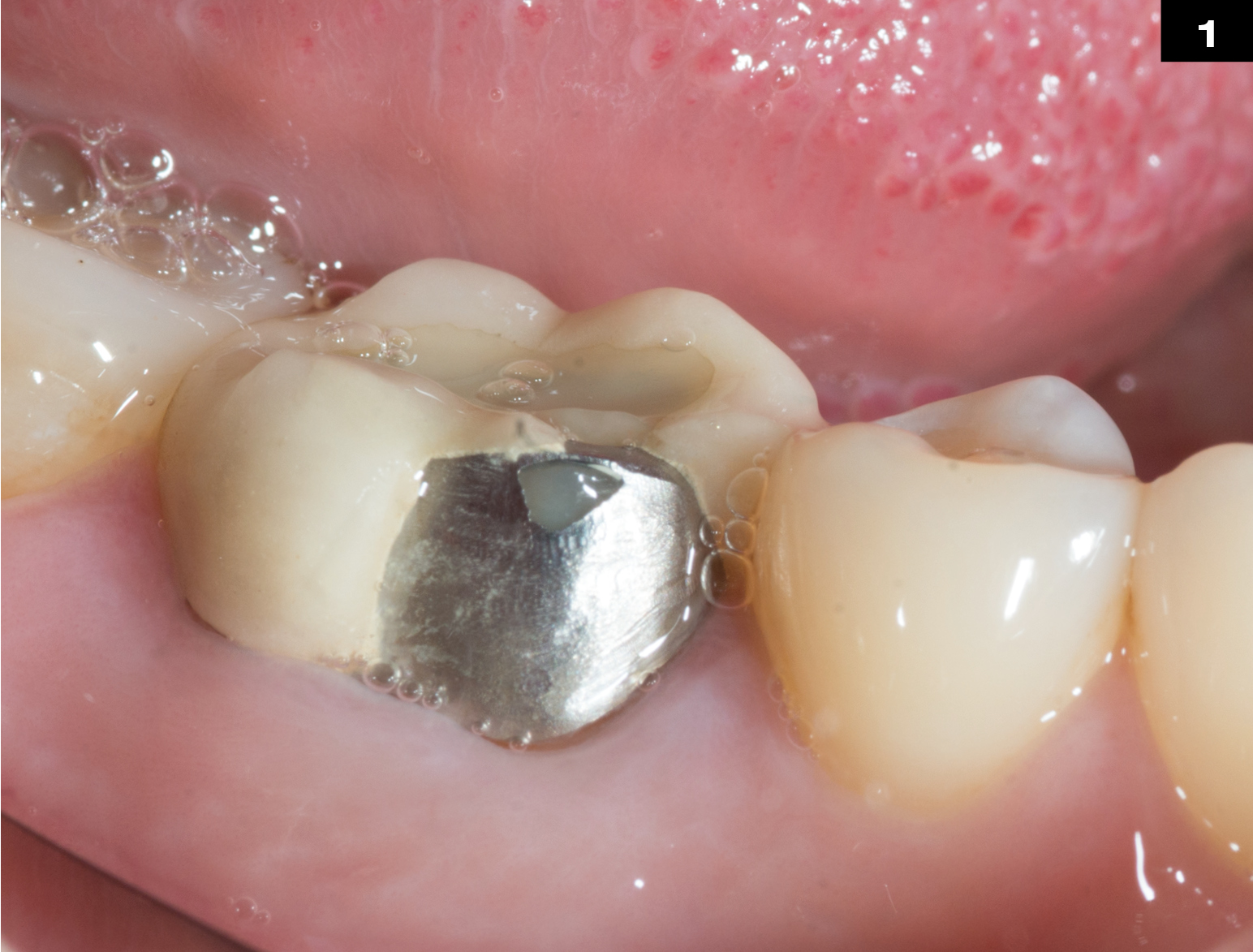
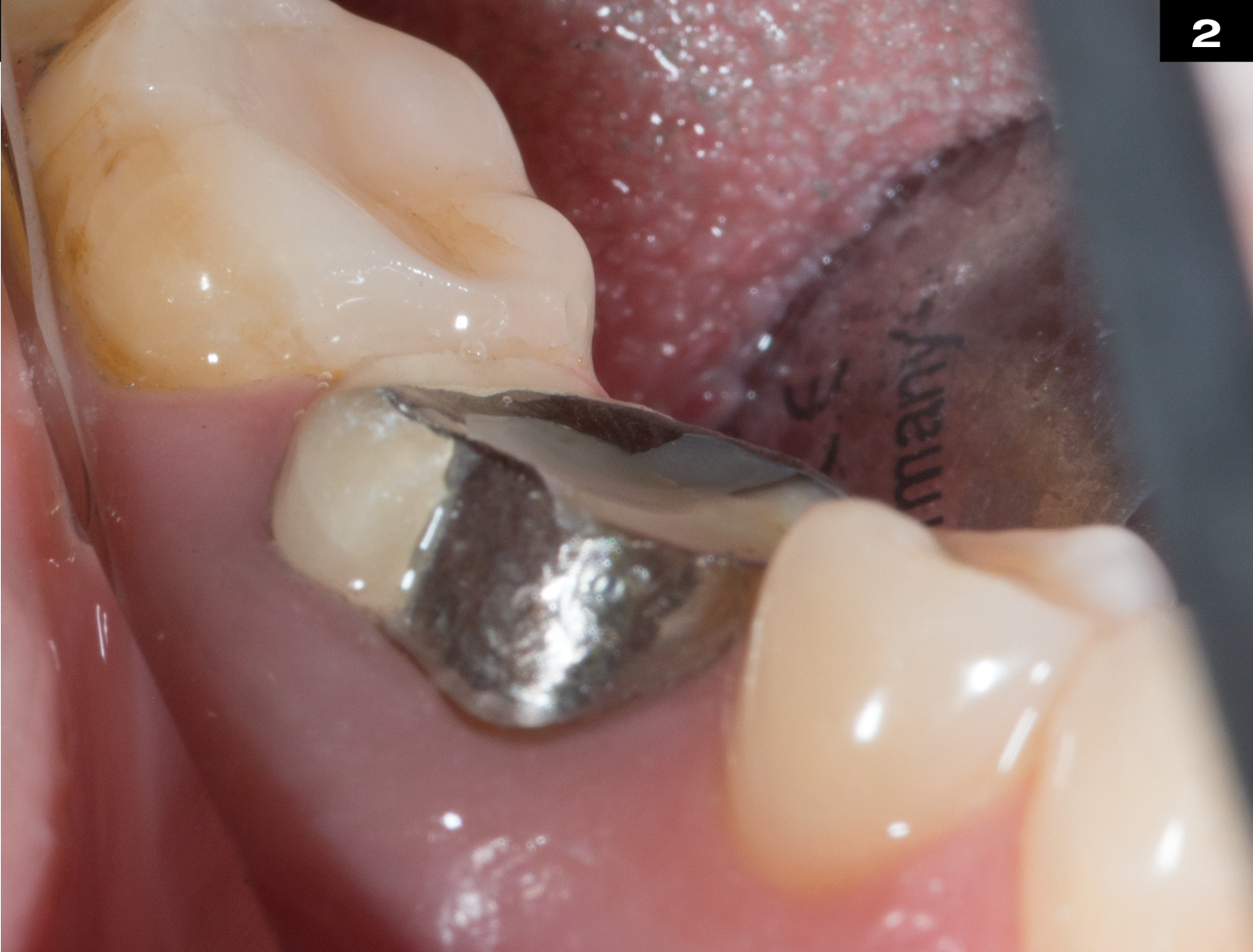
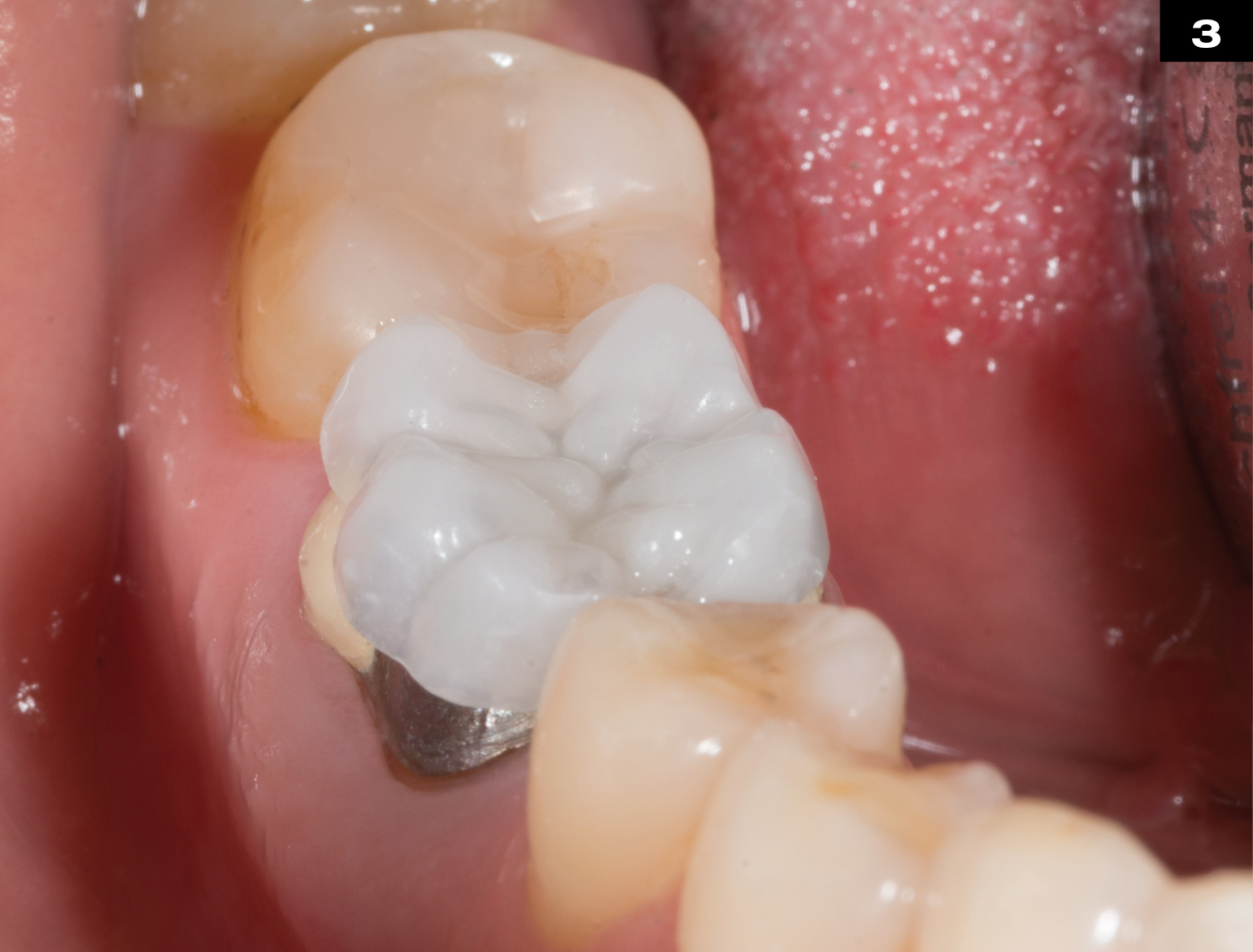
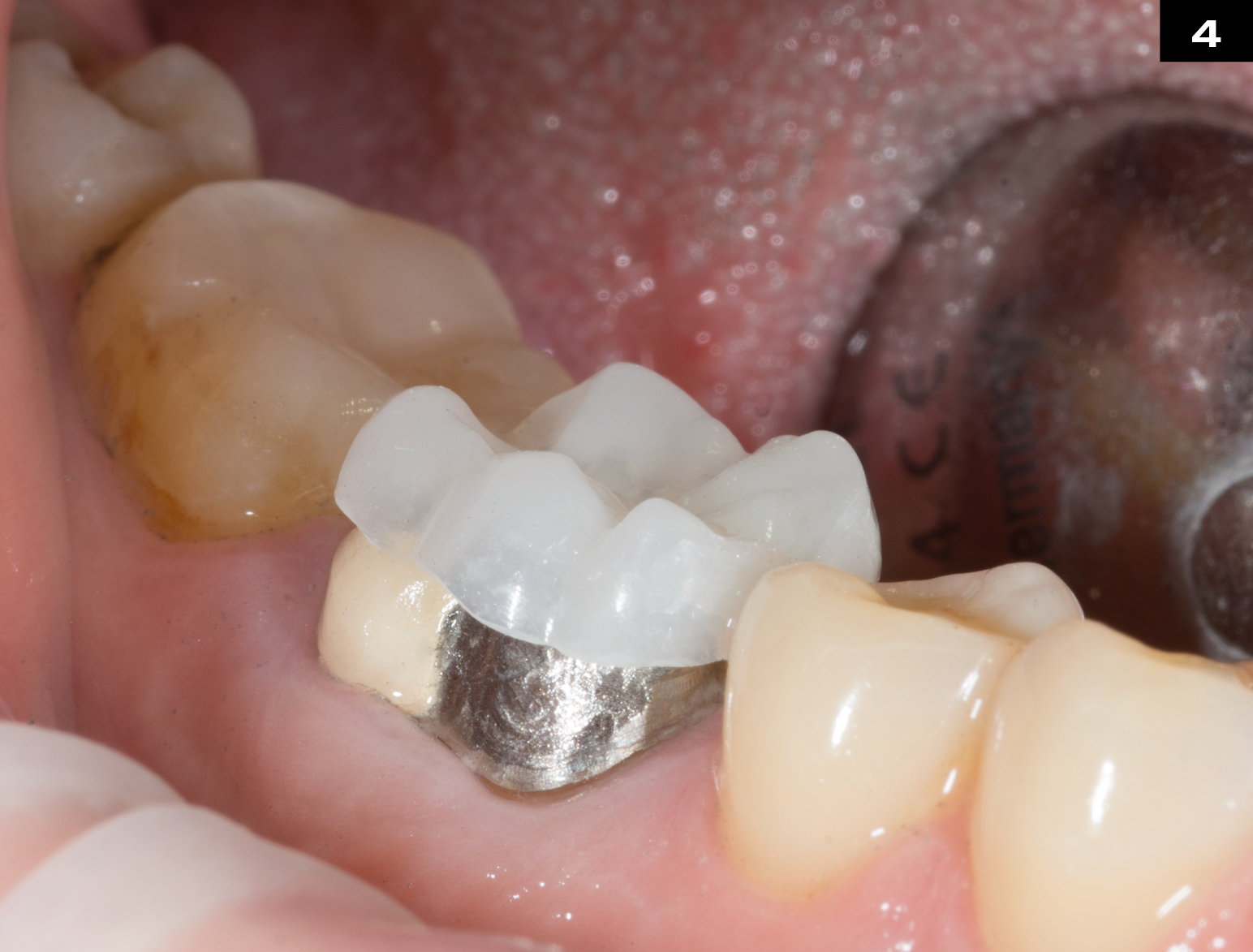
OCCLUSIONVD
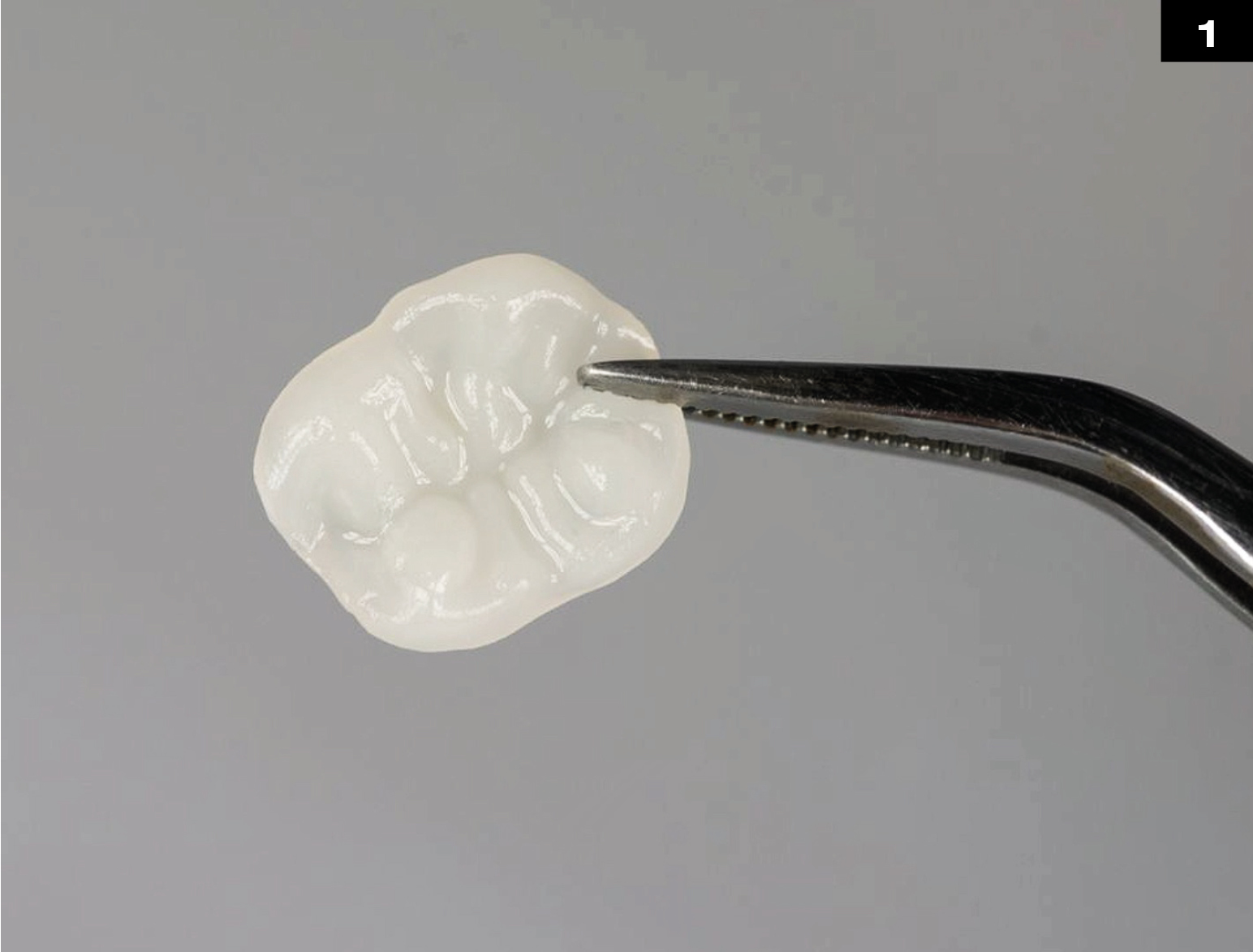
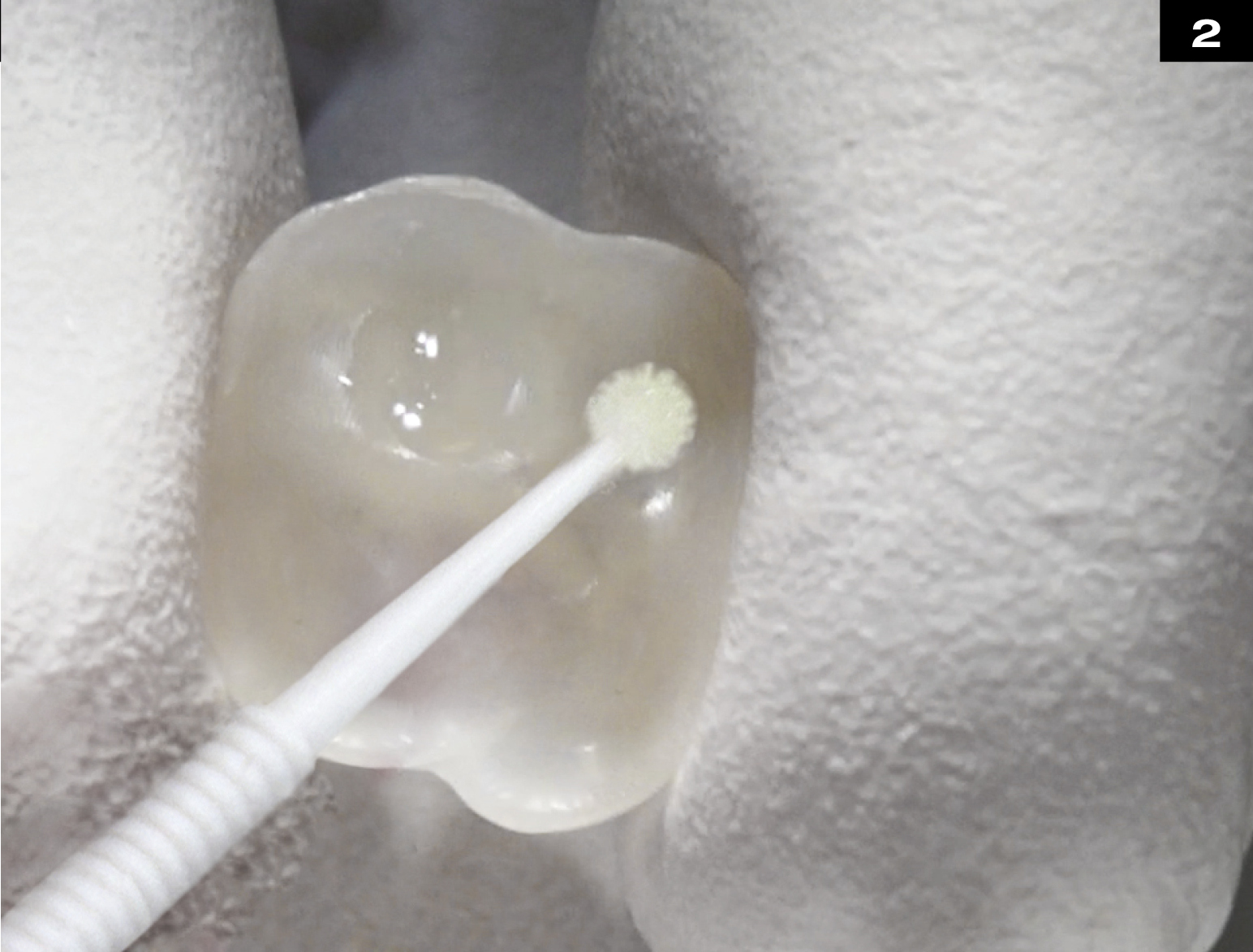
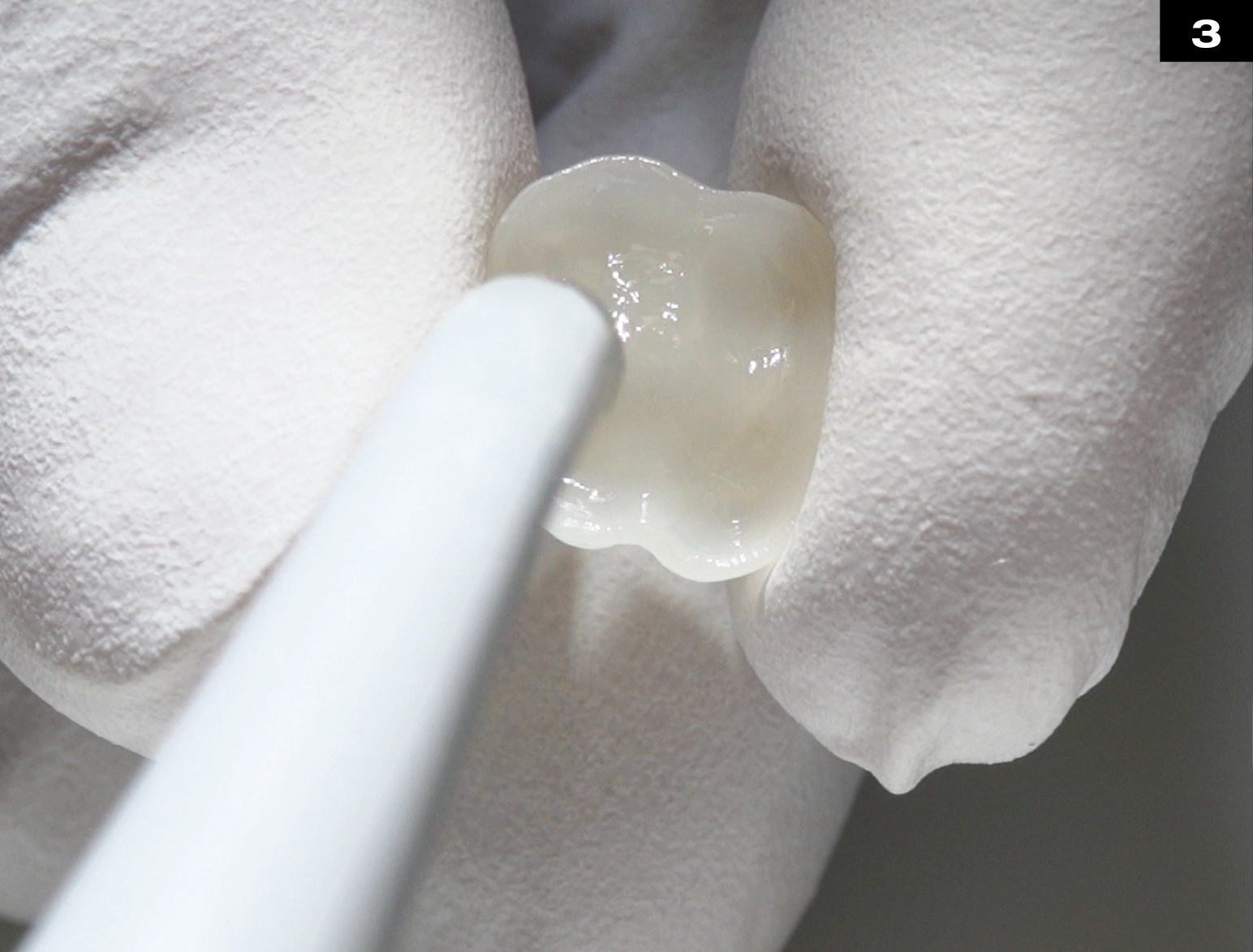

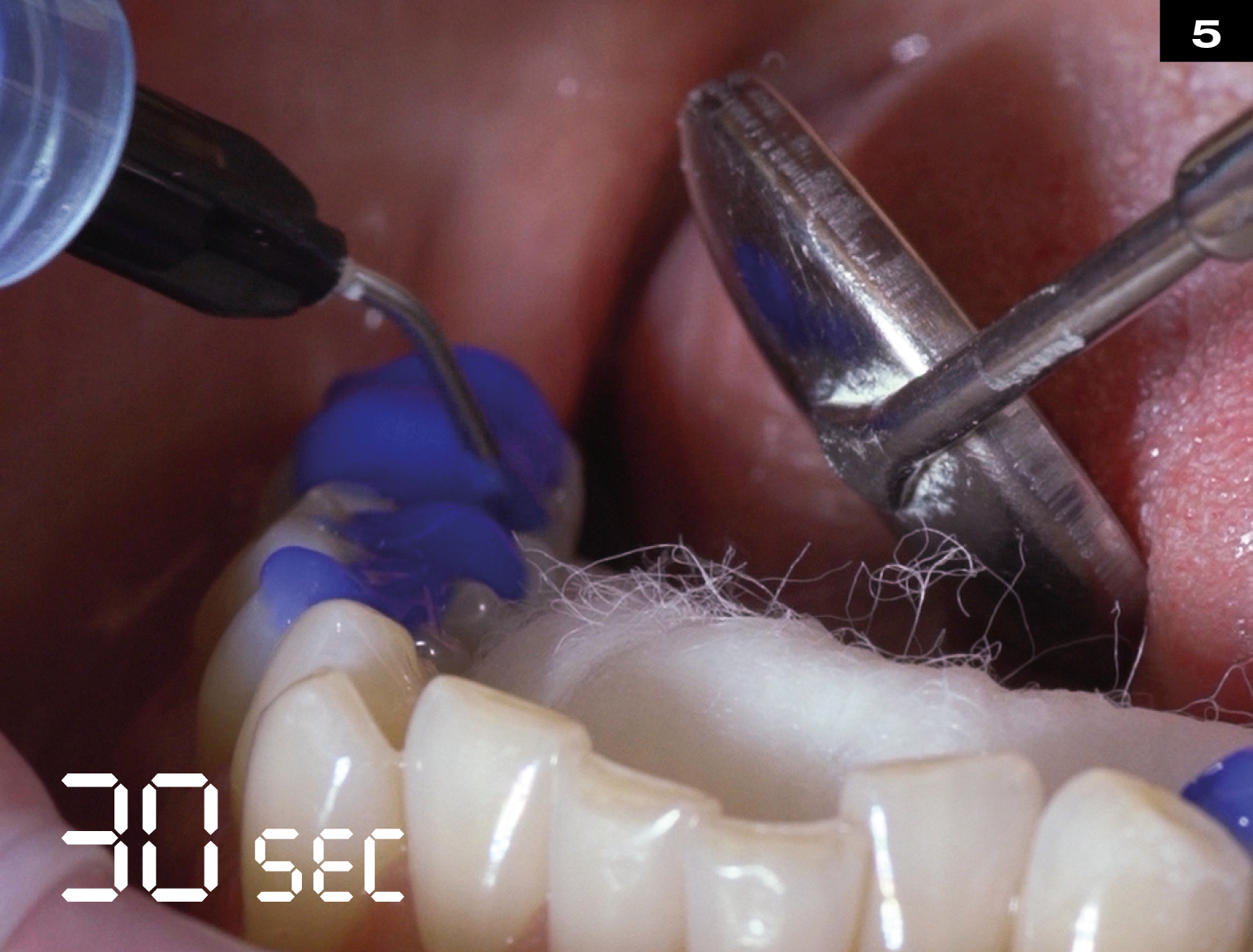
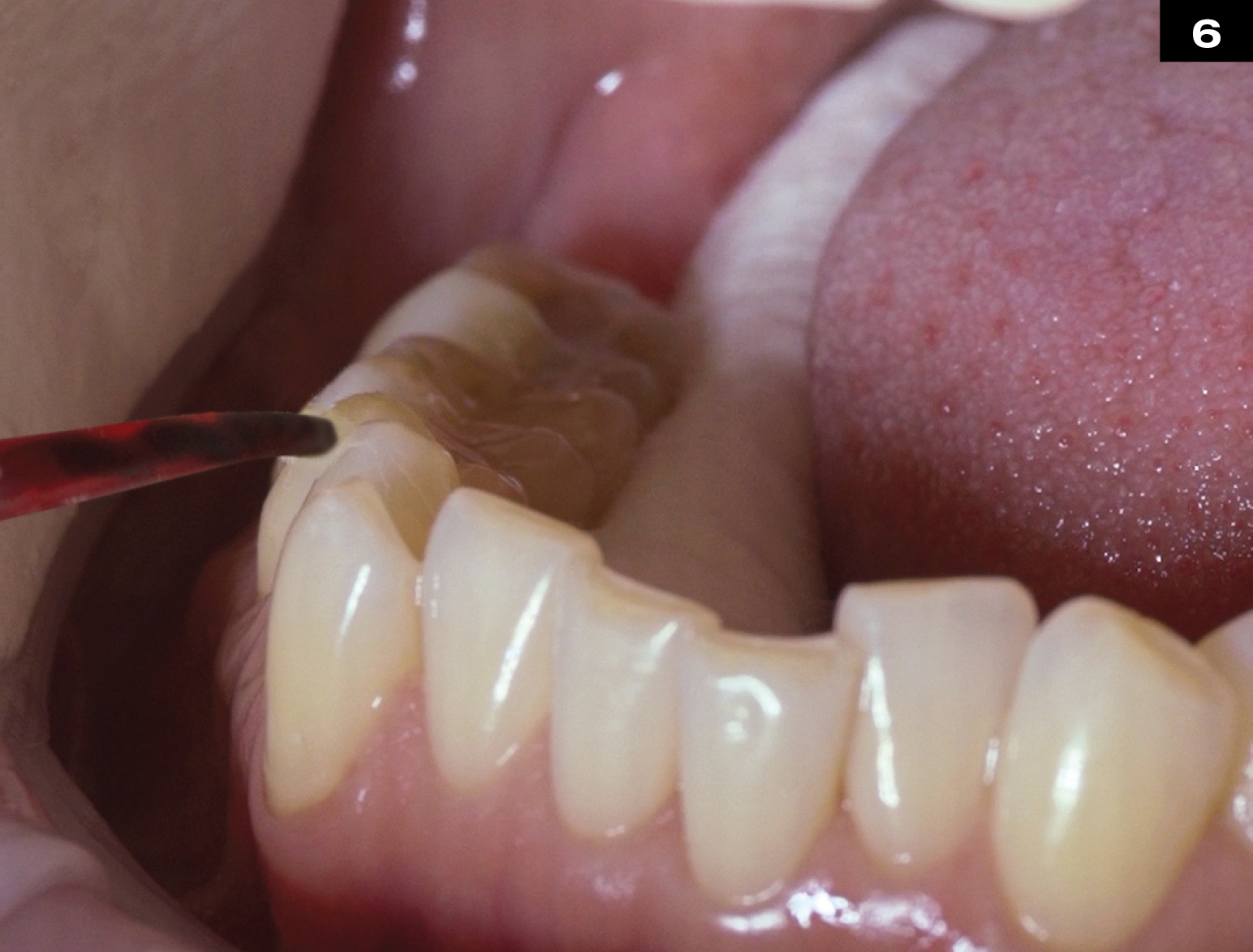
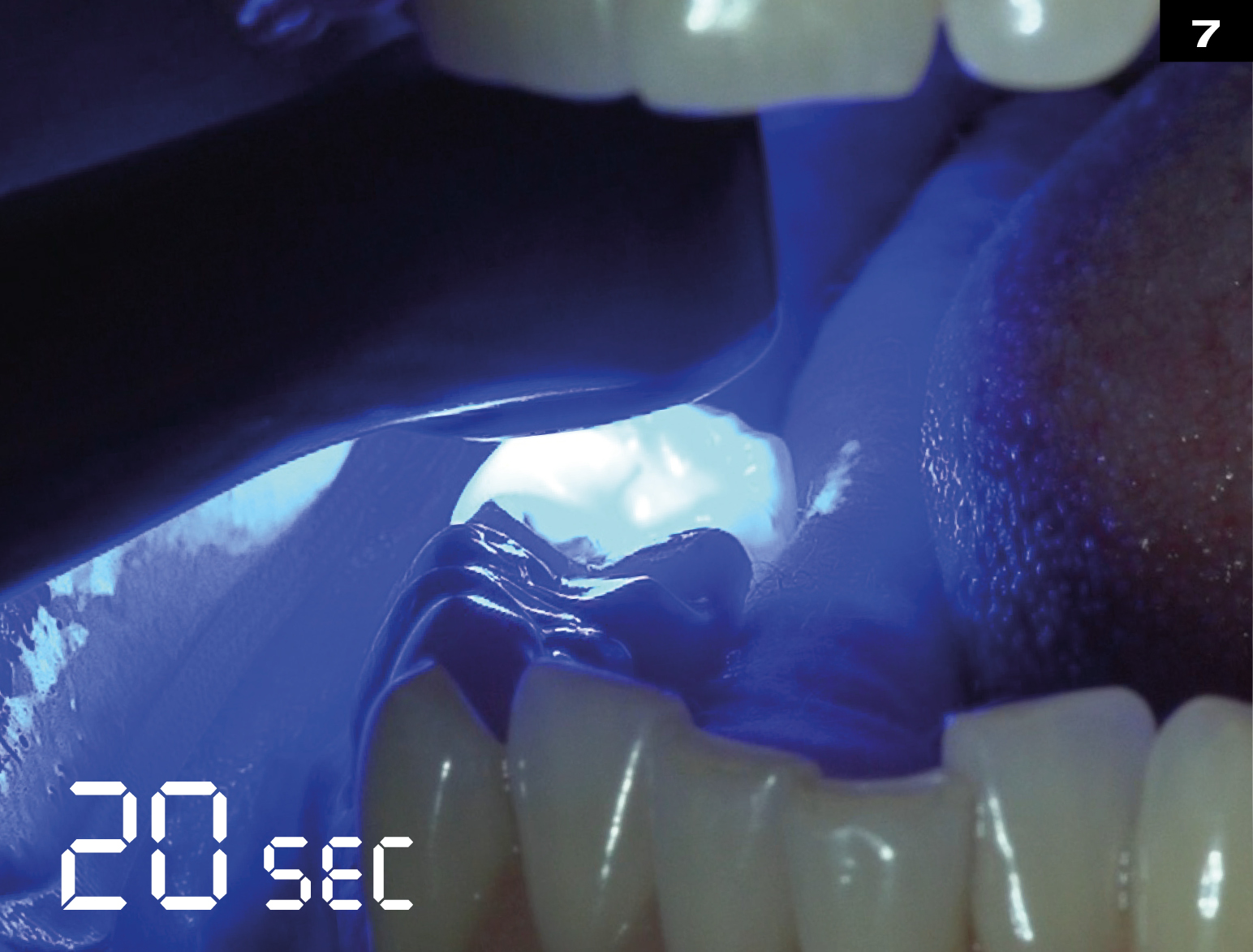
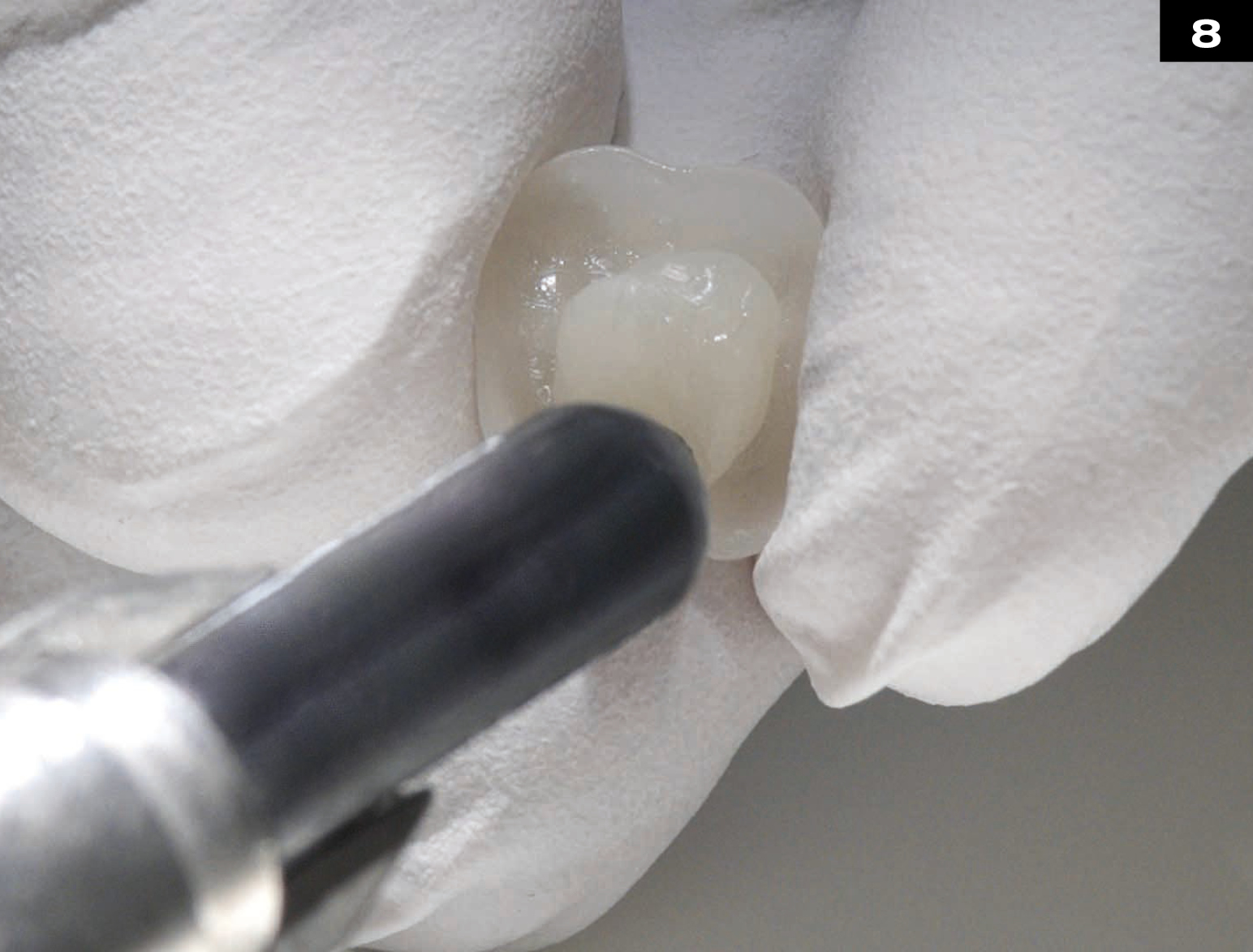
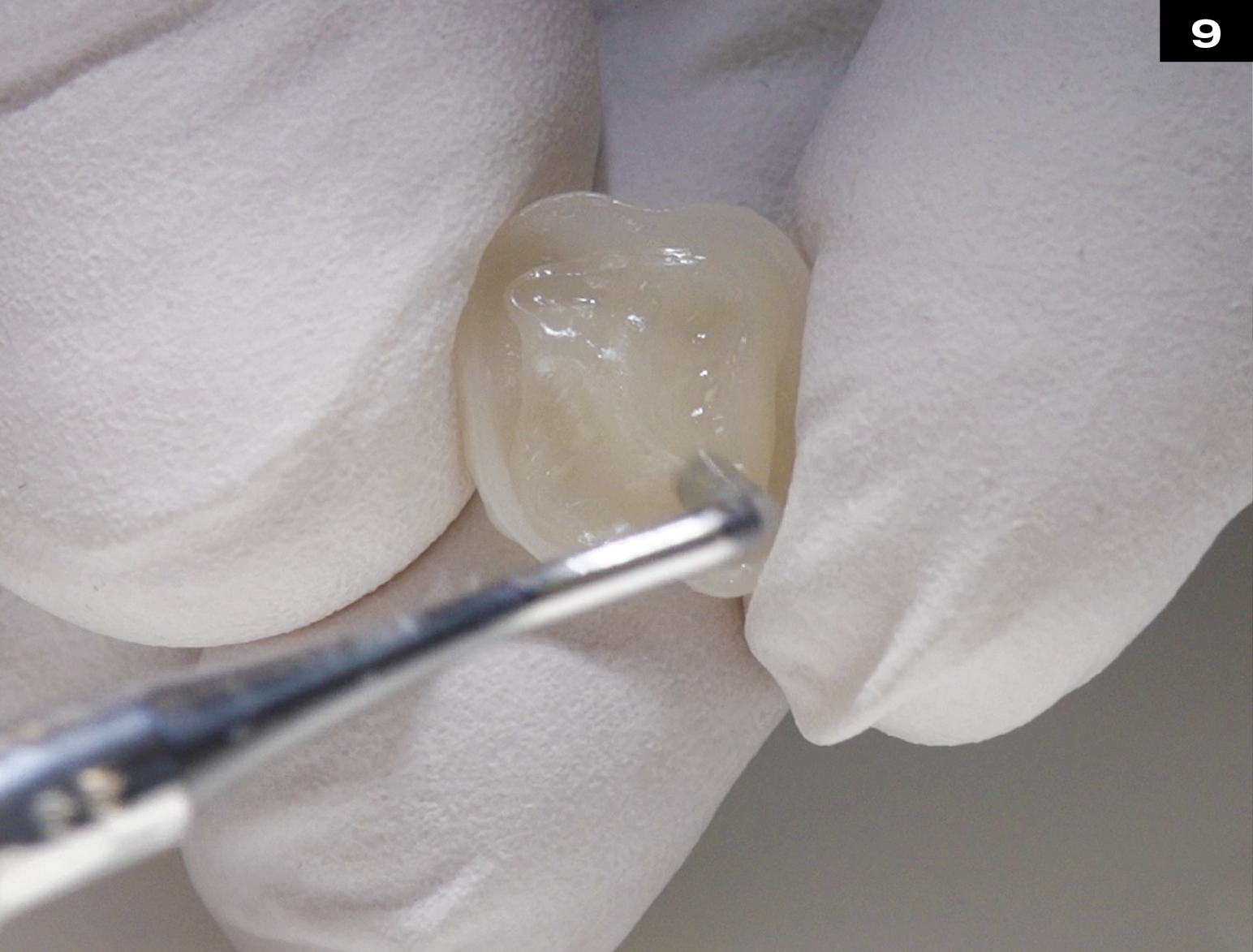
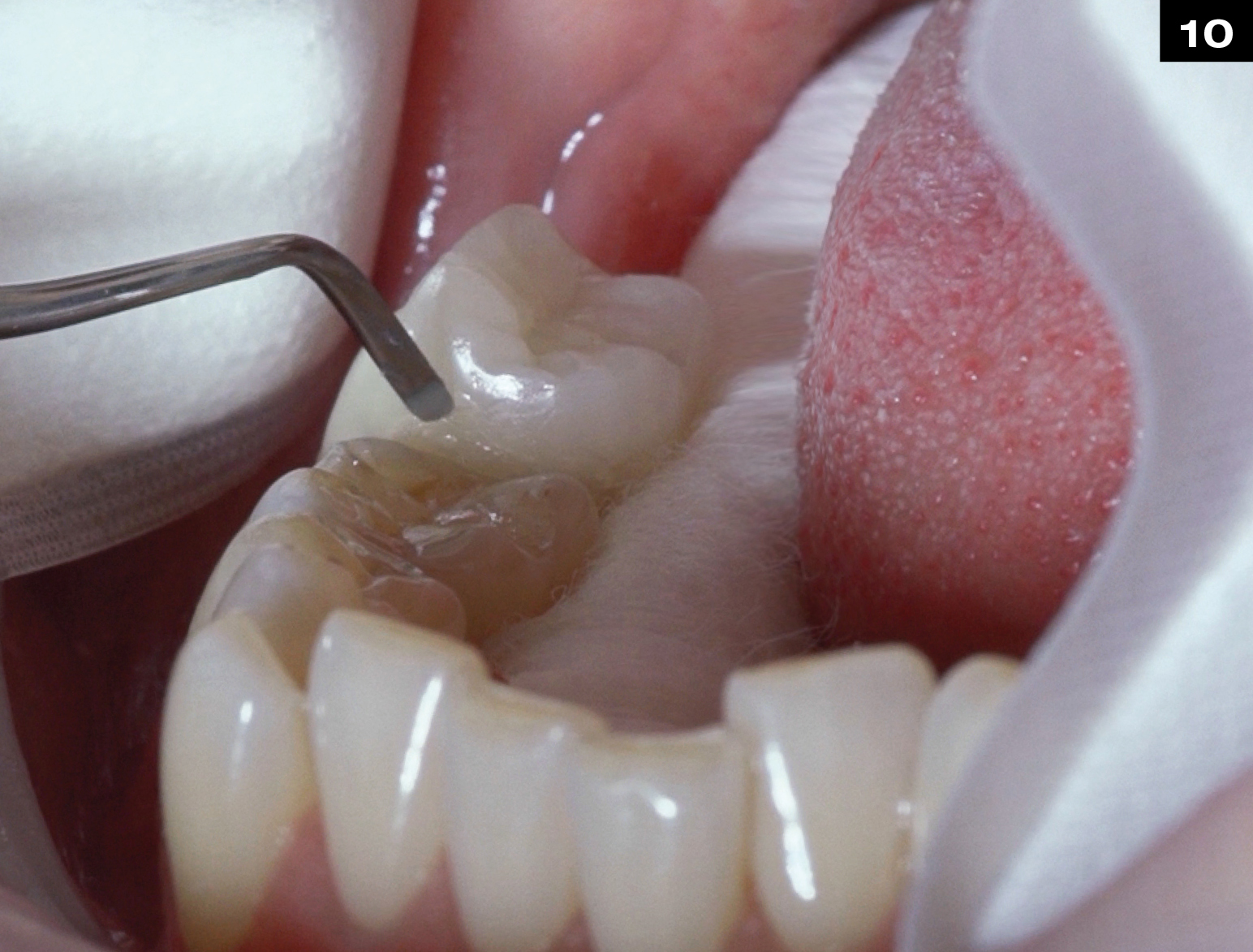

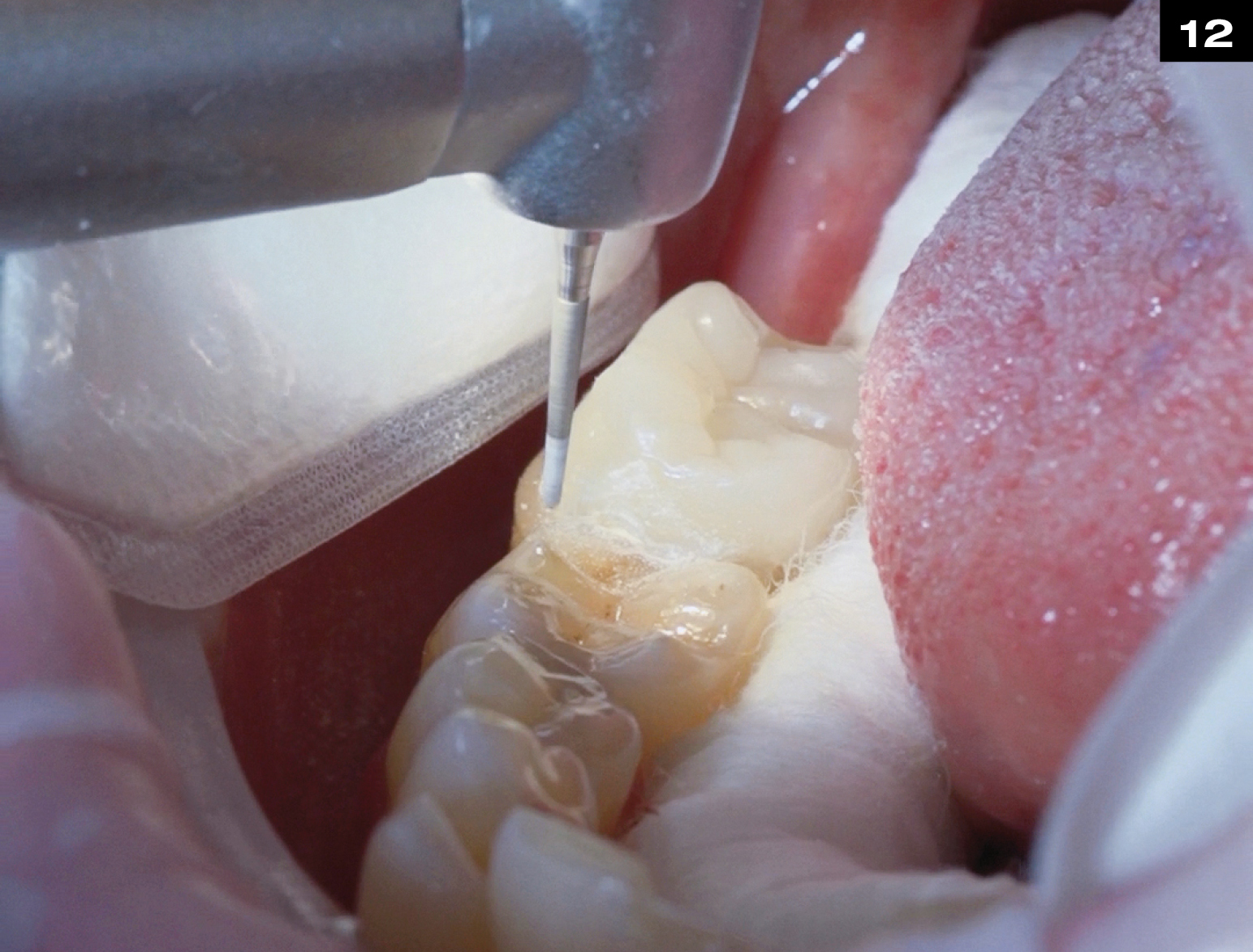
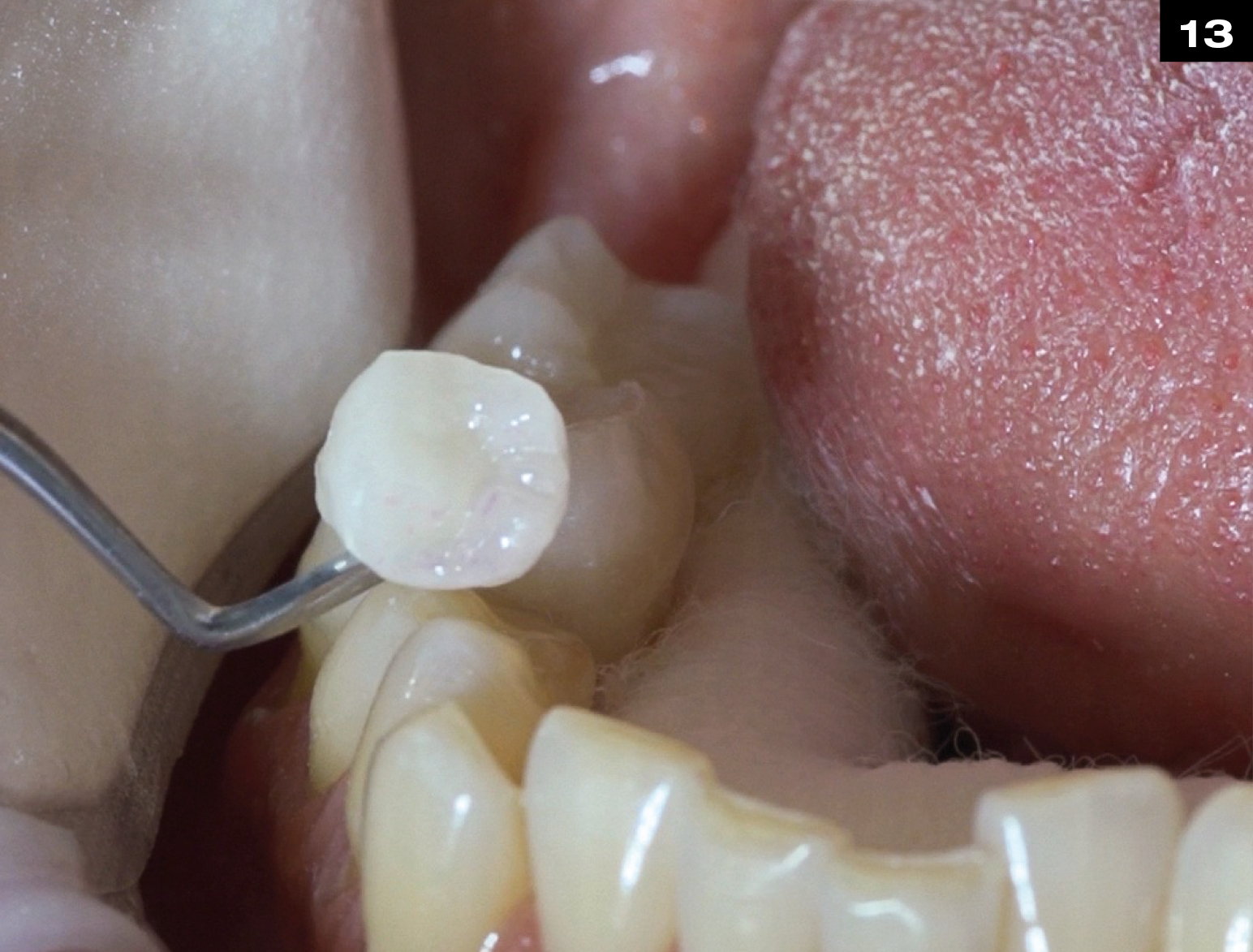
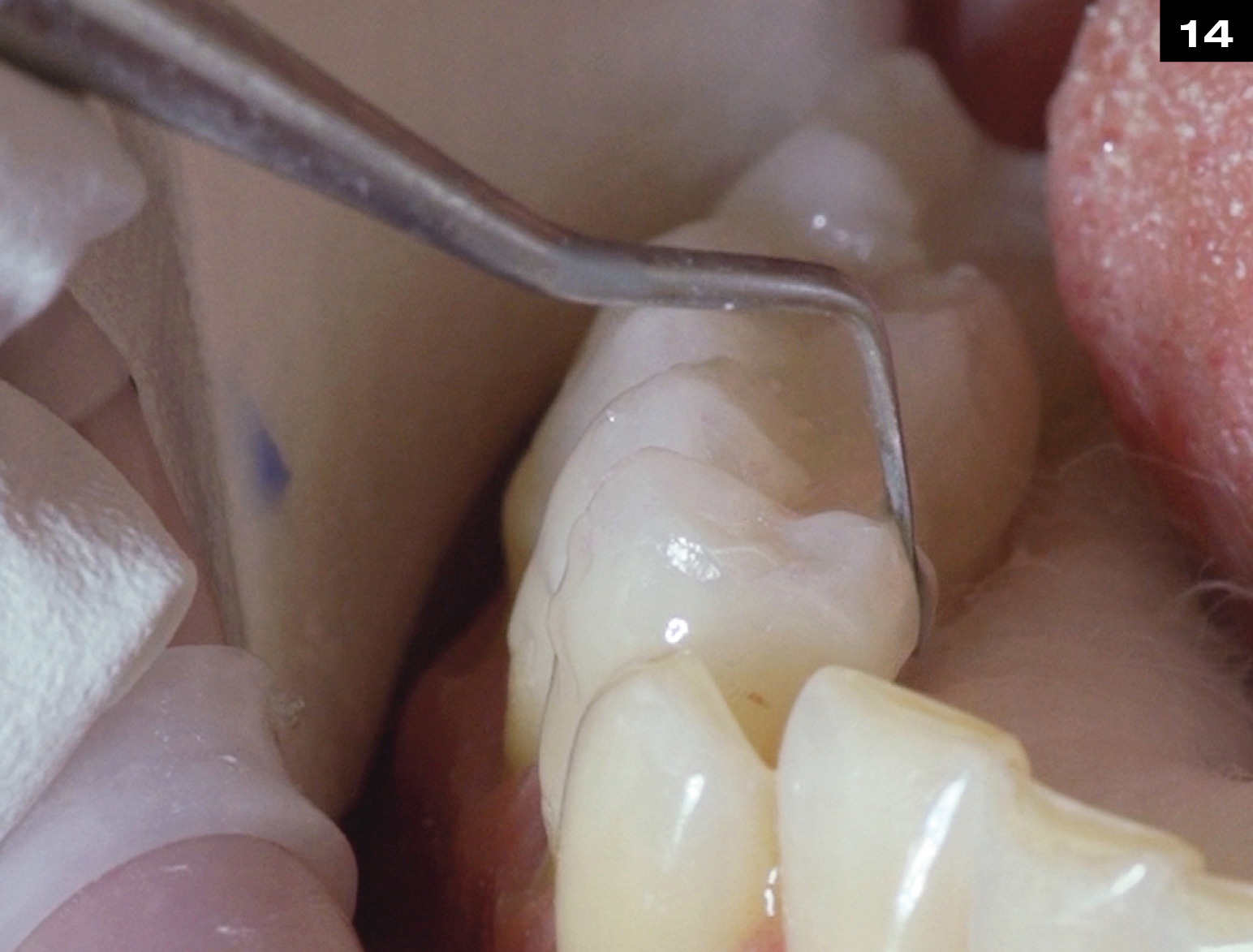
METAL CERAMIC CROWN REPAIR
After endodontic treatment
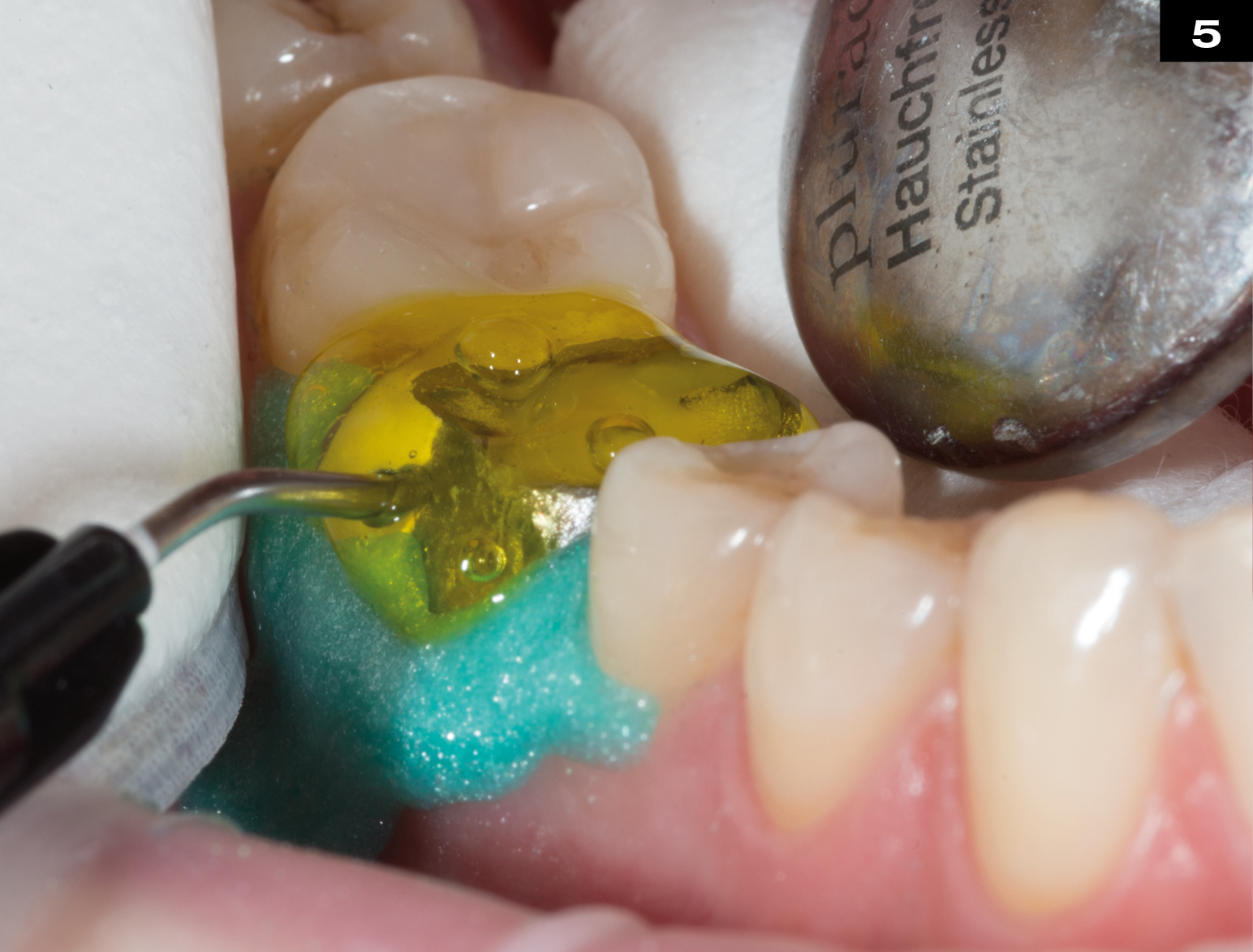
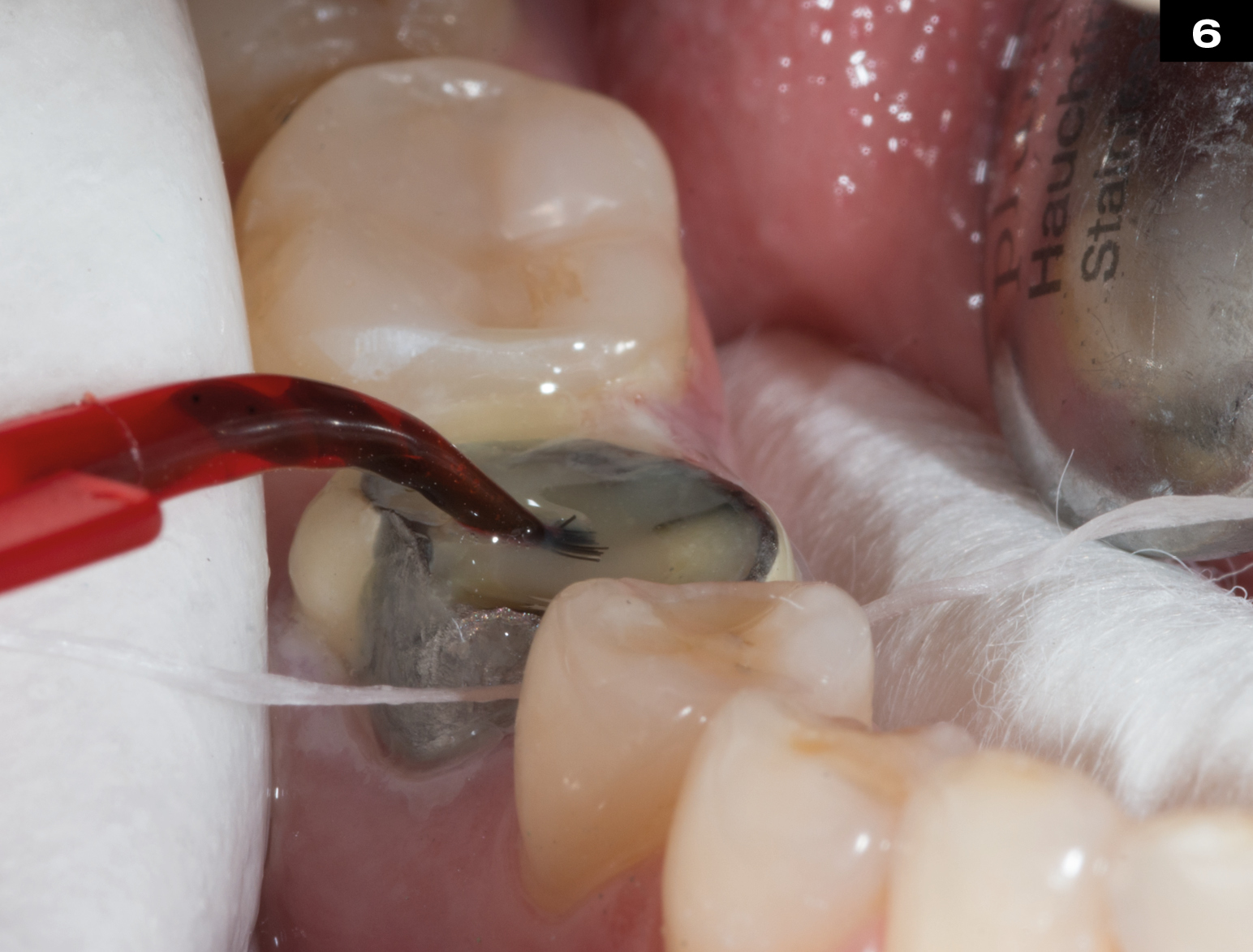

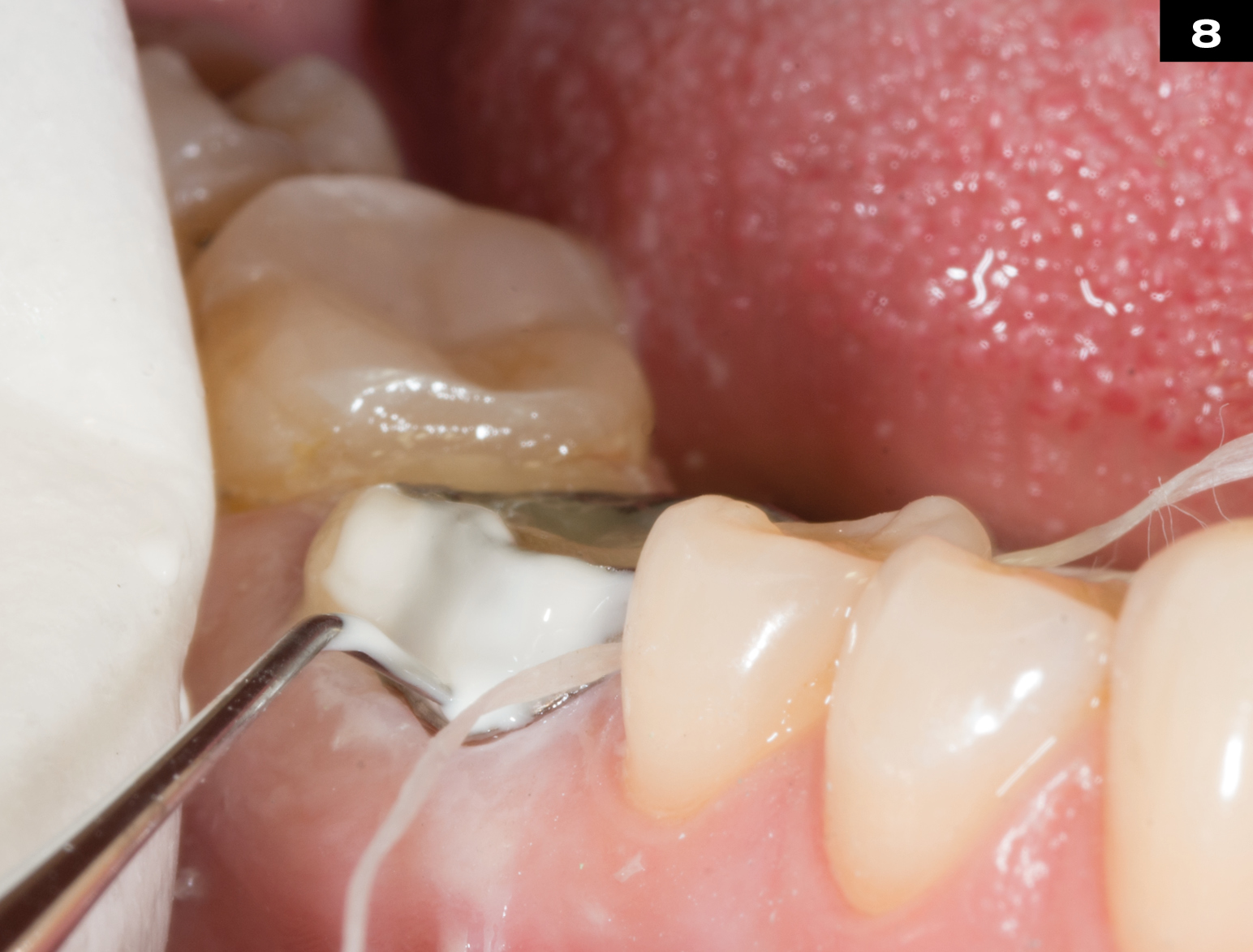
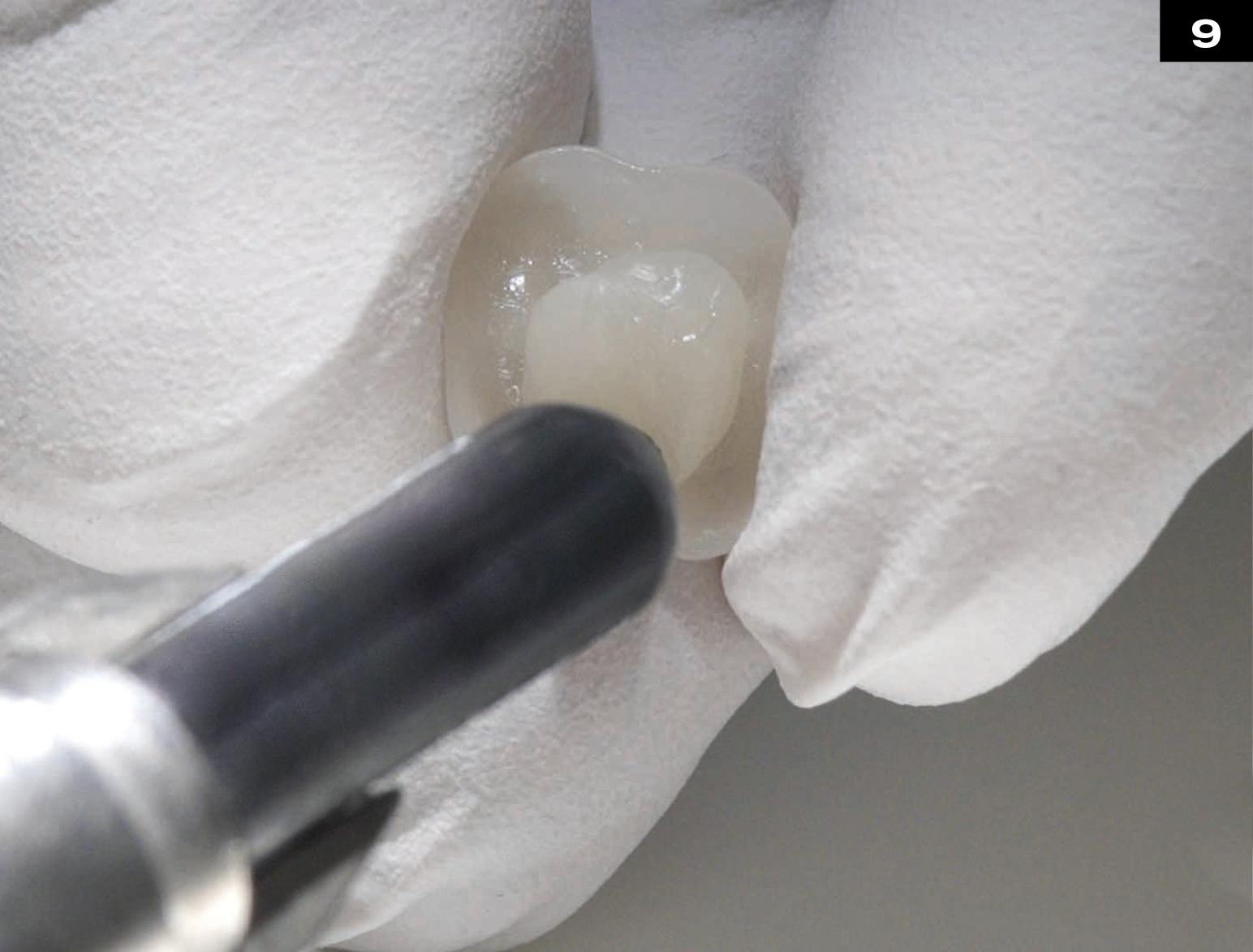

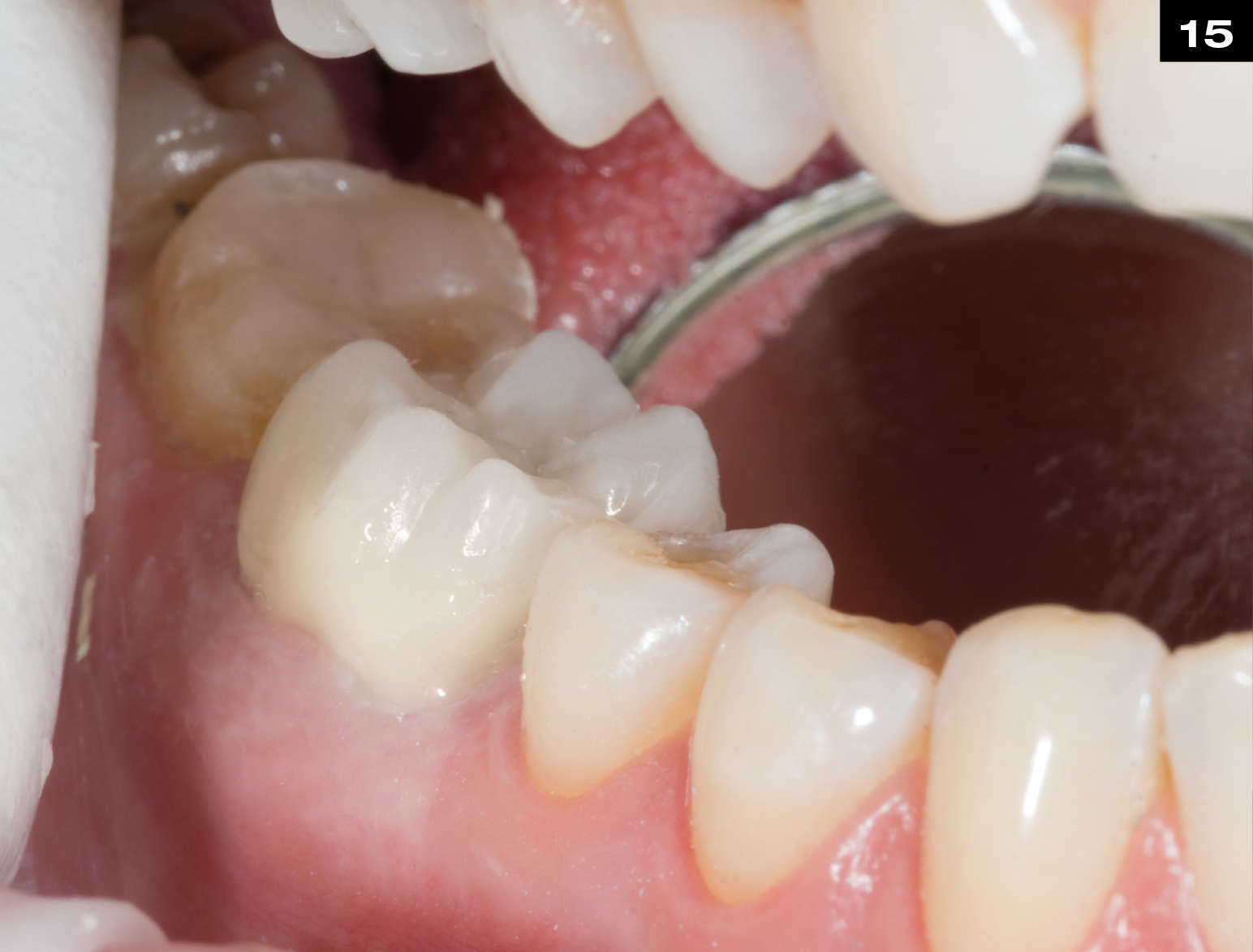
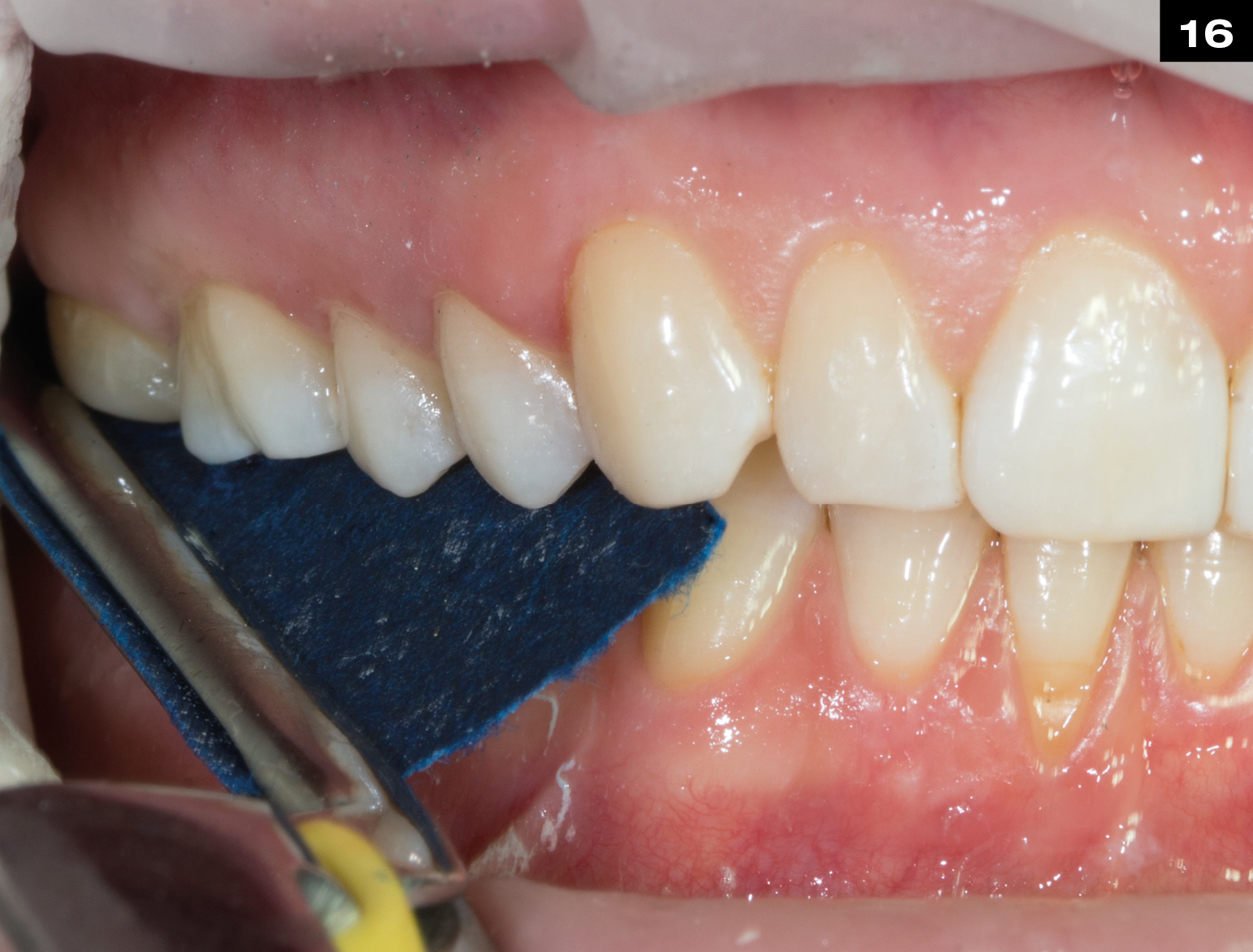
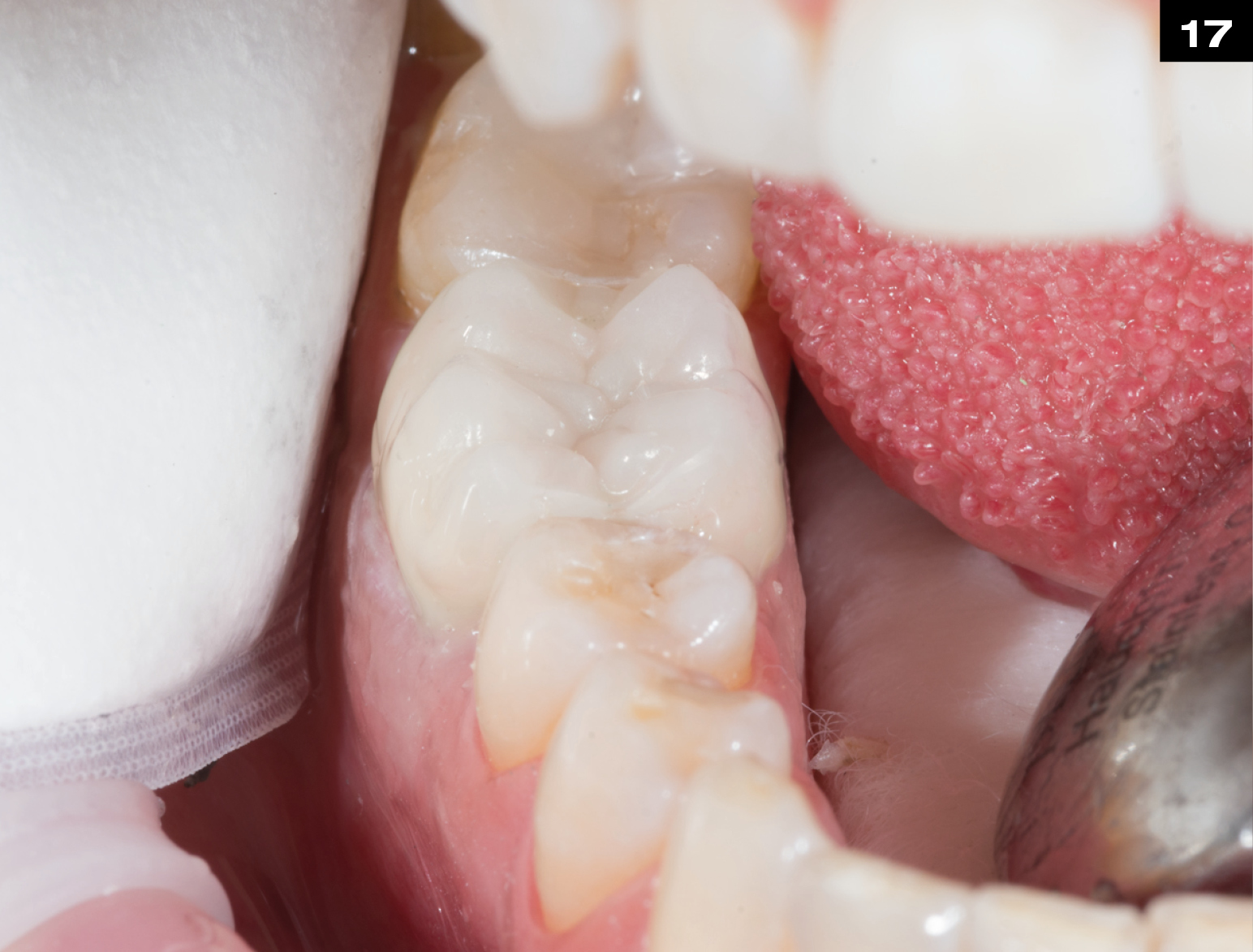
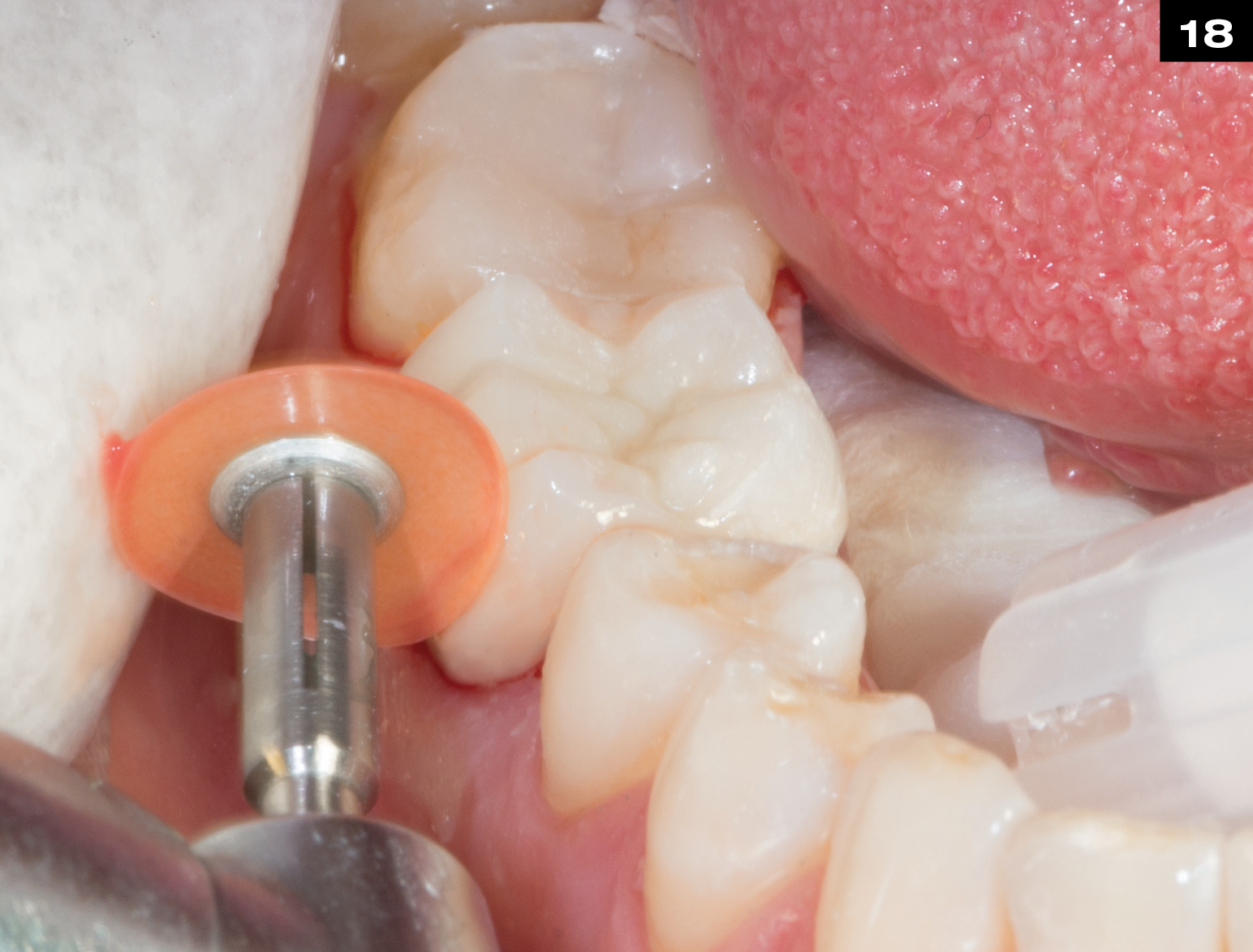
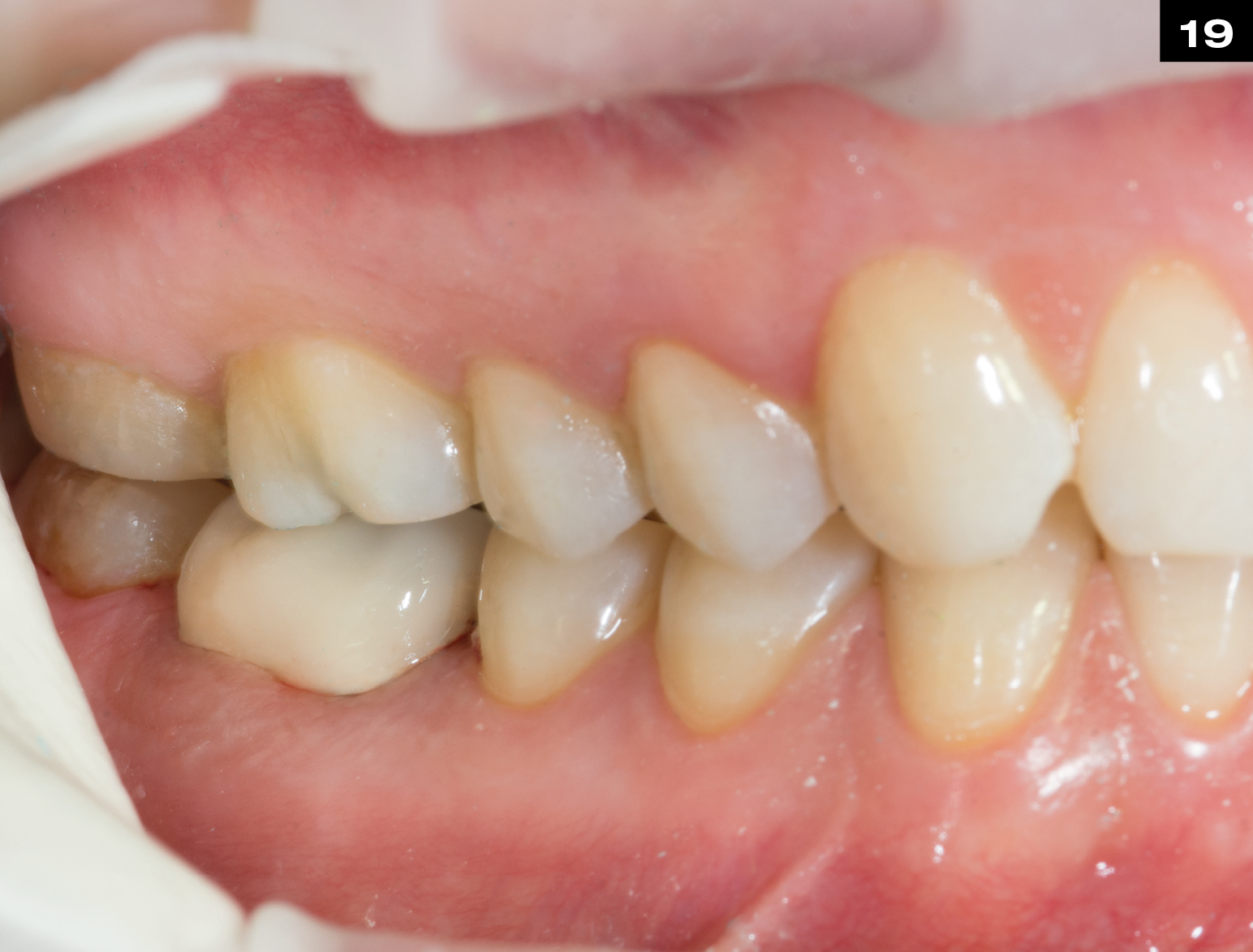
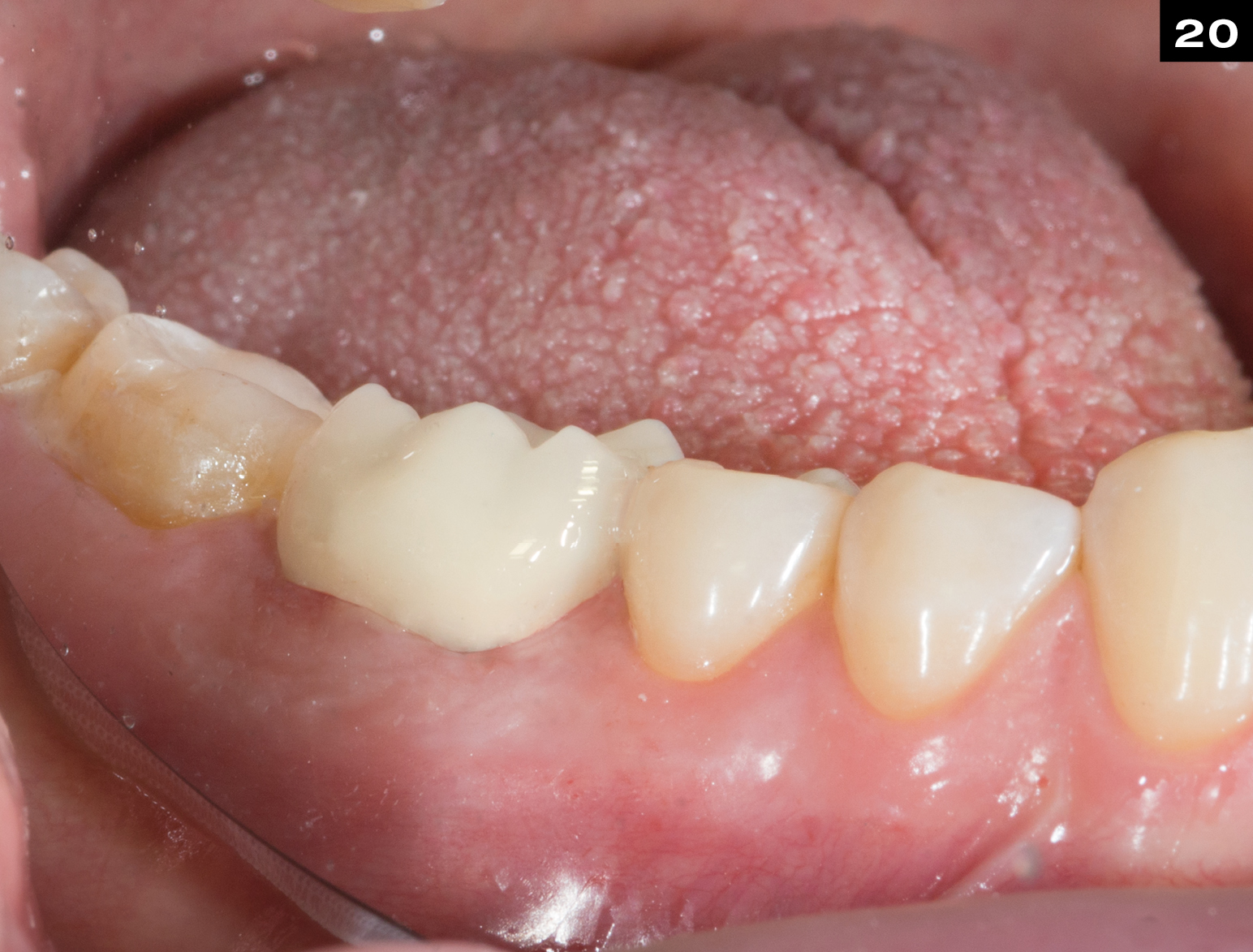
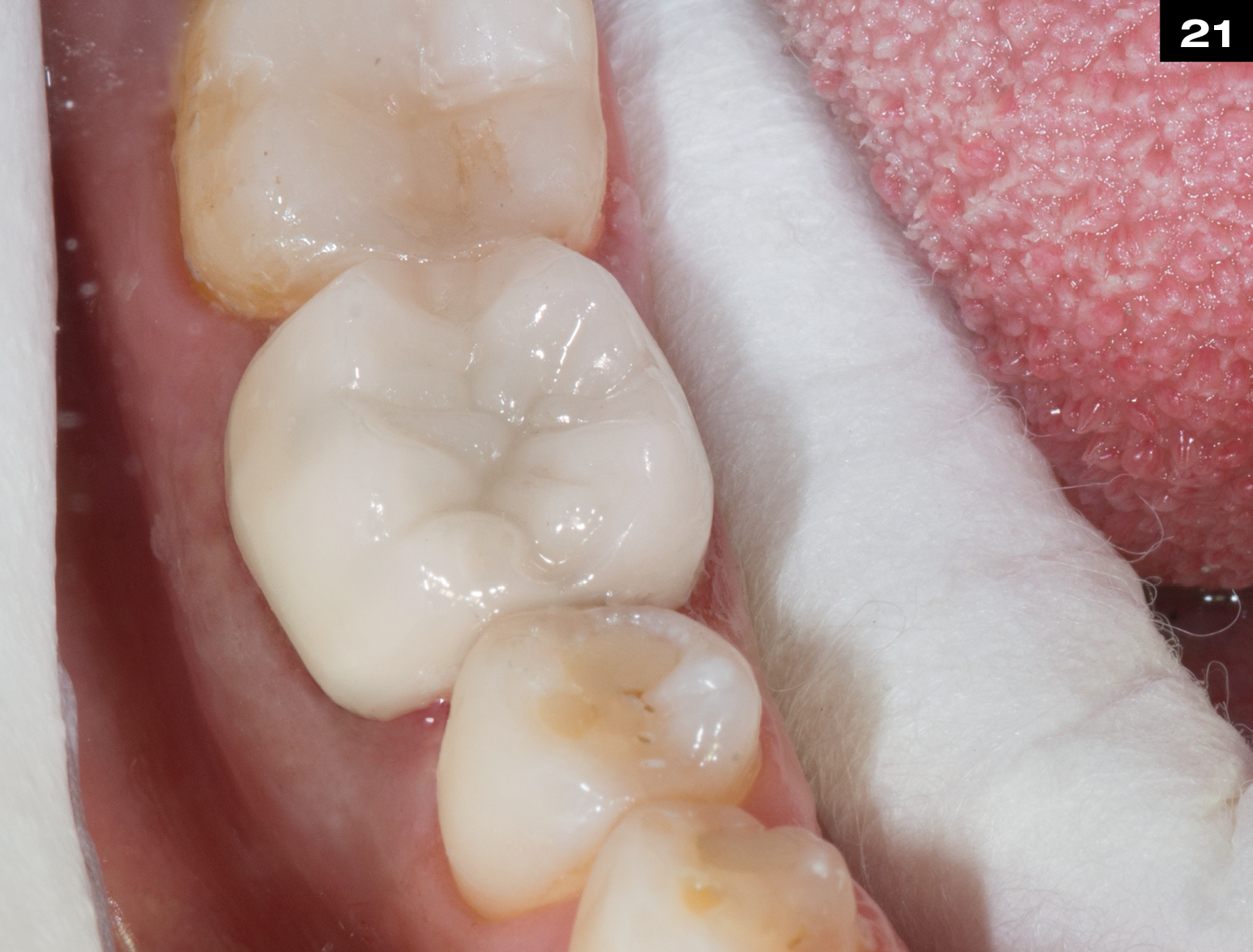
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
- Low shrinkage due to nano-technology and high amount of filler 83 %
- Good abrasion resistance
- Very good physical and mechanical properties
- Antibacterial surface due to zinc and fluorine particles in t he filler
- Easy polishing
- Natural fluorescence and opalescence
| N.-H. COMPOSITE | N.-H. FLOWABLE COMPOSITE | OCCLUSIONVD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural Strength | 150 MPa | 120 MPa | 200 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 480 MPa | 350 MPa | 550 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 12.5 (dentin) - 16 GPa (enamel) | 6 GPa | 20 GPa |
| Surface Hardness | 80 HV | 68 HV | 95 HV |
| Polymerization Shrinkage | 2,50 % | N.A. | — |
(Source: internal data from edelweiss dentistry)
THE TECHNICAL ASPECTS
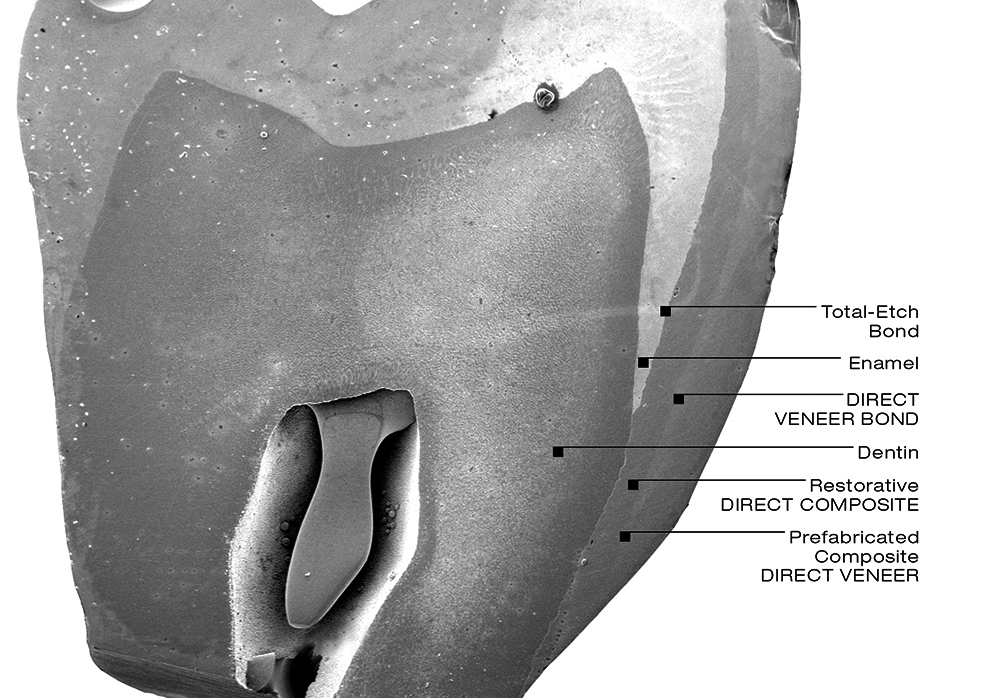
View of a sectioned extracted human molar with a cemented prefabricated composite VENEER / OCCLUSIONVD bonded to half of the enamel surface and the other half to the dentin surface.
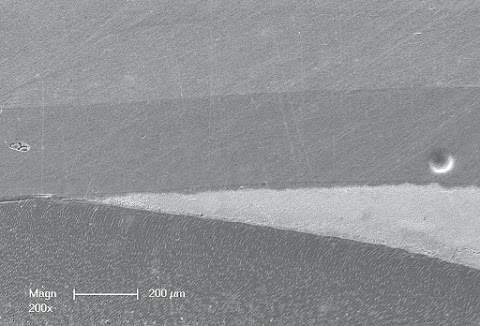
The most relevant observation made was obtained upon the evaluation of the inner adaptation of the restoration. No defects were visible at the interface of the enamel or in between the restorative composite and the VENEER / OCCLUSIONVD, which confirmed the excellent bond strength and stability at both interfaces (dentin/enamel to composite, composite to VENEER / OCCLUSIONVD).
FATIGUE BEHAVIOR
Fatigue behavior for composite VENEER / OCCLUSIONVD: A recent in vitro study demonstrated that prefabricated composite VENEER / OCCLUSIONVD cemented onto the enamel and dentin surface of molars, effectively resisted simulated functional fatigue and load testing. Virtually no defects were observed at both the enamel and dentin margins, either before or after loading, which typically represents the most vulnerable area of a restoration.
UNIVERSITÉ DE GENÈVE
Prof. Dr. Didier Dietschi D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent Specialist SVPR Assoc. Professor